Abstract
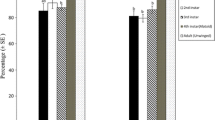
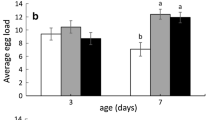
Several aspects of parasitism of the pea aphid,Acyrthosiphon pisum (Harris), by the mite parasiteAllothrombium pulvinum Ewing, were examined in the laboratory. Larvae ofA. pulvinum were fastmoving mites that find their host by contact of their foretarsi with the host. They can attach to all parts of the host body, but insert their chelicerae only into weakly sclerotized parts such as intersegmental membranes. Of the attached larval mites, most (63.5–74.1%) were on the thorax of their hosts, regardless of host size. In hosts of small and medium size, the ventral side receives most parasitism, whereas in large hosts the lateral sites are most often attacked. Larval mites prefer large hosts when allowed to select between pairs of large and small hosts, but show no significant preference when allowed to choose between pairs of large and medium hosts or pairs of medium and small hosts. In two-choice tests, larval mites prefer previously parasitized hosts to umparasitized hosts, which results in superparasitism of the hosts. When the mite load is fiveA. pulvinum kills all small hosts within three days, and all medium hosts and 50% of large hosts within four days, the reproduction of surviving adult aphids were significantly reduced. Host-finding behavior, attachment site preference, host size selection, superparasitism, and effect on hosts are briefly reviewed for larval parasites of Trombidiidae. The potential role of larvalAllothrombium in integrated and biological aphid control is also discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bode, E., 1980. Die braunlichrote SamtmilbeAllothrombium fuliginosum (Herm.), (Acari: Trombidiidae) als Parasit der bleichen getreideblattlausMetropolophium dirhodum (Walk.). Mitt. Dtsch. Ges. Allg. Angew. Entomol., 2: 57–58.
Chen, P.-L., Wang, X.-Y., Si, J.-C. and Li, D.-L., 1981. Observation on the behaviour ofAllothrombium sp., a natural enemy of two-spotted spider mite. Kunchong Zhishi, 18: 160–162 (in Chinese).
Davis, R., 1961. A mite,Allothrombium mitchelli, new to science, predator on the balsam woolly aphid. Proc. Entomol. Soc. Wash., 63: 269–272.
Eickwort, G.C., 1983. Potential use of mites as biological control agents of leaf-feeding insects. In: M.A. Hoy and G.L. Cunningham (Editors), Biological Control of Pests by Mites, University of California Press/ANR Publishing. Oakland, CA, pp. 41–52.
Ewing, H.E., 1917. New Acarina. Part. II. Descriptions of new species and varieties from Iowa, Missouri, Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio. Bull. Am. Mus. Nat. Hist., 37: 149–173.
Feider, Z., 1956. Acarieni noi, parasiti pe insecte daunatoare apartinind genuluiPhillotreta. An. Stiint. Univ. A1 I Cuza, Iasi, (S.N.), 2: 119–161.
Feider, Z., 1977. Contribution a la connaissance des larves d'acariens du bassin ariental de la Mediterranee. Isr. J. Zool., 26: 100–113.
Feider, Z. and Agekian, H., 1967. Une nouvelle acarien parasite des pucerans. Trav. Mus. Hist. Nat. Grigore Antipa, 7: 73–80.
Howard, C.W., 1918. A preliminary report on the Trombidiidae of Minnesota. Rep. State Entomol. Minn., 17: 111–144.
Huffaker, C.B., 1948. An improved cage for work with small insects. J. Econ. Entomol., 41: 648–649.
Hughes, P.R., Hunter, R.E. and Leigh, T.F., 1966. A light-weight leaf cage for small arthropods. J. Econ. Entomol., 59: 1024–1025.
Lindquist, E.E., 1983. Some thoughts on the potential for use of mites in biological control, including a modified concept of parasitoids. In: M.A. Hoy and G.L. Cunningham (Editors), Biological Control of Pests by Mites. University of California Press/ANR Publishing, Oakland, CA, pp. 12–20.
Moss, W.W., 1960. Description and mating behaviour ofAllothrombium lerouxi, new species, (Acarina: Trombidiidae), a predator of small arthropods in Quebec orchards. Can. Entomol., 92: 898–905.
Oudemans, A.C., 1912. Die bis jetzt bekannten Larven von Trombidiidae und Erythraeidae. Zool. Jahrb., Suppl., 14: 1–230.
Robaux, P., 1974. Recherches sur le developpement et la biologie des acariens “Thrombidiidae”. Mem. Mus. Hist. Nat., Ser. A (Zool)., 85: 1–186.
Severin, H.C., 1944. The grasshopper mite,Eutrombidium trinogum (Herm.), an important enemy of grasshoppers. S.D. Agric. Stn. Tech. Bull., 3: 1–36.
Snedecor, G.W. and Cochran, W.G., 1989. Statistical methods (8th edition), Iowa State University Press, Ames.
Thompson, W.R. and Simmonds, F.J., 1965. A catalogue of the parasites and predators of insect pests. Section 4. Host Predator Catalogue. Commonwealth Agricultural Bureaux, Oxford, Great Britain, 198 pp.
Welbourn, W.C., 1983. Potential use of trombidioid and erythraeoid mites as biological control agents of insects. In: M.A. Hoy and G.L. Cunningham (Editors), Biological Control of Pests by Mites. University of California Press/ANR Publishing, Oakland, CA, pp. 103–140.
Xin, J.-L., 1984. Current status and potentials for use of mites as biological control agents in China. In: P.L. Adkisson and S. Ma (Editors), Proc. Chinese Academy of Science and United States National Academy of Science Joint Symp., Biological Control of Insects, 25–28 September 1982, Beijing, China. Science Press, Beijing, pp. 282–287.
Young, O.P. and Welbourn, W.C., 1987. Biology ofLasioerythraeus johnstoni (Acari: Erythraeidae), ectoparasitic and predaceous on the tarnished plant bug,Lygus lineolaris (Hemiptera: Miridae), and other arthropods. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am., 80: 243–250.
Zhang, Z.-Q., 1987. Perspective of the utilization of trombidioid mites in IPM. Plant Prot., 13: 40–41 (in Chinese).
Zhang, Z.-Q., 1988. Two common mites ofAllothrombium Berlese in China. Kunchong Zhishi, 25: 172–174 (in Chinese).
Zhang, Z.-Q. and Xin, J.-L., 1989a. Biology ofAllothrombium pulvinum (Acariformes: Trombidiidae), a potential biological control agent of aphids in China. Exp. Appl. Acarol., 6: 101–108.
Zhang, Z.-Q. and Xin, J.-L., 1989b. Studies on the morphology and life history ofAllothrombium pulvinum Ewing (Acariformes: Trombididae). Acta Entomol. Sinica, 32(2): 192–199 in Chinese, with English abstract).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, ZQ. Parasitism ofAcyrthosiphon pisum byAllothrombium pulvinum (Acariformes: Trombidiidae): Host attachment site, host size selection, superparasitism and effect on host. Exp Appl Acarol 11, 137–147 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01246086
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01246086