Summary
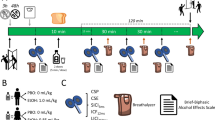
The effects of alprazolam 1 mg both alone and in combination with 0.5 g/kg of alcohol were examined on self-ratings of intoxication and measures of central and peripheral activity such as EEG, auditory evoked response, tremor at 90, 150 and 210 min post drug. Forty-eight healthy volunteers were assigned randomly to 4 independent groups who received: alprazolam and placebo drink, alprazolam and alcohol, placebo capsule and alcohol, placebo capsule and placebo drink respectively.
Alprazolam decreased the amplitudes of the 3 potentials of the evoked response, decreased activity in the 8–13 Hz and increased activity in the 13.5–26 Hz wavebands of the EEG and decreased the frequency at which fusion was perceived. Alcohol prolonged reaction time and increased tremor. The effects were not always additive and alprazolam was dominant in the combination.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen D, Curran HV, Lader M (1991) The effects of repeated doses of clomipramine and alprazolam on physiological, psychomotor and cognitive functions in normal subjects. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 40: 355–362
Aranko K, Seppälä T, Pellinen J, Mattila MJ (1985) Interaction of diazepam or lorazepam with alcohol. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 28: 559–565
Bond AJ, James DC, Lader MH (1974) Physiological and psychological measures in anxious patients. Psychol Med 4: 364–373
Bond A, Lader M (1983) Correlations among measures of response to benzodiazepines in man. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 18: 295–298
Bond A, Lader M, Shrotriya R (1983) Comparative effects of a repeated dose regime of diazepam and buspirone on subjective ratings, psychological tests and the EEG. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 24: 463–467
Bond A, Silveira JC, Lader M (1991) Effects of single doses of alprazolam and alcohol alone and in combination on psychological performance. Hum Psychopharm 6: 219–228
Dawson GW, Jue SG, Brogden RN (1984) Alprazolam. A review of its pharmacodynamic properties and efficacy in the treatment of anxiety and depression. Drugs 27: 132–147
Ellinwood EH, Heatherly DG, Nikaido AM, Bjornsson TD, Kilts C (1985) Comparative pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of lorazepam, alprazolam and diazepam. Psychopharmacology 86: 392–399
Ellinwood EH, Nikaido AM, Heatherly DG, Bjornsson TD (1987) Benzodiazepine pharmacodynamics: evidence for biophase rate limiting mechanisms. Psychopharmacology 91: 168–174
Itil TM, Saletu B, Marasa J, Mucciardi AN (1971) Digital computer analysed awake and sleep EEG (sleep prints) in predicting the effects of triazolobenzodiazepine (U-31, 889). Pharmakopsych Neuropsychopharm 5: 225–240
Krobroth PD, Smith RB, Erb RJ (1988) Tolerance to alprazolam after intravenous bolus and continuous infusion: psychomotor and EEG effects. Clin Pharmacol Ther 43: 270–277
Linnoila M, Stapleton JM, Lister R, Moss H, Lane E, Ganger A, Eckardt MJ (1990) Effects of single doses of alprazolam and diazepam, alone and in combination with ethanol, on psychomotor and cognitive performance and on autonomic nervous system reactivity in healthy volunteers. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 39: 21–28
O'Shea B (1989) Alprazolam: just another benzodiazepine? Irish J Psychol Med 6: 89–94
Sellers EM, Busto U (1982) Benzodiazepines and alcohol: Assessment of the effects and consequences of psychotropic drug interactions. J Clin Psychopharmacol 2: 249–262
Subhan Z, Harrison C, Hindmarch I (1986) Alprazolam and Lorazepam. Single and Multiple-Dose Effects on Psychomotor Skills and Sleep. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 29: 709–712
Tyrer PJ, Lader MH (1974) Physiological and psychological effects of dl-propranolol, d-propranolol, and diazepam in induced anxiety. Br J Clin Pharmacol 1: 379–385
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bond, A.J., Silveira, J.C. & Lader, M.H. The effects of alprazolam alone and combined with alcohol on central integrative activity. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 42, 495–498 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00314857
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00314857