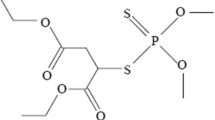
Abstract
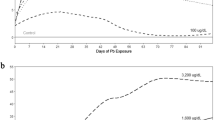
The toxic effects of buprofezin on Daphnia magna after both chronic and acute exposures were evaluated according to OECD guidelines. A 48-h acute exposure of buprofezin resulted in daphnid immobility at an EC50 of 0.44 mg/L. In a 14 days chronic exposure of buprofezin (0, 0.025, 0.05, 0.10 and 0.15 mg/L), the development and reproduction of daphnids were all significantly affected and the body length was more sensitive than other observed parameters. However, the adverse effects of buprofezin on parental daphnids can be passed on to their offspring and cannot be recovered in a short time.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anonymous (2010) Conclusion on pesticide peer review: conclusion on the peer review of the pesticide risk assessment of the active substance buprofezin. EFSA J 8:1624
European Commission (1996) Technical guidance document in support of commission directive 93/67/EEC on risk assessment for new notified substances and commission regulation (EC) No 1488/94 on risk assessment for existing substances, part II. Office for Official Publications of the European Communities, Luxembourg
Li S, Tan Y (2011) Hormetic response of cholinesterase from Daphnia magna in chronic exposure to triazophos and chlorpyrifos. J Environ Sci 23:852–859
Nasr HM, Badawy MEI, Rabea EI (2010) Toxicity and biochemical study of two insect growth regulators, buprofezin and pyriproxyfen, on cotton leafworm Spodoptera littoralis. Pestic Biochem Physiol 98:198–205
NRA (National Registration Authority) (2001) Evaluation of the new active Buprofezin in the product applaud insecticide. National Registration Authority for Agriculture and Veterinary Chemicals, Canberra
OECD (Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development) (1998) Daphnia magna reproduction test. OECD guidelines for testing of chemicals, vol 211. Paris, France
OECD (Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development) (2004) Daphnia sp. acute immobilization test. OECD guidelines for testing of chemicals, vol. 202. Paris, France
Prabhaker N, Toscano NC (2007) Toxicity of the insect growth regulators, buprofezin and pyriproxyfen, to the glassy-winged sharpshooter, Homalodisca coagulata say (Homoptera: Cicadellidae). Crop Prot 26:495–502
Villarroel MJ, Sancho E, Ferrando MD, Andreu E (2003) Acute, chronic and sublethal effects of the herbicide propanil on Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 53:857–864
Wang C, Chen F, Zhang Q, Fang Z (2009) Chronic toxicity and cytotoxicity of synthetic pyrethroid insecticide cis-bifenthrin. J Environ Sci 21:1710–1715
Zalizniak L, Nugegoda D (2006) Effect of sublethal concentrations of chlorpyrifos on three successive generations of Daphnia carinata. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 64:207–214
Acknowledgments
The present study was financially supported by Special Fund for Agro-scientific Research in the Public Interest: study on comprehensive cultivation techniques for pesticide risk assessment (No.20090354-02). Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the funding agency.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yong Liu and Suzhen Qi contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Qi, S., Zhang, W. et al. Acute and Chronic Toxicity of Buprofezin on Daphnia Magna and the Recovery Evaluation. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 89, 966–969 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-012-0802-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-012-0802-9