Abstract
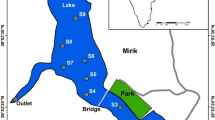
Industrialization coupled with urbanizaton has led to stress in the Buckingham Canal which runs parallel to Bay of Bengal at a distance of around 1 km from the coastline. 4 sediment cores were collected along Ennore — Pulicat stretch to determine acid leachable trace metal concentration. Core samples were collected using gravity corer. The cores were sliced horizontally at 2.5 cm to determine the grain size, sediment composition, pH, organic matter, calcium carbonate, acid leachable trace metals; cadmium, chromium, copper, lead, zinc. The trace metals were extracted using acid mixture containing hydro fluoric acid, nitric acid and sulphuric acid and analysed by atomic emission spectrophotometer. In an attempt to infer anthropogenic input from geogenic input, several approaches including comparison with sediment quality guidelines — ecotoxicological sense of heavy metal contamination and classification by quantitative indexes such as geoaccumalation index, anthropogenic factor, enrichment factor, contamination factor and degree and pollution load index was attempted. Grain size analysis and sediment composition of core samples shows Ennore is sandy in nature having a neutral pH. Organic matter enrichment is observed to a higher extent in core 3. Core 2 at a depth of 5 cm shows organic matter of 9.4 %. calcium carbonate is totally absent at the surface sediments in core 2. Cores collected within the canal showed a higher heavy metal concentration than the cores collected from Pulicat lagoon and 2 km into the Ennore Sea. The trace metal concentration for cadmium, lead and zinc in Ennore does not pose a threat to the sediment dwelling fauna whereas chromium and copper are likely to pose a threat. Quantitative indexes place Ennore under moderately polluted. Ennore is likely to face a serious threat of metal pollution with the present deposition rates unless stringent pollution control norms are adopted.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agemian, H.; Chau, A. S. Y., (1976). Evaluation of extraction technique for 450 the determination of metals in aquatic sediments. Analyst, 101, 761–767 (7 pages).
Angelidis, M. O.; Aloupi, M., (1997). Assessment of metal concentrations in shallow coastal sediments around Mytilene, Greece. Interm. J. Environ. Anal. Chem., 68 (2), 281–293 (13 pages).
Araujo, M. F. D.; Bernard, P. C.; VanGrieken, R. E., (1988). Heavy metal contamination in sediments from the Belgium Coast and Scheldt estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull., 19, 269–73 (5 pages).
Bakan, G; Ozkoc, H. B., (2007). An ecological risk assessment of the impact of heavy metals in surface sediments on biota from the mid-Black Sea coast of Turkey. Int. J. Environ. Stud., 64 (1), 45–57 (13 pages).
Baptista Neto, J. A.; Smith, B. J.; McAllister, J. J., (2000). Heavy metal concentrations in surface sediments in a nearshore environment, Jurujuba Sound, Southeast Brazil. Environ. Pollut., 109 (1), 1–9 (9 pages)
Birch, G., (2003). A scheme for assessing human impacts on coastal aquatic environments using sediments. in: Woodcoffe, C. D., Furness, R. A. (Eds.), Coastal GIS 2003. Wollongong University Papers in Center for Maritime Policy, 14, Australia.
Boyden, C. R.; Aston, S. R.; Thornton, I., (1979). Tidal and seasonal variation of trace elements in two Cornish estuaries. Estuarine Coast Mar. Sci., 9 (3), 303–317 (15pages).
Bryan, G. W.; Langston, W. J., (1992). Bioavailability, accumulation and effects of heavy metals in sediments with special reference to United Kingdom estuaries: a review. Environ. Pollut., 76 (2), 89–131 (43 pages).
DOD, (2001). Coastal ocean monitoring and prediction system. Department of Ocean Development. Annual Report., 37-110.
Ergin, M.; Saydam, C.; Basturk, O.; Erdem, E.; Yoruk, R., (1991). Heavy metal concentrations in surface sediments from the two coastal inlets (Golden Horn Estuary and _Izmit Bay) of the northeastern Sea of Marmara. Chem. Geo., 91 (3), 269–285 (16 pages).
Everaart, J. M.; Fischer, C. V., (1992). The distribution of heavy metals (Cu, Zn, Cd, Pb) in the fine fraction of surface sediments of the North Sea. Neth. J. Sea Res., 29 (4), 323–331 (9 pages).
Fergusson, J. E., (1990). The heavy elements: Chemistry, environmental impact and health effects, Pergamon Press, Oxford, England.
Folk, R. L.; Ward, W. C., (1957). Brazos river bar: A study in the significance of grain size parameters. J. Sediment Petrol., 27 (1), 3–27 (25 pages).
Förstner, U.; Wittman, G. T. W., (1983). Metal Pollution in the Aquatic Environment. Springer Heidelberg., 486.
Gaillard, J. F.; Pauwells, H.; Michard, G., (1989). Chemical diagenesis of coastal marine sediments. Oceanol. Acta., 12, 175–187 (13 pages).
Gaudette, H. E.; Flight, W. R.; Toner, L.; Folger, D. W., (1974). An inexpensive titration method for the determination of organic carbon in recent sediments. J. Sediment Petrol., 44 (1), 249–253 (5 pages).
Gibbs, R. J., (1977). Transport phases of transition metals in the Amazon and Yukon Rivers. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull., 88 (6), 829–843 (14 pages).
Hakanson, L., (1980). Ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res., 14 (5), 975–1001 (26 pages).
Hart, B., (1982). Uptake of trace metals by sediments and suspended particulates: A review. Hydrobiologia., 91 (1), 299–313 (15 pages).
Horowitz, E.; Elrick, K., (1987). The relation of stream sediment surface area, grain size and surface area to trace element chemistry. Appl. Geochem., 2 (4), 437–451 (14 pages).
Jayapraksh, M., (2002). A geochemical assessment of heavy metal pollution in Ennore creek, North of Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India. Ph.D. Thesis. 46-47.
Jonathan, M. P.; Ram-Mohan, V., (2003). Heavy metals in sediments of the inner shelf off the Gulf of Mannar, southeast coast of India. Mar. Pollut. Bull., 46 (2), 258–268 (11 pages).
Kalavani, J., (2007). Pollution induced inter and intra specific changes in the benthic community structure in the Buckingham canal, Ennore. Ph.D. thesis., 73-74.
Keil, R. G.; Montlucon, D. B.; Prahl, F. R.; Hedges, J. I., (1994). Sorptive preservation of labile organic matter in marine sediments. Nature, 370, 549–552 (4 pages).
Krumbein, W. C.; Pettijohn, F. J., (1938). Manual of sedimentary petrography. D. Appleton Century Co. Inc., New York. 549-551.
Loring, D. H.; Rantala., (1992). Manual for the geochemical analyses of marine sediments and suspended particulate matter. Earth-Sci. Rev., 32 (4) 235–283 (49 pages).
Luoma, S. N.; (1990). Processes affecting metal concentrations in estuarine and coastal marine sediments. Heavy metal in the marine Environment., CRC press., Boca Raton, FL, 51–66.
McKay, J. L.; Pedersen, T. F.; Mucci, A., (2007). Sedimentary redox conditions in continental margin sediments (N. E. Pacific) — Influence on the accumulation of redox-sensitive trace metals. Chem. Geol., 238 (3-4), 180–196 (17 pages).
Moore, P. A.; Reddy, K. R.; Fisher, M. M., (1989). Phosphorus flux between sediment and overlying water in Lake Okeechobee, Florida: spatial and temporal variations. J. Environ. Qual., 27 (6), 1428–1439 (12 pages).
Mucha, A. P.; Vasconcelos, M. T. S. D.; Bordalo, A. A., (2003). Macrobenthic community in the Doura estuary: Relations with trace metals and natural sediment characteristics. Environ. Pollut., 121 (2), 169–180 (12 pages).
Muller, G., (1979). Schwermetalle in den Sedimenten des Rheins Veranderungen seit. Umschau. 79 (24), 778–783 (6 pages). Muthumanickam, J., (2003). Geochemical assessment of heavy metal pollution in Ennore Creek, North of Chennai, India. University of Madras (India), 298.
Nadia, B. E.; Badr Anwar, A.; El-Fiky Alaa R.; Mostafa, Bandr A.; Al-Mur., (2009). Metal pollution records in core sediments of some Red Sea coastal areas, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Environ. Monit. Assess., 155 (1-4), 509–526 (18 pages).
Nouri, J.; Karbassi, A. R.; Mirkia, S., (2008). Environmental management of coastal regions in the Caspian Sea. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 5 (1), 43–52 (10 pages)
Nouri, J.; Mahvi, A. H.; Babaei, A.; Ahmadpour, E., (2006). Regional pattern distribution of groundwater fluoride in the Shush aquifer of Khuzestan County Iran Fluoride. Fluoride., 39 (4), 321–325 (5 pages).
Pekey, H., (2006). Heavy metal pollution assessment in sediments of Izmit Bay, Turkey. Environ. Monitor. Assess., 123 (1-3), 219–231 (13 pages).
Perin, G.; Bonardi, M.; Fabris, R.; Simoncini, B.; Manente, S.; Tosi, L.; Scotto, S., (1997). Heavy metal pollution in central Venice Lagoon bottom sediments: evaluation of the metal bioavailability by geochemical speciation procedure. Environ. Tech., 18 (6), 593–604 (12 pages).
Ruiz-Ferna’ndez, A. C.; Pa’ez-Osuna, F.; Hillaire-Marcel, C.; Soto-Jime’nez, M.; Ghaleb, B., (2001). Principal component analysis applied to assessment of metal pollution from urban wastes in the Culiaca’n river estuary. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 67 (5), 741–748 (9 pages).
Samarghandi, M. R.; Nouri, J.; Mesdaghinia, A. R.; Mahvi, A. H.; Naseri, S.; Vaezi, F., (2007). Efficiency removal of phenol, lead and cadmium by means of UV/TiO2/H2O2 processes. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 4 (1), 10–25 (16 pages).
Schiff, K. C.; Weisberg, S. B., (1999). Iron as a reference element for determining trace metal enrichment in Southern California coast shelf sediments. Mar. Environ. Res., 48 (2), 161–176 (16 pages).
Spencer, K. L.; Macleod, C. L., (2002). Distribution and partioning of heavy metals in estuarine sediment cores and implications for the use of sediment quality guidelines. Hydrol. Earth System Sci., 6 (6), 989–998 (13 pages).
SPSS., (1995). Professional statistics 6.1. Marija J. Norusis/ SPSS Inc, Chicago.
Szefer, P.; Geldon, J.; Ahmed Ali, A.; Paez Osuna, F.; Ruiz-Fernandes, A. C.; GuerroGaivan, S. R., (1998). Distribution and association of trace metals in soft tissue and byssus of Mytella strigata and other benthal organisms from Mazatlan Harbour, Mangrove Lagoon of the northwest coast of Mexico. Environ. Int., 24 (3), 359–374 (16 pages).
Tam, N. F. Y.; Wong, Y. S., (2000). Spatial variation of heavy metals in surface sediments of Hong Kong mangrove swamps. Environ. Pollut., 110 (2), 195–205 (11 pages).
Taulis, M. E., (2005). Metal contaminants in leachate from sanitary landfills, in: Moore, T. A.; Black, A.; Centeno, J. A.; Harding, J. S.; Trumm, D. A. (Eds.), Metal contaminants in New Zealand, Resolutionz Press, Christchurch, New Zealand, 173–190.
Tomlinson, D. C.; Wilson, J. G.; Harris, C. R.; Jeffery, D. W., (1980). Problems in the assessment of heavy metals levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgol. Wiss. Meeresunters., 33 (1-4), 566–575 (10 pages).
Turekian, K. K.; Wedepohl, K. H., (1961). Distribution of the elements in some major units of the Earth’s crust. Bull. Geol. Soc. Am., 72 (2), 175–192 (18 pages).
Vinodhini, R.; Narayanan, M., (2008). Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in organs of fresh water fish Cyprinus carpio (Common carp). Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 5 (2), 179–182 (4 pages).
Voutsinou-Taliadouri, F., (1995). A weak acid extraction method as a tool for the metal pollution assessment in surface sediments. Mikrochimica Acta., 119 (3-4), 243–249 (7 pages).
Zvinowanda, C. M.; Okonkwo, J. O.; Shabalala, P. N.; Agyei, N.M., (2009). A novel adsorbent for heavy metal remediation in aqueous environments. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech. 6 (3), 425–434 (10 pages).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seshan, B.R.R., Natesan, U. & Deepthi, K. Geochemical and statistical approach for evaluation of heavy metal pollution in core sediments in southeast coast of India. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 7, 291–306 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326139
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326139