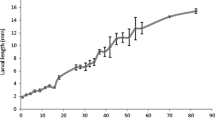
Synopsis
The normal occurrence of spontaneous sex inversion among teleosts is a recent item within current concepts on vertebrate reproductive physiology. Investigations on the subject are mostly descriptive and deal with morphological and behavioral aspects. The concept of social control of sex inversion has been received with great interest. However, research on physiological processes that take place inside a fish when it changes sex must be rated as fragmentary. Steroid hormones are supposed to play a major role in sex inversion. But a cause and effect relationship has not yet been established. More experimental studies on more types of ambisexual species are badly needed. Future work will show whether recent findings on H-Y antigen might open a new approach to answering some of our questions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References cited
Atz, J.W. 1964. Intersexuality in fishes. pp. 145–232. In: A.J. Marshall & C.N. Armstrong(ed.) Intersexuality in Vertebrates Including Man, Academic Press, New York.
Bruslé, S. 1987. Sex-inversion of the hermaphroditic, protogynous teleost Coris julis L. (Labridae). J. Fish Biol. 30: 605–616.
Callard, G.V. 1982. Aromatase in the teleost brain and pituitary: role in hormone action. pp. 40–43. In: C.J.J. Richter & H.J.Th. Goos (ed.) Proceedings of the International Symposium on Reproductive Physiology of Fish, Pudoc Wageningen, Wageningen.
Chan, S.T.H., O. Wai-sum & S.W.B. Hui. 1975. The gonadal and adenohypophysial functions of natural sex reversal. pp. 201–221. In: R. Reinboth(ed.) Intersexuality in the Animal Kingdom, Springer Verlag, New York.
Chan, S.T.H. & S.B. Yeung. 1983. Sex control and sex reversal in fish under natural conditions. pp. 171–222. In: W.S. Hoar, D.J. Randall & E.M. Donaldson (ed.) Fish Physiology, Vol. 9 B, Academic Press, New York.
Chen, F.J., M. Chow, T.M. Chao & R. Lim. 1977. Artificial spawning and larval rearing of the grouper Epinephelus tauvina (Forskal) in Singapore. Singapore J. Pri. Ind. 5: 1–21.
Choat, J.H. & D.R. Robertson. 1975. Protogynous hermaphroditism in fishes of the family scaridae. pp. 263–283. In: R. Reinboth(ed.) Intersexuality in the Animal Kingdom, Springer Verlag, New York.
D'Ancona, U. 1940–1941. Preliminary observations and considerations on hermaphroditism and sexual differentiation of Sparus auratus L. Publ. Staz. Zool. Nap. 18: 313–336. (In Italian).
D'Ancona, U. 1949a. Gonad differentiation and sex reversal in sparids. Arch. Oceanogr. Limnol. 6: 97–163. (In Italian).
D'Ancona, U. 1959b. Hermaphroditism and sex change in Teleostei. Experientia 5: 381–389. (In Italian).
D'Ancona, U. 1956. Morphogénèse et differentiation sexuelle chez les poissons téléostéens. Bull. Soc. Zool. France 81: 219–229.
Fishelson, L. 1970. Protogynous sex reversal in the fish Anthias squamipinnis (Teleostei, Anthiidae) regulated by the presence or absence of a male fish. Nature (London) 227: 90.
Fostier, A., B. Jalabert, R. Billard, B. Breton & Y. Zohar. 1983. The gonadal steroids. pp. 277–372. In: W.S. Hoar, D.J. Randall & E.M. Donaldson (ed.) Fish Physiology, Vol. 9 A, Academic Press, New York.
Fricke, H. 1983. Social control of sex: field experiments with the anemonefish Amphiprion bicinctus. Z. Tierpsychol. 61: 71–77.
Fricke, H. & S. Fricke. 1977. Monogamy and sex change by aggressive dominance in coral reef fish. Nature (London) 266: 830–832.
Hunter, G.A. & E.M. Donaldson. 1983. Hormonal sex control and its application to fish culture. pp. 223–303. In: W.S. Hoar, D.J. Randall & E.M. Donaldson (ed.) Fish Physiology, Vol. 9 B, Academic Press, New York.
Kuhn, R. 1976. Morphologische und histologische Untersuchungen zum Geschlechtswechsel von Thalassoma pavo (L.), einem diandrisch protogynen Lippfisch aus dem Mittelmeer. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Zoology, University of Mainz, Mainz. 136 pp.
Idler, D.R., R. Reinboth, J.M. Walsh & B. Truscott. 1976. A comparison of 11-hydroxytestosterone and 11-ketotestosterone in blood of ambisexual and gonochoristic teleosts. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 30: 517–521.
Leitz, T. 1987. Social control of testicular steroidogenic capacities in the Siamese fighting fish Betta splendens. J. Exp. Zool. 244: 473–478.
Nakamura, M., T.F. Hourigan, K. Yamauchi & E.G. Grau. 1988. Histological and ultrastructural evidence for the role of gonadal steroid hormones in sex change in the protogynous wrassa: Thalassoma duperrey. Env. Biol. Fish. (in press).
Pechan, P., S.S. Wachtel & R. Reinboth. 1979. H-Y antigen in the teleost Differentiation 14: 189–192.
Peter, R.E. 1983. The brain and neurohormones in teleost reproduction. pp. 97–135. In: W.S. Hoar, D.J. Randall & E.M. Donaldson (ed.) Fish Physiology, Vol. 9 A, Academic Press, New York.
Reinboth, R. 1962. Morphologische and funktionelle Zweigeschlechtlichkeit bei marinen Teleostiern (Serranidae, Sparidae, Centracanthidae, Labridae). Zool. Jb. (Physiol.) 69: 405–480.
Reinboth, R. 1963. Experimentell induzierter Geschlechtswechsel bei Fischen. Verb. dtsch. Zool. Ges., München: 67–73.
Reinboth, R. 1967a. Zum Problem der amphisexuellen Fische. Verh. dtsch. Zool. Ges., München: 316–325.
Reinboth, R. 1967b. Diandric teleost species.Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 9: abstract 146.
Reinboth, R. 1968. Protogynie bei Papageifischen (Scaridae). Z. Naturforsch. 23b: 852–855.
Reinboth, R. 1970. Intersexuality in fishes. pp. 515–543. In: K.G. Benson & J.G. Philipps(ed.) Hormones and the Environment, Memoirs Soc. Endocrinol. 18, Cambridge University Press, London.
Reinboth, R. 1973. Dualistic reproductive behavior in the protogynous wrasse Thalassoma bifasciatum and some observations on its daynight changeover. Helgol. wiss. Meeresunters. 24: 74–91.
Reinboth, R. 1975. Spontaneous and hormone-induced sexinversion in wrasses (Labridae). Pubbl. Staz. Zool., Napoli, Suppl. 39: 550–573.
Reinboth, R. 1977. Thalassoma bifasciatum (Labridae) - Paarund Gruppenlaichen im Korallenriff. Film E 1776, IWF Göttingen. Publ. R. Reinboth, Publ. Wiss. Film, Sekt. Biol. Ser. 10, Nr. 3/E 1776, 15 pp.
Reinboth, R. 1980a. Can sex inversion be environmentally induced? Biol. Reprod. 22: 49–59.
Reinboth, R. 1980b. Behavioral aspects in sex inversion in certain fishes. pp. 271–286. In: J.E. Bardach, J.J. Magnuson, R.C. May & J.M. Reinhardt(ed.) Fish Behavior and Its Use in the Capture and Culture of Fishes, Conference Proceedings 5, ICLARM, Manila.
Reinboth, R. 1982. The problem of sexual bipotentiality as exemplified by teleosts. Reprod. Nutr. Develop. 22: 397–403.
Reinboth, R. 1983. The peculiarities of gonad transformation in teleosts. Differentiation 23 (Suppl.): 82–86.
Reinboth, R. 1985. Ambisexuality in teleosts — a challenge to endocrinologists. pp. 579–581. In: B. Lofts & W.N. Holmes(ed.) Current Trends in Comparative Endocrinology, University Press, Hong Kong.
Reinboth, R. 1986. Exceptional features of gonadal differentiation in teleosts. pp. 103–111. In: A. Eshkol, B. Eckstein, N. Dekel, H. Peters & A. Tsafriri (ed.) Development and Function of the Reproductive Organs, Serono Symposia Review No. 11.
Reinboth, R. & B. Becker. 1984. In vitro studies on steroid metabolism by gonadal tissues from ambisexual teleosts. I. Conversion of 14C-testosterone by males and females of the protogynous wrasse Coris julis L. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 55: 245–250.
Reinboth, R., B. Becker & M. Latz. 1986. In vitro studies on steroid metabolism by gonadal tissues from ambisexual teleosts. II. Conversion of 14C-androstenedione by the heterologous gonadal tissues of the protandric sea bream Pagellus acarne (Risso). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 62: 335–340.
Reinboth, R., A. Mayerova, C. Ebensperger & U. Wolf. 1987. The occurrence of the serological sex-specific (Sxs) antigen in the diandric protogynous wrasse Coris julis (L.) (Labridae, Teleostei). Differentiation 34: 13–17.
Robertson, D.R. 1972. Social control of sex reversal in a coral reef fish. Science 177: 1007–1009.
Robertson, D.R. & R.R. Warner. 1978. Sexual patterns in the labroid fishes of the Western Caribbean: II. The parrot fishes (Scaridae). Smithson. Contrib. Zool. 255: 1–26.
Ross, R.M. 1981. Experimental evidence for stimulation and inhibition of sex change in the Hawaiian reef fish Thalassoma duperrey. Proc. Fourth Intern. Coral Reef Symp. (Manila) 2: 575–580.
Ross, R.M., G.S. Losey & M. Diamond. 1983. Sex change in a coral reef fish: Dependence of stimulation and inhibition on relative size. Science 221: 574–575.
Ross, R.M. 1984. Anatomical changes associated with sex reversal in the fish Thalassoma duperrey (Teleostei: Labridae). Copeia 1984: 245–248.
Shapiro, D.Y. 1981. Behavioural changes of protogynous sex reversal in a coral reef fish in the laboratory. Anim. Behav. 29: 1185–1198.
Shapiro, D.Y. & R.H. Boulon, Jr. 1982. The influence of females on the initiation of female-to-male sex change in a coral reef fish. Hormones and Behavior 16: 66–75.
Smith, C.L. 1972. A spawning aggregation of Nassau grouper, Epinephelus striatus (Bloch). Trans. Amer. Fish. Soc. 101: 257–261.
Stephan, P. 1901. De I'hermaphrodisme chez les vertébrés. Ann. Fac. Sc. Marseille 12: 23–157.
Tang, F., S.T.H. Chan & B. Lofts. 1974. Effect of steroid hormones on the process of natural sex reversal in the ricefield eel, Monopterus albus (Zuiew). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 24: 227–241.
Thresher, R.E. 1984. Reproduction in reef fishes. T.F.H. Publication, Neptune City. 399 pp.
Wachtel, S.S., S.S. Ohno & C.G. Koo. 1975. Possible role for H-Y antigen in the primary determination of sex. Nature (London) 257: 235.
Warner, R.R. & D.R. Robertson. 1978. Sexual patterns in the labroid fishes of the Western Caribbean. 1. The wrasses (Labridae). Smithson. Contrib. Zool. 254: 1–27.
Wolf, U. & C. Ebensperger. 1987. Serologic H-Y antigen in the homogametic sex. Conference on ‘Evolutionary mechanisms in sex determination’, Memphis, Tennessee, May 4–8 (in press).
Yeung, W.S.B., M.N. Adai, S.W.B. Hui & S.T.H. Chan. 1985. The ultrastructural and biosynthetic characteristics of steroidogenic cells in the gonad of Monopterus albus (Teleostei) during natural sex reversal. Cell Tissue Res. 239: 383–394.
Yeung, W.S.B. & S.T.H. Chan. 1987. The plasma sex steroid profiles in the freshwater, sex-reversing teleost fish, Monopterus albus (Zuiew). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 65: 233–242.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dedicated to Prof. Dr. Hans M. Peters on his 80th birthday.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reinboth, R. Physiological problems of teleost ambisexuality. Environ Biol Fish 22, 249–259 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00004891
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00004891