Summary
-
1.
We used laser vibrometry and free field sound stimulation to study the frequency responses of the eardrum and the lateral body wall of awake male Eleutherodactylus coqui.
-
2.
The eardrum snowed one of two distinct frequency responses depending on whether the glottis was open (GO response) or closed (GC response) during the measurement.
-
3.
The lateral body wall vibrated with a maximum amplitude close to that of the eardrum and in the same frequency range.
-
4.
Covering the frog's body wall with vaseline reduced the vibration amplitude of the GC response by up to 15 dB.
-
5.
When a closed sound delivery system was used to stimulate a local area of the body wall the eardrum also showed one of two types of responses.
-
6.
These results suggest that sound is transmitted via the lung cavity to the internal surface of the eardrum. This lung input has a significant influence on the vibrations of the eardrum even when the glottis is closed.
-
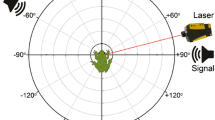
7.
The vibration amplitude of the eardrum changed with the angle of sound incidence. The directionality was most pronounced in a narrow frequency range between the two main frequencies of the conspecific advertisement call.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GC :
-
glottis closed
- GO :
-
glottis open
- IVAD :
-
interaural vibration amplitude difference
References
Aertsen AMHJ, Vlaming MSMG, Eggermont JJ, Johannesma PIM (1986) Directional hearing in the grassfrog (Rana temporaria L.). II. Acoustics and modelling of the auditory periphery. Hearing Res 21:17–40
Anson M, Pinder AC, Keating MJ, Chung SH (1985) Acoustic vibration of the amphibian eardrum studied by white noise analysis and holographic interferometry. J Acoust Soc Am 78:916–923
Chung SH, Pettigrew AG, Anson M (1981) Hearing in the frog: Dynamics of the middle ear. Proc R Soc Lond B 212:459–485
Eggermont JJ (1988) Mechanisms of sound localization in anurans. In: Fritzsch B, Ryan MJ, Wilczynski W, Hetherington TE, Walkowiak W (eds) The evolution of the amphibian auditory system. John Wiley & Sons, New York Chichester Brisbane Toronto Singapore, pp 307–336
Ehret G, Tautz J, Schmitz B, Narins PM (1990) Hearing through the lungs:Lung-eardrum transmission of sound in the frog Eleutherodactylus coqui. Naturwissenschaften 77:192–194
Feng AS (1980) Directional characteristics of the acoustic receiver of the leopard frog (Rana pipiens): A study of eighth nerve auditory responses. J Acoust Soc Am 68:1107–1114
Feng AS, Capranica RR (1976) Sound localization in anurans.I. Evidence of binaural interaction in dorsal medullary nucleus of ullfrogs (Rana catesbeiana). J Neurophysiol 39:871–881
Feng AS, Capranica RR (1978) Sound localization in anurans. II. Binaural interaction in superior olivary nucleus of the green tree frog (Hyla einerea). J Neurophysiol 41:43–54
Fletcher NH, Thwaites S (1979) Physical models for the analysis of acoustical systems in biology. Q Rev Biophys 12:25–65
Gans C (1974) Biomechanics: An approach to vertebrate biology. JB Lippincott Company, Philadelphia Toronto
Gerhardt HC, Rheinlaender J (1980) Accuracy of sound localization in a miniature dendrobatid frog. Naturwissenschaften 67:362–363
Klump GM, Gerhardt HC (1989) Sound localization in the barking treefrog. Naturwissenschaften 76:35–37
Michelsen A, Larsen ON (1978) Biophysics of the ensiferan ear. I. Tympanal vibrations in bushcrickets (Tettigoniidae) studied with laser vibrometry. J Comp Physiol 123:193–203
Michelsen A, Jørgensen MB, Christensen-Dalsgaard J, Capranica RR (1986) Directional hearing of awake, unrestrained treefrogs. Naturwissenschaften 73:682–683
Narins PM, Capranica RR (1976) Sexual differences in the auditory system of the tree frog Eleutherodactylus coqui. Science 192:378–380
Narins PM, Capranica RR (1978) Communicative significance of the two-note call of the treefrog Eleutherodactylus coqui. J Comp Physiol 127:1–9
Narins PM, Smith SL (1986) Clinal variation in anuran advertisement calls: basis for acoustic isolation? Behav Ecol Sociobiol 19:135–141
Narins PM, Ehret G, Tautz J (1988) Accessory pathway for sound transfer in a neotropical frog. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:1508–1512
Palmer AR, Pinder AC (1984) The directionality of the frog ear described by a mechanical model. J Theor Biol 110:205–215
Passmore NI, Capranica RR, Telford SR, Bishop PJ (1984) Phonotaxis in the painted reed frog (Hyperolius marmoratus). The localization of elevated sound sources. J Comp Physiol A 154:189–197
Pinder AC, Palmer AR (1983) Mechanical properties of the frog ear: vibration measurements under free- and closed-field acoustic conditions. Proc R Soc Lond B 219:371–396
Rheinlaender J, Gerhardt HC, Yager DD, Capranica RR (1979) Accuracy of phonotaxis by the green treefrog (Hyla cinerea). J Comp Physiol 133:247–255
Rheinlaender J, Walkowiak W, Gerhardt HC (1981) Directional hearing in the green treefrog: A variable mechanism? Naturwissenschaften 68:430–431
Wilczynski W, Resler C, Capranica RR (1987) Tympanic and extratympanic sound transmission in the leopard frog. J Comp Physiol A 161:659–669
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jørgensen, M.B., Schmitz, B. & Christensen-Dalsgaard, J. Biophysics of directional hearing in the frog Eleutherodactylus coqui . J Comp Physiol A 168, 223–232 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00218414
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00218414