Abstract
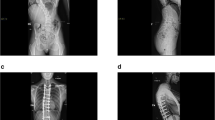
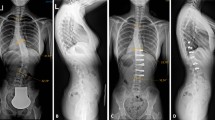
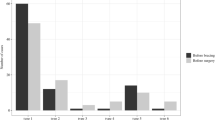
The natural history of scoliosis in the literature concerning the idiopathic and neuromuscular scoliosis in myelomeningocelet patients (MMC) are compared to our own results in 12 patients with MMC and 89 patients operated because of an idiopathic scoliosis. According to known experiences the natural history of scoliosis in MMC is progression even after the end of growth. The chance of developing a scoliosis increases with the patients, age and the level of the lesion. The higher the level of paralysis the more common is a spinal deformity. In literature the progression rate of MMC scoliosis is 2,5–3,5° per year, with the idiopathic pattern 0,5–0,65° per year after end of growth. Our own results of surgically treated patients show a rate of progression of 6,2° per year in MMC. The surgical treatment must start before a severe spinal deformity has developed because of the higher rate of operative complications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banta J, S Whiteman, PM Dyck, DL Hartleib, D Gilbert: Fifteen year review of myelodysplasia. J Bone Jt Surg 58-A (1976) 726
Barden GA, LC Meyer, FH Stelling III: Myelodysplastic—Fate of those followed for twenty years or more. J Bone Jt Surg 57-A (1975) 643
Beyeler J. Progredienz und Symptomatik bei Lumbalskoliosen. Vortrag gehalten auf der Sitzung des Arbeitskreises Skoliose anläßlich der 25. Jahrestagung der Vereinigung Süddeutscher Orthopäden in BadenBaden am 30. 4. 1977
Bunch WH: Myelomeningocele. In: Lovell W, R Winter (Eds): Pediatric Orthopedics. Lippincott, Philadelphia 1986
Bunch WM, TB Scarff, V Dvonch: Progressive neurological loss in myelomeningocele patients. Orthop Trans 5 (1981) 32
Bunnell WP The natural history of idiopathic scoliosis. In: supplementary programm, 19th Annual Meeting of the Scoliosis Research Society, Orlando 49–52 (1984)
Carstens C, J Vetter, U Niethard: Die Entwicklung der Lähmungsscoliose bei der Myelomeningocele. Z Orthop 128 (1990) 174
Clarisse P: Prognostic evolutif des scolioses idiopathiques mineures de 10 degrees to 29 degrees en periode de croissance. Doctoral thesis, Univ. Claude Bernard, Lyon 1974
Cobb JR: Outline for the study of scoliosis. Am Acad Orthop 5 (1948) 261
Collis DK, IV Ponseti: Long-term follow-up of patients with idiopathic scoliosis not treated surgically. J Bone Jt Surg 51-A (1969) 425
Hall PF: Abortion of fetuses with spina bifida? (Letter) Can Med Assoc J 121 (1979) 846
Hall PV, RE Lindseth, RK Campbell, JE Kalsbeck: Myelodysplasia and developmental scoliosis: a manifestation of syringomyelia. Spine 1 (1976) 48
Heine J, H Reher: Die Progredienz der unbehandelten idiopathischen Skoliose bis Wachstumsabschluß. Z Orthop 113 (1975) 87
Heine J: Die Lumbalskoliose, Ferdinand Enke Verlag, Stuttgart 64–71 (1980)
Lonstein JE, JM Carlson: The prediction of curve progression in untreated idiopathic scoliosis during growth. J Bone Jt Surg 66-A (1984) 1061
Mackel J, R Lindseth: Scoliosis in Myelodysplasia. J Bone Jt Surg 57-A (1975) 1031
Moe JH, JA Byrd: Idiopathic scoliosis. In: Bradford D, J Lonstein, JH Moe, J Ogilvie, R Winter (Eds): Moe's Textbook of scoliosis and other spinal deformities. WB Saunders Company, Philadelphia 1987
Moe JH, RB Winter, DS Bradford, JE Lonstein: Scoliosis and other spinal deformities. WB Saunders, Philadelphia 1978
Niethard FU, J Pfeil: Orthopädie. Hippokrates Verlag. Stuttgart 1989
Peyer J: Die Skoliose beim Erwachsenen. Z Orthop 113 (1975) 577
Pigott H: The natural history of scoliosis in myelodysplasia. J Bone Jt Surg 62-B (1980) 54
Raycroft J, B Curtis: Spinal curvature in MMC: natural history and etiology. Proceedings of the Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons: Symposium on MMC. CV Mosby, St. Louis 1972
Rogala EH, D Drummond, J Gurr: Scoliosis: incidence and natural history, a prospective epidemiological study. J Bone Jt Surg 60-A (1978) 173
Roth K: Spinal deformities in myelomeningocele: a radiologic assessment. In: Harrington PR (Ed). Scoliosis. Lippincott, Philadelphia 1971
Shurtleff D, R Goiney, L Gordon, N Livermore. Myelodysplasia: the natural history of kyphosis and scoliosis. A preliminary report. Dev Med Child Neurol 18 (1976) 126
Tachdjian MO: Pediatric Orthopedics, Vol 1, WB Saunders Company, Philadephia 1773–1871 (1990)
Winter RB: Myelomeningocele. In: Bradford D, J Lonstein, J Moe, J Ogilvie, RB Winter (Eds). Moe's Textbook of scoliosis and other spinal deformities. WB Saunders Company, Philadelphia 1987
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eysel, P., Hopf, C., Schwarz, M. et al. Development of scoliosis in myelomeningocele. Differences in the history caused by idiopathic pattern. Neurosurg. Rev. 16, 301–306 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00383841
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00383841