Abstract
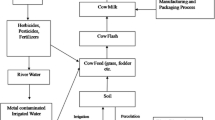
The present investigation was carried out to assess the residues levels of five metals (Cadmium, Copper, Lead, Iron and Zinc) in cow milk collected from different sites in El-Qaliubiya governorate, Egypt. A total of 100 cow milk samples were collected from twenty cows in each location sites during the morning milking in the period from March to April, 2011. The highest average concentration are those of iron (16.38 μg/g) followed by zinc (10.75 μg/g) and lead (4.404 μg/g), while the lowest mean concentration are 2.836 and 0.288 μg/g for copper and cadmium, respectively. The results showed that most of the milk samples from the different sites containing all the studied metals with concentration higher than those recommended for milk by international dairy federation standard and Codex.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou Ayana A, El Deen AG, El-Metwally M (2011) Behavior of certain lactic acid bacteria in the presence of pesticides residues. Int J Dairy Sci 6:44–57
Abou-Arab K (1991) Microbiological and compositional quality of dairy products in relation to some pollutants. MSc thesis, Ain-Shams University, Egypt
Alloway B, Ayres D (1993) Chemical principles of environmental pollution “inorganic pollutants”. Black Academic and professional, London, pp 140–160
Codex Alimentarius Commission (2007) Joint FAO/WHO food standards programme. Codex committee on methods of analysis and sampling, twentyeighth session, Budapest, Hungary, 5–9 March 2007
Jeng L, Lee J, Lin Y (1994) Determine cadmium and lead in raw milk by graphite furan atomic absorption spectrophotometer. J Dairy Sci 77:945–949
Lant G, Lomolino G, Cagnin M, Spttoli P (2006) Content and characterisation of minerals in milk and in Crescenza and Squaacquerne Italian fresh cheese by ICP-OES. Food Control 17:229–233
Mitchell E (1981) Trace metal level in Queensland dairy products. Aust J Dairy Technol 6:70–73
Pennigton A, Schoen A, Salmon D, Young B, Johnson D, Marts W (1995) Composition of core foods of the US food supply, 1982–1991. J Food Compos Anal 8:171–217
IDF Standard (1979) Metal contamination in milk and milk products. International Dairy Federation Bulletin. Document no. A. Doe 37
Tripathi M, Raghunath R, Sastry N, Krishnamoorthy M (1999) Daily intake of heavy metals by infants through milk and milk products. Sci Total Environ 227:229–235
Wahlberg N, Flachier A, Lane S, Sangfors O (2001) Environmental impact and metal exposure of aquatic ecosystems of rivers contaminated by small scale gold mining: the Puyango river basin, southern Ecuador. Sci Total Environ 278:239–261
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malhat, F., Hagag, M., Saber, A. et al. Contamination of Cows Milk by Heavy Metal in Egypt. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 88, 611–613 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-012-0550-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-012-0550-x