Abstract
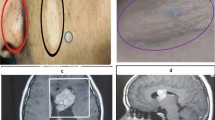
Tuberous sclerosis is a neurocutaneous syndrome with a wide variety of clinical, pathologic, and radiologic manifestations. Intracranial phakomatosis has been reported to include subependymal nodules; cortical tubers, and subependymal giant-cell astrocytomas. Subependymal giant-cell astrocytomas are rare, benign brain tumors of unknown histogenesis which cause increased intracranial pressure, seizures, and focal neurologic signs. The only treatment of these tumors is total surgical removal, because they are not sensitive to irradiation and chemotherapy. We report a patient with tuberous sclerosis who underwent surgery for a large subependymal giant-cell astrocytoma.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akluwalia CK, PT Chandrasoma: Cytomorphology of subependymal giant cell astrocytoma. A case report. Acta Cytol 37 (1993) 197–200
Altermatt HT, BW Scheithauer: Cytomorphology of subependymal giant-cell astrocytoma. Acta Cytol 36 (1992) 171–175
Bell DG, BF King, RR Hattery, et al: Imaging characteristics of tuberous sclerosis. AJR 156 (1991) 1081–1086
Boesel CP, GW Paulson, EJ Kosnik, et al: Brain hamartomas and tumors associated with tuberous sclerosis. Neurosurgery 4 (1979) 410–417
Chow CW, GL Klug, EA Lewis: Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma in children. An unusual discrepancy between histological and clinical features. J Neurosurg 68 (1988) 880–883
Fujiwara S, T Takaki, T Hikita, et al: Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma associated with tuberous sclerosis. Do subependymal nodules grow? Childs Nerv System 5 (1989) 43–44
Gomez MR: Tuberous Sclerosis. New York. Raven Press 1979
Gomez MR: Factors determining outcome in tuberous sclerosis. Int Pediatr 4 (1989) 127
Margo CE, JP Barletta, JA Staman: Giant cell astrocytoma of the retina in tuberous sclerosis. Retina 13 (1993) 155–159
Menor F, L Marti-Bonmati, F Mulas, et al: Neuroimaging in tuberous sclerosis: a clinicoradiological avaluation in pediatric patients. Pediatr Radiol 22 (1992) 485–489
Oikawa S, K Sakamoto, N Kobayashi: A neonatal huge subependymal giant cell astrocytoma: case report. Neurosurgery 35 (1994) 748–750
Painter MJ, D Pang, M Ahdab-Barmada, et al: Connatal brain tumors in patient with tuberous sclerosis. Neurosurgery 14 (1984) 570–573
Shepherd CW, BW Scheithauer, MR Gomez, et al: Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma: A clinical, pathological, and flowcytometric study. Neurosurg 28 (1991) 864–868
Tanaka J, S Kawakami, K Hashimoto: Immunocytochemistry of subependymal giant cell astrocytoma associated with tuberous sclerosis (in Japanese). No To Hattatsu 21 (1989) 222–226
Winter J: Computed tomography in diagnosis of intracranial tumors versus tubers in tuberous sclerosis. Acta Radiol 23 (1982) 337–344
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ergün, R., Ökten, A.İ., Yaman, M. et al. Subependymal giant-cell astrocytoma associated with tuberous sclerosis: Case report. Neurosurg. Rev. 21, 185–188 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02389330
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02389330