Abstract
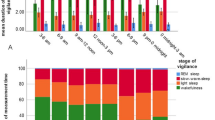
Polygraphic studies were performed in 14 fullterm newborns. The sleep behavior of the infants was correlated to the serum Mg level. Correlations could be demonstrated between serum Mg and active sleep, as well as between serum Mg and quiet sleep. With increasing serum Mg quiet sleep increased, whereas active sleep decreased. After Mg injection quiet sleep increased and active sleep decreased even more. There were also corresponding correlations between serum Mg and rapid eye movements, submental muscle tone, and gross body movements.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker RM, Boston RC, Boyes TE, Leaver DD (1979) Variations in the response of sheep to experimental magnesium deficiency. Res Vet Sci 26:129–133
Berend N (1914) Die Magnesiumsulfatbehandlung der spasmophilen Krämpfe. Monatsschr Kinderheilk 12:269–332
Borges LF, Gücer G (1978) Effect of magnesium on epileptic foci. Epilepsia 19:81–91
Bradley PB, Brimblecombe RW (1972) Biochemical and pharmacological mechanisms underlyving behavior. In: Progress in brain research, Vol 36. Elsevier Publishing Company, Amsterdam London New York
Brezinova V, Oswald I, Dunleavy DLF, MacLean AW (1973) Chronic studies of tricyclic drugs. In: The nature of sleep. International Symposium 1981. G Fischer, Stuttgart
Brown JK, Cockburn F, Forfar JO (1972) Clinical and chemical correlates in convulsions of the newborn. Lancet I:135–138
Cadilhac J, Passouant P (1975) Neurochemical interpretation of the suppression of paradoxical sleep by chlomipramine. In: Sleep 1974, 2nd Europ Congr Sleep Res, Rome 1974, Karger, Basel
del Castillo J, Katz B (1954) The effect of magnesium on the activity of motor nerve endings. J Physiol 124:553–559
Charnock JS, Simonson LP (1978) Vatiations in (Na++K+)-ATPase and Mg2+-ATPase activity of the ground squirrel brain during hibernation. Comp Biochem Physiol 59-B: 223–229
Chhaparwal BC, Pohowalla JN (1966) Magnesium levels in serum and in CSF in children. Indian J Pediat 33: 145–148
Chutkow JG, Meyers S (1968) Chemical changes in the cerebrospinal fluid and brain in magnesium deficiency. Neurology 18:963–974
Durlach J (1976) Neurological manifestations of magnesium imbalance. In: Vinken PJ, Bruyn GW (eds) Handbook of clinical neurology, Vol 28: Metabolite and deficiency diseases of the nervous system, Part II. North Holland Publishing Comp, Amsterdam
Freemon FR (1973) Clinical pharmacology of sleep: a critical review of all-night electroencephalographic studies. Behav Neuropsych 5:49–60
Fukuda Y, Loeschke HH (1977) Effect of H+ on spontaneous neuronal activity in the surface layer of the rat medulla oblongata in vitro. Pflügers Arch 371:125–134
Gabriel M, Albani M (1977) Rapid eye movement sleep, apnea, and cardiac slowing influenced by phenobarbital administration in the neonate. Pediatrics 60:426–430
Goldberg J, Stein RJ (1978) Seasonal variation in suddeninfant-death syndrome. Lancet II:107
Gould JB, Lee AFL, James O, Sander L, Teager H, Fineberg N (1977) The sleep state characteristics of apnea during infancy. Pediatrics 59:182–194
Hoppenbrouwers T, Hodgman JE, Harper RM, Hofmann E, Sterman MB, McGinty DJ (1977) Polygraphic studies of normal infants during the first six months of life: III. Incidence of apnea and periodic breathing. Pediatrics 60: 418–425
Itil TM (1973) The effects of minor and major transquillizers on digital computer sleep prints. In: The Nature of Sleep. International Symposium 1971. G Fischer, Stuttgart
Klose E (1914) Beobachtungen über die therapeutische Wirkung des Kalziums und des Magnesiums bei der Spasmophilie. Monatsschr Kinderheilk 13:517–578
Krasts IV, Chemeris NK, Veprintsev BN (1978) Ionic selectivity of excitable neurone membrane: are there any separate potential-dependent channels for Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+? Comp Biochem Physiol 61 A:519–527
Masslow M (1914) Über Veränderungen der Atmungskurven bei Kindern mit spasmophilen Symptomen unter dem Einfluß von äußeren Reizen und die Bedeutung dieser Veränderungen für die Diagnose der latenten Tetanie. Monatsschr Kinderheilk 13:99–112
Maxion H (1968) Erfahrungen mit Tegretal im polygraphischen Schlaf-EEG. Nervenarzt 39:547–549
Meier-Koll A, Mikschiczek D, Hofmann A, Kohler Th, Kriesche H (1973) Polygraphische Schlafstudien an jugendlichen Drogenabhängigen. Z EEG-EMG 4:68–77
Peltner HU, Dralle D (1977/78) Hypomagnesiämische Krämpfe beim Neugeborenen, jahreszeitliche Häufung? Pädiat Prax 19:345–350
Polc P, Haefely W (1975) Effects of flunitrazepam on the sleep of cats. In: Sleep 1974, 2nd Europ Congr Sleep Res, Rome 1974. Karger, Basel
Radil-Weiss T, Syka J, Skvaril J, Popelar J (1975) Functional organisation of reticular core under different states of vigilance. In: Sleep 1974, 2nd Europ Congr Sleep Res, Rome 1974. Karger, Basel
Rajan KS, Davis JM, Colburn RW, Jarke FH (1972) Metal chelates in the storage and transport of neurotransmitters: formation of mixed ligand chelates of Mg2+-ATP with biogenic amines. J Neurochem 19:1099–1116
Stein IM, White A, Kennedy JL, Merisalo RL, Chernoff H, Gould JB (1979) Apnea recordings of healthy infants at 40, 44, and 52 weeks postconception. Pediatrics 63:724–730
Tissot R (1965) The effects of certain drugs on the sleep cycle in man. In: Progress in brain research, Vol 18: Sleep mechanisms. Elsevier Publishing Comp, Amsterdam London New York
Turner TL, Cockburn F, Forfar JO (1977) Magnesium therapy in neonatal tetany. Lancet I:283–284
de Weer P (1976) Axoplasmic free magnesium levels and magnesium extrusion from squid giant axons. J Gen Physiol 68:159–178
Zoglo DP, Luckey DW, Fraikor AL (1979) Birth rate and sudden infant death. Lancet II:260
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dralle, D., Bödeker, R.H. Serum magnesium level and sleep behavior of newborn infants. Eur J Pediatr 134, 239–243 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00441479
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00441479