Abstract
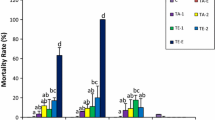
Studies were carried out to determine the toxicity of some selected pesticides on fresh water fish in a tropical environment. The uptake of the pesticides lindane, pentachlorophenol (PCP), and propoxur, which are frequently used on farms, and in industries as well as by loggers and timber men on wood were studied in concrete ponds at the University of Cape Coast, in Ghana. The fish used for the study were Oreochromis niloticus, Clarias gariepinus, and Chrysicthys nigrodigitatus. They were obtained from cultured ponds in the Cape Coast and Mankessim districts in the Central Region and Weija Dam, in the Greater Accra region of Ghana. Single high lethal concentration (SD) or acute treatment and cumulative/chronic (or multiple minor) lethal concentration (CD) treatment were employed in administering the pesticides to the fish via water. Gas chromatograph electron capture detector analysis was done on the dead fish to see the extent of ingestion. The LC50 values obtained for lindane on the three fish samples were as follows: Chrysicthys – 0.38 mg L−1; Oreochromis – 0.42 mg L−1, and Clarias – 1.2 mg L−1. Mortalities occurred in fish within 3–5 days of application. For the PCP on Chrysicthys, Oreochromis, and Clarias species the LC50 values were 0.42, 0.32 and 0.64 mg L−1, respectively, for over a 2- to 3-day period. For a three-time influx period of propoxur the LC50 for Chrysicthys, Oreochromis, and Clarias, were 22.0, 30.40, and 45.04 (all in mg L−1), respectively. The results obtained indicated that the pesticides had adverse effects on the general growth and reproduction of fish as shown by gonadosomatic indices.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asabere-Ameyaw A (2001) Observation on the reproductive biology and recruitment of the big eye grunt, Brachydeuterus auritus (Pisces: Haemutidae) in Ghana. J Ghana Sci Assoc 33:14–21
Davies J (1999) Animal research and development. J Anim Res Inst 4:123–125
American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (1980) Threshold Limit Values for Chemical Substances and Physical Agents in the Workroom Environment with Intended Changes, 6500 Glenway Avenue, Bldg. D-7, Cincinnati, OH 45211–4438, P 323
Mizell M, Romig E, Hartley W, Thiyagarajah A (1995) Sex on the brain but the heart is not really in it: developmental heart defects associated with aquatic pollution and microinjection of hexachlorobenzene into the Japanese Medaka embryo Biol Bull 189(2):196–197
Mizell M, Stegeman JJ, Romi E, Smolowitz R, Schlezinge J, Katayani R, Woodin B, Mortensen M (1996) Chemically induced cardiovascular defects in developmental stages of vertebrates: dose-response and phenotypic comparisons in Medaka and Zebrafish exposed to aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonists. Bio. Bull. 191:294–295
Morley K, Dyer A (1985) Facts about pesticides, Ministry of Environment Publication, ON
Nellor M (1999) ‘Ban on pesticides; in Heil Ann (edn) L.I.C.E. Lindane isn’t cooling for the environment. Sanitation District of Los Angeles Country, L.A. for United States Environmental Protection Agency
Pastor A, Hernadez F, Medina R, Lopez FI, Conesa M (1988) Organochlorine pesticides in marine organisms from the Castellan and Valencia Coasts of Spain. Mar Pollut Bull 19(55):235–238
Stainier DYR, Fishman MC (1994) The zebra fish as a model system to study cardiovascular development. Trends Cardiovasc Med 4: 207–212
Weinbach EC (1957) Biochemical basis for the toxicity of pentachlorophenol. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 43(5):393–397
Acknowledgments
We thank the government of Ghana for the financial support and the farmers in the study area.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hanson, R., Dodoo, D.K., Essumang, D.K. et al. The Effect of some Selected Pesticides on the Growth and Reproduction of Fresh Water Oreochromis niloticus, Chrysicthys nigrodigitatus and Clarias gariepinus . Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 79, 544–547 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-007-9279-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-007-9279-3