Summary
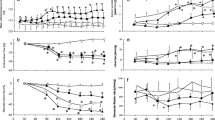
The effects of atrial natriuretic factor (ANF) 15 pmol/kg/min on renal function were studied in 7 normal male volunteers during maximal water diuresis. Subjects were studied in neutral salt balance either before, or after, seven days treatment with 40 mg oral frusemide. The post-frusemide state was associated with activation of the renin-angiotensin system (RAAS) and generally higher noradrenaline levels; this state was also associated with sodium retention, mainly due to enhanced distal nephron reabsorption.
Without diuretic pretreatment ANF produced a natriuresis and diuresis associated with inhibition of both proximal and distal nephron sodium reabsorption. In contrast, after frusemide pretreatment, ANF caused an increase in water excretion (urinary flow rate) but no change in sodium excretion. In the post-diuretic condition ANF did not affect renal tubular handling of sodium.
The enhanced tubular reabsorption of sodium post-frusemide, and the failure of ANF to suppress this, could be due to activation of the RAAS and SNS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biollaz J, Bidiville J, Diezi J, Waeber B, Nussberger J, Brunner-Ferber F, Gomez H, Brunner HR (1987) Site of action of synthetic atrial natriuretic peptide evaluated in humans. Kidney Int 32: 537–546
Brown J, Cott L (1987) Renal mechanisms of human α-atrial natriuretic peptide in man. J Physiol 387: 31–46
McMurray J, Seidelin PH, Struthers AD (1988) Evidence for a proximal and distal nephron action of atrial natriuretic factor in man. Naphron (in press)
Johnston CI, Arnolda L, Tsunoda K, Hodsman P (1987) Atrial natriuretic factor in congestive heart failure. In: Brenner BM, Laragh JH (eds) Biologically active atrial peptides, vol 1. Raven Press, New York, pp 89–95
McMurray J, Struthers AD (1987) The role of neuroendocrine abnormalities in the enhanced sodium and water retention of chronic heart failure. Pharmacol Toxicol 61: 209–214
Morgan DA, Peuler JD, Koephe JP, DiBona GF, Mark AL (1986) The renal sympathetic nerves attenuate the natriuretic effects of atrial peptides. Clin Res 34: 937A
Koephe JP, DiBona GF (1987) Blunted natriuresis due to atrial natriuretic peptide in chronic sodium retaining disorders. Am J Physiol 252: F865–871
McMurray J, Struthers AD (1988) Renal effects of angiotensin II, ANP and their interaction in man. J Hypertens 5: 559–562
Wilcox CS, Mitch WE, Kelly RA, Skorecki K, Meyer TW, Friedman PA, Souney PF (1983) Response of the kidney to furosemide I. Effects of salt intake and renal compensation. J Lab Clin Med 102: 450–458
Roberts CJC, Daneshmend TK (1981) Assessment of natriuretic drugs. Br J Clin Pharmac 12: 465–474
Brown MJ, Jenner DA (1981) Novel double-isotope technique for enzymatic assay of catecholamines, permitting high precision, sensitivity and plasma sample capacity. Clin Sci 61: 591–598
Kelly RA, Wilcox CS, Mitch WE, Meyer TW, Souney PF, Rayment CM, Friedman PA, Swartz (1983) Response of the kidney of furosemide II. Effect of captopril on sodium balance. Kidney Int 24: 233–239
Wilcox CS, Guzman NJ, Mitch WE, Kelly RA, Maroni BJ, Souney PF, Rayment CM, Braun L, Colucci R, Loon NR (1987) Na+, K+ and BP homeostasis in man during furosemide: Effects of prazosin and captopril. Kidney Int 31: 135–141
Weidman P, Hellmueller B, Uehlinger DE, Lang RE, Gnaedinger MP, Hasler L, Shaw S, Bachmann C (1986) Plasma levels and cardiovascular, endocrine and excretory effects of atrial natriuretic peptide during different sodium intakes in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 62: 1027–1036
Cuneo RC, Espiner EA, Nicholls MG, Yandle TG, Joyce SL, Gilchrist NL (1986) Renal, haemodynamic and hormonal responses to atrial natriuretic peptide infusions in normal man and effect of sodium intake. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 63: 946–953
Gaillard CA, Koomans HA, Boer WH, Boer P, Dorhout-Mers EJ (1987) Atrial natriuretic peptide and sodium intake: Blunted effects in the normal sodium-retaining kidney. Neth J Med 30: 10–16
Solomon LR, Atherton JC, Bobinski H, Green R (1987) Effect of dietary sodium chloride and posture on plasma immunoreactive atrial natriuretic peptide concentrations in man. Clin Sci 72: 201–208
McMurray J, Struthers AD (1988) Arginine vasopressin dissociates the natriuresis and diuresis due to ANF in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol (in press)
Freeman RH, Davis JO, Vari RC (1984) Renal response to atrial natriuretic factor in conscious dogs with caval constriction. Am J Physiol 248: R495-R500
Bayliss J, Norell M, Canepa-Anson R, Sutton G, Poole-Wilson P (1987) Untreated heart failure: Clinical and neuroendocrine effects of introducing diuretics. Br Heart J 57: 17–22
Francis GS, Goldsmith SR, Levine TB, Olivari MT, Cohn JN (1984) The neurohumoral axis in congestive heart failure. Ann Int Med 101: 370–377
Crozier IG, Nicholls MG, Ikram H, Espiner EA, Gomez HJ, Warner NJ (1986) Haemodynamic effects of atrial peptide infusion in heart failure. Lancet 2: 1242–1245
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McMurray, J., Struthers, A.D. Frusemide pretreatment blunts the inhibition of renal tubular sodium reabsorption by ANF in man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 35, 333–338 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00561360
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00561360