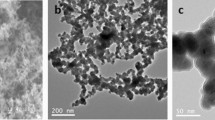
Abstract
Nitrates are considered hazard compounds for human health due to their tendency to be reduced to nitrites, in particular in reducing environment. Nano zero valent iron (nZVI) represents an efficient and low-cost adsorbent/reductive agent for nitrate removal from groundwater and wastewaters and a little addition of a second metal species (Cu, Pd, Ni, Ag) has proven to increase process effectiveness, by enhancing stability and oxidation resistance of nanoparticles. In this work Cu/Fe nanoparticles were loaded in a NO3 − solution (100 mg L−1) and the removal efficiency was tested by monitoring nitrate concentration at selected time intervals. Results showed that the nitrate removal process involves both reduction and adsorption processes: the removal mechanism has been investigated, and the pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order-adsorption kinetic models were successfully tested.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida JS, Reis MAM, Carrondo MJT (1995) Competition between nitrate and nitrite reduction in denitrification by Pseudomonas fluorescens. Biotechnol Bioeng 46:476–484
Aytimur G, Di Palma L, Merli C (2008) Experimental validation of a model for the cycle of nitrogen in a step sludge recirculation activated sludge system with denitrification. Environ Technol 29:591–601
Bae BU, Jung YH, Han WW, Shin HS (2002) Improved brine recycling during nitrate removal using ion exchange. Water Res 36:3330–3340
Chen Z, Wang T, Jin X, Chen Z, Megharaj M, Naidu R (2013) Multifunctional kaolinite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron used for the adsorption and degradation of crystal violet in aqueous solution. J Colloid Int Sci 398:59–66
Chun CL, Baer DR, Matson DW, Amonette JE, Penn RL (2010) Characterization and reactivity of iron nanoparticles prepared with added Cu, Pd, and Ni. Environ Sci Technol 44(13):5079–5085
Cirtiu CM, Raychoudhury T, Ghoshal S, Moores A (2011) Systematic comparison of the size, surface characteristics and colloidal stability of zero valent iron nanoparticles pre- and post-grafted with common polymers. Colloid Surf. A 390:95–104
De Filippis P, Di Palma L, Scarsella M, Verdone N (2013) Biological denitrification of high rate wastewater: a comparison between three electron donors. Chem Eng Trans 32:319–324
Di Palma L, Gueye MT, Petrucci E (2015) Hexavalent chromium reduction in contaminated soil: a comparison between ferrous sulphate and nanoscale zero-valent iron. J Hazard Mater 281:70–76
Fanning JC (2000) The chemical reduction of nitrate in aqueous solution. Coord Chem Rev 199:159–179
He F, Zhao D (2007) Manipulating the size and dispersibility of zerovalent iron nanoparticles by use of carboxymethyl cellulose stabilizers. Environ Sci Technol 41(17):6216–6221
He F, Zhao D, Liu J, Roberts CB (2007) Stabilization of Fe–Pd nanoparticles with sodium carboxymethyl cellulose for enhanced transport and dechlorination of trichloroethylene in soil and groundwater. Ind Eng Chem Res 46:29–34
Hörold S, Vorlop KD, Tacke T, Sell M (1993) Development of catalysts for a selective nitrate and nitrite removal from drinking water. Catal Today 17(1–2):21–30
Hosseini SM, Ataie-Ashtiani B, Kholghi M (2011) Nitrate reduction by nano-Fe/Cu particles in packed column. Desalination 276(1):214–221
Hwang YH, Kim DG, Ahn YT, Moon CM, Shin H (2010) Fate of nitrogen species in nitrate reduction by nanoscale zero valent iron and characterization of the reaction kinetics. Water Sci Technol 61:705–712
Hwang YH, Kim DG, Shin HS (2011) Mechanism study of nitrate reduction by nano zero valent iron. J Hazard Mater 185:1513–1521
Italian Environmental Regulation, Environmental standards assessment, G.U. n. 88 of 14 April 2006
Kapoor A, Viraraghavan T (1997) Nitrate removal from drinking water-review. J Environ Eng 123(4):371–380
Kim DG, Hwang YH, Shin HS, Ko SO (2015) Kinetics of nitrate adsorption and reduction by nano-scale zero valent iron (NZVI): effect of ionic strength and initial pH. J Civil Eng 20:175–187
Li XQ, Cao J, Zhang WX (2008) Stoichiometry of Cr(VI) immobilization using nanoscale zerovalent iron (nZVI): a study with high-resolution X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (HR-XPS). Ind Eng Chem Res 47(7):2131–2139
Liou YH, Lo SL, Lin CJ, Kuan WH, Weng SC (2005a) Chemical reduction of an unbuffered nitrate solution using catalyzed and uncatalyzed nanoscale iron particles. J Hazard Mater 127(1):102–110
Liou YH, Lo SL, Lin CJ, Kuan WH, Weng SC (2005b) Effects of iron surface pretreatment on kinetics of aqueous nitrate reduction. J Hazard Mater 126(1–3):189–194
Martin JE, Herzing AA, Yan W, Li XQ, Koel BE, Kiely CJ, Zhang WX (2008) Determination of the oxide layer thickness in core-shell zerovalent iron nanoparticles. Langmuir 24(8):4329–4334
Montesinos VN, Quici N, Halac EB, Leyva AG, Custo G, Bengio S, Litter MI (2014) Highly efficient removal of Cr(VI) from water with nanoparticulated zerovalent iron: understanding the Fe(III)–Cr(III) passive outer layer structure. Chem Eng J 244:569–575
Nurmi JT, Tratnyek PG, Sarathy V, Baer DR, Amonette JE, Pecher K, Driessen MD (2005) Characterization and properties of metallic iron nanoparticles: spectroscopy, electrochemistry, and kinetics. Environ Sci Technol 39(5):1221–1230
O’Carroll D, Sleep B, Krol M, Boparai H, Kocur C (2013) Nanoscale zero valent iron and bimetallic particles for contaminated site remediation. Adv Water Resour 51:104–122
Powell RM, Puls RW, Blowes DW, Vogan JL, Gillham RW, Powell PD, Schultz D, Landis R, Sivavec T (1998) Permeable reactive barrier technologies for contaminant remediation. EPA/600/R-98/125, US Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Research and Development, Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response, Washington DC
Rodríguez-Maroto JM, García-Herruzo F, García-Rubio A, Gómez-Lahoz C, Vereda-Alonso C (2009) Kinetics of the chemical reduction of nitrate by zero-valent iron. Chemosphere 74(6):804–809
Scherer MM, Richter S, Valentine RL, Alvarez PJJ (2000) Chemistry and microbiology of permeable reactive barriers for in situ groundwater clean up. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 30(3):363
Siciliano A (2015) Use of nanoscale zero-valent iron (NZVI) particles for chemical denitrification under different operating conditions. Metals 5(3):1507–1519
Singh R, Misra V, Singh RP (2012) Removal of Cr(VI) by nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) from soil contaminated with tannery wastes. B Environ Contam Toxicol 88(2):210–214
Sparis D, Mystrioti C, Xenidis A, Papassiopi N (2013) Reduction of nitrate by copper-coated ZVI nanoparticles. Desalin Water Treat 51:2926–2933
Sun YP, Li XQ, Cao J, Zhang WX, Wang HP (2006) Characterization of zero-valent iron nanoparticles. Adv Colloid Int Sci 120(1):47–56
Taipei Veterans General Hospital, http://www.vghtpe.gov.tw/tcfund/infomation/200106017.htm
Wang W, Jin ZH, Li TL, Zhang H, Gao S (2006) Preparation of spherical iron nanoclusters in ethanol–water solution for nitrate removal. Chemosphere 65(8):1396–1404
Wang A, Qian H, Yang Y, Zhang Z, Naman C, Xu X (2010) Reduction of hexavalent chromium by carboxymethyl cellulose-stabilized zero-valent iron nanoparticles. J Contam Hydrol 114:35–42
Wang T, Lin J, Chen Z, Megharaj M, Naidu R (2014) Green synthesized iron nanoparticles by green tea and eucalyptus leaves extracts used for removal of nitrate in aqueous solution. J Clean Prod 83:413–419
Yabusaki S, Cantrell K, Sass B, Steefe LC (2001) Multicomponent reactive transport in an in situ zero-valent iron cell. Environ Sci Technol 35(7):1493
Yang GCC, Lee HL (2005) Chemical reduction of nitrate by nanosized iron: kinetics and pathways. Water Res 39:884–894
Zhang Y, Li Y, Li J, Hu L, Zheng X (2011) Enhanced removal of nitrate by a novel composite: nanoscale zero valent iron supported on pillared clay. Chem Eng J 171(2):526–531
Zhou L, Le Thanh T, Gong J, Kim JH, Kim EJ, Chang YS (2014a) Carboxymethyl cellulose coating decreases toxicity and oxidizing capacity of nanoscale zerovalent iron. Chemosphere 104:155–161
Zhou S, Li Y, Chen J, Liu Z, Wang Z, Na P (2014b) Enhanced Cr(VI) removal from aqueous solutions using Ni/Fe bimetallic nanoparticles: characterization, kinetics and mechanism. RSC Adv 4(92):50699–50707
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vilardi, G., Di Palma, L. Kinetic Study of Nitrate Removal from Aqueous Solutions Using Copper-Coated Iron Nanoparticles. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 98, 359–365 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-016-1865-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-016-1865-9