Abstract
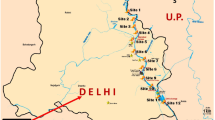
Metal contamination of Ganga river in relation to atmospheric deposition was investigated. The data reveled that, although Cr and Cu remained below their maximum admissible concentrations, levels of Cd and Pb in mid-stream waters at five out of six stations were higher than their respective maximum admissible concentration. About 62% of water samples contained Ni above its maximum admissible concentration of 20 μg L−1. Metal concentrations in water showed significant correlation and seasonal synchrony with atmospheric deposition. The study forms the first report on air-driven metal contamination of Ganga and has relevance from human health perspectives.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA (1989) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 17th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington
Azimi S, Ludwig A, Thévenot DR, Colin JL (2003) Trace metal determination in total atmospheric deposition in rural and urban areas. Sci Total Environ 308:247–256. doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(02)00678-2
Borbely–Kiss I, Koltay E, Szabo GY, Bazo L, Tar K (1999) Composition and sources of urban and rural atmospheric aerosols in Eastern Hungary. J Aerosol Sci 30:369–391. doi:10.1016/S0021-8502(98)00051-2
Bragazza L (2006) Heavy metals in bog waters: an alternative way to assess atmospheric precipitation quality? Global Planet Changes 53:290–298. doi:10.1016/j.gloplacha.2006.03.011
Eder A, Offiong OE (2002) Evaluation of water quality pollution indices for heavy metal contamination monitoring. A case study from Akpabuyo–Odukpani area, Lower Cross River Basin (Southeastern Nigeria). GeoJournal 57:295–304. doi:10.1023/B:GEJO.0000007250.92458.de
Eisenreich SJ (1980) Atmospheric input of trace metals to Lake Michigan. Water Air Soil Pollut 13:287–301. doi:10.1007/BF02145474
Pandey J, Agrawal M (1994) Evaluation of air pollution phytotoxicity in a seasonally dry tropical urban environment using three woody perennials. New Phytol 126:53–61. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.1994.tb07529.x
Pandey J, Pandey U (2009) Accumulation of heavy metals in dietary vegetables and cultivated soil horizon in organic farming system in relation to atmospheric deposition in a seasonally dry tropical region of India. Environ Monit Assess 148:61–74. doi:10.1007/s10661-007-0139-8
Pandey J, Agrawal M, Khanam N, Narayan D, Rao DN (1992) Air pollutants concentrations in Varanasi, India. Atmos Environ 26 B:91–98
Schwartz J (1994) Air pollution and daily mortality: a review and meta-analysis. Environ Res 64:26–35. doi:10.1006/enrs.1994.1004
Sharma RK, Agrawal M, Marshall F (2007) Heavy metal contamination of soil and vegetables in suburban areas of Varanasi, India. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 66:258–266. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2005.11.007
Siegel FR (2002) Environmental geochemistry of potentially toxic metals. Springer–Verlag, Berlin
Singh RK, Agrawal M (2005) Atmospheric deposition around a heavily industrialized area in a seasonally dry tropical environment of India. Environ Pollut 138:142–152. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2005.02.009
Thornton GJP, Dise NB (1998) The influence of catchment characteristics, agricultural activities and atmospheric deposition on the chemistry of small streams in the English Lake District. Sci Total Environ 216:63–75. doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(98)00138-7
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to Coordinator, Centre of Advanced Study in Botany, Banaras Hindu University for facilities and University Grants Commission, New Delhi for funding support [Grant No. 32 – 383/2006 (SR)].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pandey, J., Shubhashish, K. & Pandey, R. Metal Contamination of Ganga River (India) as Influenced by Atmospheric Deposition. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 83, 204–209 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-009-9744-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-009-9744-2