Abstract
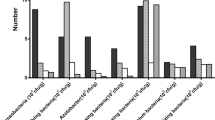
To provide scientific information for GAP of P. notoginseng and guiding the farmers and enterprises of Chinese medicine, dynamics of carbendazim residue in the Chinese medicinal herb, P. notoginseng and cultivated soil was studied at Wenshan County in 2008. The half lives of carbendazim in P. notoginseng were 5.92–6.82 day (soil), 6.71–6.77 day (fresh leaf), 3.29–3.93 day (fresh root), and 31.50–36.67 day (powder of the dry root) separately. Carbendazim residues in P. notoginseng were more stable during storage stage than growing stage.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbarsha MA, Kadalmani B, Girija R, Faridha A, Hamid KS (2001) Spermatotoxic effect of carbendazim. Ind J Exp Biol 39:921–924
Anastassiades M, Schwack W (1998) Analysis of carbendazim, benomyl, thiophanate methyl and 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid in fruits and vegetables after supercritical fluid extraction. J Chromatogr A 825:45–54
Burrows LA, Edwards CA (2004) The use of integrated soil microcosms to assess the impact of carbendazim on soil ecosystems. Ecotoxicology 13(1):143–161
Cuppen JGM, Van den Brink PJ, Camps E, Uil KF, Brock TCM (2000) Impact of the fungicide carbendazim in freshwater microcosms. I. Water quality, breakdown of particulate organic matter and responses of macroinvertebrates. Aquat Toxicol 48:233–250
Feng G, Chen Y, Wang Y, Wang C, Chen Z, Xiang C (2003) Standard operating procedure of prevention for control of main diseases of Panax notoginseng (draft). Chin J Res Pract Chin Med S1:47–48
Han X (2005) Control of diseases of Panax notoginseng. Chin J Beijing Agric 06:16
Han J, Hu W (1996) Influence of Panax notoginseng (PNS) on pathological action of oxygen free radicals in central nervous system damage. Chin J Chin Pharmacol Bull 12:487–489
Jin R, Gui W, Shou L, Wu H, Zhu G (2005) Residues and degradation dynamics of carbendazim in orange and soil. Chin J Jiangsu Agric Sci 02:111–114
Ma L, Wang C, Zhang Q, Du L, Chen J, Xiao P (1998) Effects of Panax notoginseng saponins on blood supply and energy metabolism of brain tissues. Chin J Chin Pharmacol Bull 14:27–29
Nakai M, Hess RA (1997) Effects of carbendazim (methyl 2-benzimidazole carbamate; MBC) on Meiotic Spermatocytes and subsequent spermatogenesis in the rat testis. Anat Rec 247:379–387
Nannipieri P, Bollag JM (1991) Use of enzymes to detoxify pesticide-contaminated soils and waters. J Environ Qual 20:510–517
Tian J, Jin H, Pen F, Du Q, Lin C (2006) Residue of carbendazim at growth period of ginseng. Chin J Chin Tradit Herb Drugs 09:1413–1415
Wei H, Lin J, Wang T, Wu J (2009) Residue dynamics of carbendazim in Radix Ophiopogonis and soil. Chin J Pestic Sci 11(4):467–471
White CM, Fan C, Song J, Tsikouris JP, Chow M (2001) An evaluation of the haemostatic effects of hydrophilic, alcohol, and lipophilic extracts of notoginseng. Pharmacotherapy 21:773–777
Xiang Y, Gao C, Pang G, Hao Y, Fang H, Chun X, Yu Y (2008) Degradation dynamics of carbendazim in soil and its effects on soil microbial community diversity. Chin J Acta Edologica Sinica 04:699–704
Zhang H, Wang Y, Lu Z (2006) The residue dynamic of carbendazim 40% SC in soybean and soil. Chin J Agrochem 10:695–696
Zhou J, Huang W, Wu M, Yang C, Feng G, Wu Z (1975) Thiterpenoids from Panax Linn and their relationship with taxonomy and geographical distribution. Chin J Acta Phytotax Sin 13:29–48
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Research funds: National S&T Major Special Project on Major New Drug Innovation. Item Number: 2009ZX09502-027.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J., Wei, H., Sui, X. et al. Dynamics of Carbendazim Residue in Panax notoginseng and Soil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 84, 469–472 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-010-9970-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-010-9970-7