Abstract
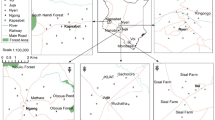
Water and soil samples from the area were therefore analyzed for their lead and zinc content. Computation of pollution statuses of lead and zinc revealed topsoil lead geoaccumulation indices of −0.143 and −0.069 and zinc geoaccumulation indices of 1.168 and 0.713 for Ishiagu and Uburu respectively. The pollution indices were determined to be 0.499 and 0.3564 for soil in Ishiagu and Uburu respectively and also 5.11 and 2.42 for water in Ishiagu and Uburu communities respectively. Water/soil concentration ratio were found to be 0.0018 and 0.0014 for lead in Ishiagu and Uburu respectively. On the other hand, the water/soil concentration ratio for zinc was computed to be 0.001 and 0.0008 for Ishiagu and Uburu respectively. These results seem to suggest that the pollution of the environment by these heavy metals in the areas were as a result of the water being contaminated by lead and zinc not necessarily their concentrations in the soil.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adie GU, Osibanjo O (2009) Assessment of soil-pollution by slag from an automobile battery manufacturing plant in Nigeria. Afr J Environ Sci Technol 3(9):239–250
Beach RS, Gershwin ME, Hurley LS (1980) Growth and development in postnatally zinc—deprived mice. J Nutr 110:201–211
Ceribasi HI, Yetis U (2001) Biosorption of Ni (II) and Pb (II) by phanaerochate, chrysosporium from a binary metal system, kinetics. Water Res 27(1):15–20
Chvapil M (1973) New aspects in the biological role of zinc: stabilizer of macromolecules and biological membrane. Life Sci 13:1041–1049
Coble YD Jr, Bardin CW, Ross GT, Darly WJ (1971) Studies of endocrime function in boys with retarded growth, delayed sexual maturation and zinc deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 32:361–367
Eletta OAA (2007) Determination of some trace metal levels in Asa river using AAS and XRF techniques. Int J Phys Sci 2(3):56–60
Ezeh HN, Anike OL, Egboka BCE (2008) Evaluation of heavy metals pollution of soil around the derelict Enyigba mines and their sources. Int J Appl Environ Sci 3(1):1–10
Forstner U, Ahlf W, Calmano W (1993) Sediment quality objectives and criteria development in Germany. Water Sci Technol 28:307–316
Hands ES (1999) Nutrients in food. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, London, pp 73
Kwapuliński J, Mirosławski J, Wiechuła D, Rochel R, Burczyk J, Sowada B, Iwanek K (1996) The use of ecotoxicological parameters for estimation of the quality of medicinal plant yielding areas. Bromatologia i Chemia Toksykologiczna XXIX(3):243–252
Lee J, Chon H, Kim K (1998) Migration and dispersion of trace elements in the rock–soil–plant system in areas underlain by black shale and slates. J Geochem Explor 65:61–78
Loska K, Wiechuła D, Barska B, Cebula E, Chojnecka A (2003) Assessment of arsenic enrichment of cultivated soils in southern Poland. Pol J Environ Stud 12(2):187–192
Miko S, Peh Z, Bukovec D, Prohic E, Kastmüller Z (2000) Geochemical baseline mapping and Pb pollution assessment of soils in the karst in Western Croatia. Nat Croat 9(1):41–59
Miller RJ, Koeppe DE (1971) Accumulation and physiological effects of lead in corn. In: Proceedings of University of Missouri, Columbia 4, pp 186–193
Müller G (1969) Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geojournal 2:108–118
Neumann J, Lopuchovsky J, Zapletal O (1990) Chemisation, agriculture, pharmacology and toxicology (In Czech), 1st edn. SZN Praha, p 304
Orisakwe OE, Igwilo IO, Afonne OJ, Maduabuchi JU, Obi E, Nduka JC (2006) Heavy metal hazards of sachet water in Nigeria. Arch Environ Occup Health 61(5):209–213
Prasad AS (1983) Clinical, biochemical and nutritional spectrum of zinc deficiency in human subjects: an update. Nutr Rev 41:197–208
Schlesinger L, Arevalo M, Arredondo S, Lonnerdal B, Stekel A (1993) Effect of a zinc-fortified formula on immunocompetence and growth of malnourished infants. Am J Clin Nutr 56:491–498
Strmiskova G (1992) Lead in the environment and food (In Slovak). Nutr Health 37:19–20
USEPA (1986) Method 3050. Acid digestion of sediments, sludges and soil. Test methods for evaluating soild waste, vol 1A, 3rd edn., EPA/SW-846. National Technical Information Services. Springfield, VA
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oje, O.A., Uzoegwu, P.N., Onwurah, I.N.E. et al. Environmental Pollution Levels of Lead and Zinc in Ishiagu and Uburu Communities of Ebonyi State, Nigeria. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 85, 313–317 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-010-0082-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-010-0082-1