Abstract.
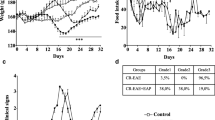
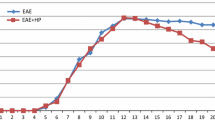
Objectives and Design: The present investigation examines the effects of increasing central nervous system (CNS) levels of nitric oxide (NO), via the administration of L-arginine, on the development of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE).¶Subjects: EAE was induced in male Lewis rats (200-250 g).¶Treatment: Normal rats were orally dosed with L-arginine (300 mg/kg body weight) once daily for 12 days. EAE-sensitised animals received L-arginine (300 mg/kg body weight) once daily from day 1 to 12 post-inoculation.¶Methods: Neurological and histological development of EAE were assessed. In addition, CNS cytosol levels of nitrite, superoxide and hydrogen peroxide were measured. Results were analysed using the Mann Whitney U-test and Chisquared test.¶Results: L-arginine administration significantly delayed disease onset (p<0.05) and reduced the severity of neurological (p<0.05) and histological (p<0.001) signs of EA E. Treatment with L-arginine caused a significant elevation in CNS nitrite concentrations (p<0.05) which in EAE-sensitised animals was associated with a concomitant and dramatic decrease in superoxide (p<0.05) and hydrogen peroxide (p<0.05) levels.¶Conclusions: The results suggest that NO may act as a protective molecule during the development of EAE possibly via the modulation of oxidant-mediated neuroinflammation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 2 May 2000; returned for revision 24 May 2000; accepted by C. J. Whelan 6 July 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scott, G., Bolton, C. L-arginine modifies free radical production and the development of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Inflamm. res. 49, 720–726 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s000110050652
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s000110050652