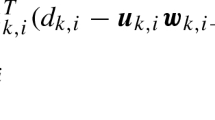Abstract
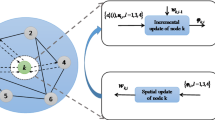
We study the node-specific parameter estimation problem, where agents in a network collaborate to obtain the different but overlapping vectors of parameters, which can be of local interest, common interest to a subset of agents, and global interest to the whole network. We assume that all the regressors and the measurements are corrupted by additive noise. For these settings, a bias-compensation recursive-least-square algorithm based on a diffusion mode of cooperation is proposed; its stability is obtained via the detailed derivation of convergence in the mean sense. In addition, a closed-form expression for the algorithm’s mean-square deviation is also provided to evaluate the steady-state performance of the whole network. Finally, we present simulation results that indicate the efficiency of the proposed method.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
All data included in this study are available upon request by contacting the corresponding author.
References
R. Abdolee, B. Champagne, A. H. Sayed. Diffusion LMS for source and process estimation in sensor networks. In 2012 IEEE Statistical Signal Processing Workshop (SSP), pp. 165–168, (2012)
S. Al-Sayed, J. Plata-Chaves, M. Muma, M. Moonen, A. Zoubir, Node-specific diffusion lms-based distributed detection over adaptive networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 66, 11 (2017)
A. Bertrand, M. Moonen, Distributed adaptive node-specific signal estimation in fully connected sensor networks–part ii: simultaneous and asynchronous node updating. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 58(10), 5292–5306 (2010)
A. Bertrand, M. Moonen, A. H. Sayed. Diffusion-based bias-compensated rls for distributed estimation over adaptive sensor networks. In 2011 19th European Signal Processing Conference, pp 1025–1029, (2011)
A. Bertrand, M. Moonen. Distributed adaptive node-specific signal estimation in fully connected sensor networks—part i: Sequential node updating. In IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 58, pp. 5277–5291 (2010)
A. Bertrand, M. Moonen, A.H. Sayed, Diffusion bias-compensated RLS estimation over adaptive networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 59(11), 5212–5224 (2011)
N. Bogdanovic, J. Plata-Chaves, K. Berberidis, Distributed incremental-based LMS for node-specific adaptive parameter estimation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 62(20), 5382–5397 (2014)
F.S. Cattivelli, A.H. Sayed, Diffusion lms strategies for distributed estimation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 58(3), 1035–1048 (2010)
F.S. Cattivelli, C.G. Lopes, A.H. Sayed, Diffusion recursive least-squares for distributed estimation over adaptive networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 56(5), 1865–1877 (2016)
J. Chen, C. Richard, A.H. Sayed, Multitask diffusion adaptation over networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 62(16), 4129–4144 (2014)
J. Chen, A. H. Sayed. On the benefits of diffusion cooperation for distributed optimization and learning. In 21st European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO 2013), pp. 1–5, (2013)
J. Chen, A.H. Sayed, Diffusion adaptation strategies for distributed optimization and learning over networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 60(8), 4289–4305 (2012)
J. Chen, S. Y. Tu, A. H. Sayed. Distributed optimization via diffusion adaptation. In IEEE International Workshop on Computational Advances in Multi-Sensor Adaptive Processing, pp. 281–284, (2011)
J. Chen, C. Richard. Performance analysis of diffusion LMS in multitask networks. In IEEE International Workshop on Computational Advances in Multi-Sensor Adaptive Processing, pp. 137–140, (2013)
J. Chen, C. Richard, A. Sayed. Adaptive clustering for multitask diffusion networks. pp. 200–204, 08 (2015)
L. Fan, L. Jia, R. Tao, Y. Wang, Distributed bias-compensated normalized least-mean squares algorithms with noisy input. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 61(11), 112210 (2018)
L.J. Jia, R. Tao, Y. Wang, K. Wada, Forward/backward prediction solution for adaptive noisy FIR filtering. Sci. China 52(6), 1007–1014 (2009)
C.G. Lopes, A.H. Sayed, Incremental adaptive strategies over distributed networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 55(8), 4064–4077 (2007)
C.G. Lopes, A. Sayed, Distributed adaptive incremental strategies: Formulation and performance analysis. vol 3, vol. 06, p. 3 (2006)
J. Lou, L. Jia, R. Tao, Y. Wang, Distributed incremental bias-compensated RLS estimation over multi-agent networks. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 60(3), 032204 (2017)
J. Plata-Chaves, N. Bogdanovic, K. Berberidis, Distributed incremental-based RLS for node-specific parameter estimation over adaptive networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 62(20), 5382–5397 (2013)
J. Plata-Chaves, M. Hasan Bahari, M. Moonen, Alexander Bertrand. Unsupervised diffusion-based LMS for node-specific parameter estimation over wireless sensor networks. 63(13), 3448–3460 (2015)
J. Plata-Chaves, N. Bogdanovic, K. Berberidis, Distributed diffusion-based LMS for node-specific adaptive parameter estimation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 63(13), 3448–3460 (2015)
A.H. Sayed, Adaptation, learning, and optimization over networks. Found. Trends Mach. Learn. 7(4), 311–801 (2014)
A.H. Sayed. Chapter 9 - diffusion adaptation over networks. In Abdelhak M. Zoubir, Mats Viberg, Rama Chellappa, and Sergios Theodoridis, editors, Academic Press Library in Signal Processing: Volume 3, volume 3 of Academic Press Library in Signal Processing, pp 323 – 453. Elsevier, (2014)
N. Takahashi, I. Yamada, A. Sayed. Diffusion least-mean squares with adaptive combiners, vol. 04, pp. 2845–2848 (2009)
N. Takahashi, I. Yamada, A.H. Sayed, Diffusion least-mean squares with adaptive combiners: formulation and performance analysis. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 58(9), 4795–4810 (2010)
M.A. Tinati, A. Rastegarnia, A. Khalili. An incremental least-mean square algorithm with adaptive combiner. vol. 01, pp. 266–269 (2010)
S.Y. Tu, A.H. Sayed, Diffusion strategies outperform consensus strategies for distributed estimation over adaptive networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 60(12), 6217–6234 (2012)
Y. Wang, W.P. Tay, W. Hu, A multitask diffusion strategy with optimized inter-cluster cooperation. IEEE J. Selected Topics Signal Process. 11(3), 504–517 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science foundation of China under Grants 41927801.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, C., Jia, L., Yang, ZJ. et al. Diffusion Bias-Compensation RLS Estimation Over Noisy Node-Specific Networks. Circuits Syst Signal Process 40, 2564–2583 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-020-01591-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-020-01591-8