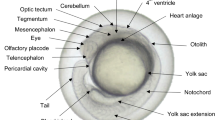
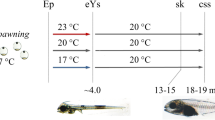
Abstract
Beyond the mere detection of presence or absence of heart beat in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos in a fish embryo test conducted referring to the OECD TG 236 at 48 hpf (hours post fertilization) onwards, embryo heart rate may serve as an additional and very sensitive endpoint in ecotoxicological studies. But by including heart rate as a sublethal endpoint, care has to be taken of separating effects exerted by a tested compound from those exerted by temperature. Therefore, profound knowledge on the natural variation of zebrafish heart rates at defined temperatures as a basis for the assessment of gained results is mandatorily needed. As such continuous information in D. rerio is lacking from the literature, we designed a study covering a span of 12°C (from 18 to 30°C in steps of 2°C) to quantify the relationship between heart rate and temperature in D. rerio embryos 48 hpf. Conducting a multiple regression analysis, we found a considerably strong relationship between treatment temperature and the log10 of the heart rate, ranging from 82.8 beats per minute at 18°C to 218.0 beats per minute at 30°C. Our results therefore may serve as a reference for heart rates measured under normal conditions to be able to detect potential effects of contaminants in other studies when working under certain temperatures.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bachmann J (2002) Entwicklung und Erprobung eines Teratogenitäts-Screening Testes mit Embryonen des Zebrabärblings Danio rerio
Barrionuevo WR, Burggren WW (1999) O2 consumption and heart rate in developing zebrafish (Danio rerio): influence of temperature and ambient O2. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 276:R505-R513
Birchard GF, Reiber CL (1996) Heart rate during development in the turtle embryo: effect of temperature. J Comp Physiol B 166:461–466
Braunbeck T, Kais B, Lammer E, Otte J, Schneider K, Stengel D, Strecker R (2015) The fish embryo test (FET): origin, applications, and future. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:16247–16261
Carlsson G, Patring J, Kreuger J, Norrgren L, Oskarsson A (2013) Toxicity of 15 veterinary pharmaceuticals in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. Aquat Toxicol 126:30–41
Chan PK, Lin CC, Cheng SH (2009) Noninvasive technique for measurement of heartbeat regularity in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. BMC Biotechnol 9:11–11
Claireaux G, Webber D, Kerr S, Boutilier R (1995) Physiology and behaviour of free-swimming Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) facing fluctuating temperature conditions. J Exp Biol 198:49–60
Denvir MA, Tucker CS, Mullins JJ (2008) Systolic and diastolic ventricular function in zebrafish embryos: influence of norepenephrine, MS-222 and temperature. BMC Biotechnol 8:21
Du J, Wang S, You H, Jiang R, Zhuang C, Zhang X (2016) Developmental toxicity and DNA damage to zebrafish induced by perfluorooctane sulfonate in the presence of ZnO nanoparticles. Environ Toxicol 31:360–371
Duan J, Yu Y, Li Y, Yu Y, Sun Z (2013) Cardiovascular toxicity evaluation of silica nanoparticles in endothelial cells and zebrafish model. Biomaterials 34:5853–5862
Félix LM, Serafim C, Martins MJ, Valentim AM, Antunes LM, Matos M, Coimbra AM (2017) Morphological and behavioral responses of zebrafish after 24 h of ketamine embryonic exposure. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 321:27–36
Fraysse B, Mons R, Garric J (2006) Development of a zebrafish 4-day embryo-larval bioassay to assess toxicity of chemicals. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 63:253–267
Gehrke PC, Fielder DR (1988) Effects of temperature and dissolved oxygen on heart rate, ventilation rate and oxygen consumption of spangled perch, Leiopotherapon unicolor (Günther 1859), (Percoidei, Teraponidae). J Comp Physiol B 157:771–782
Görge G, Nagel R (1990) Toxicity of lindane, atrazine, and deltamethrin to early life stages of zebrafish (Brachydanio rerio). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 20:246–255
Grunwald DJ, Eisen JS (2002) Headwaters of the zebrafish: Emergence of a new model vertebrate. Nat Rev Genet 3:717–724
Hallare AV, Köhler H-R, Triebskorn R (2004) Developmental toxicity and stress protein responses in zebrafish embryos after exposure to diclofenac and its solvent, DMSO. Chemosphere 56:659–666
Hallare AV, Schirling M, Luckenbach T, Köhler H-R, Triebskorn R (2005) Combined effects of temperature and cadmium on developmental parameters and biomarker responses in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. J Therm Biol 30:7–17
Hill AJ, Teraoka H, Heideman W, Peterson RE (2005) Zebrafish as a model vertebrate for investigating chemical toxicity. Toxicol Sci 86:6–19
Johnson A, Carew E, Sloman KA (2007) The effects of copper on the morphological and functional development of zebrafish embryos. Aquat Toxicol 84:431–438
Kimmel CB, Ballard WW, Kimmel SR, Ullmann B, Schilling TF (1995) Stages of embryonic development of the zebrafish. Dev Dyn 203:253–310
Lawrence C (2007) The husbandry of zebrafish (Danio rerio): a review. Aquaculture 269:1–20
Massarsky A, Dupuis L, Taylor J, Eisa-Beygi S, Strek L, Trudeau VL, Moon TW (2013) Assessment of nanosilver toxicity during zebrafish (Danio rerio) development. Chemosphere 92:59–66
Mcgrath P, Li C-Q (2008) Zebrafish: a predictive model for assessing drug-induced toxicity. Drug Discov Today 13:394–401
Mirkovic T, Rombough P (1998) The effect of body mass and temperature on the heart rate, stroke volume, and cardiac output of larvae of the rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Physiol Zool 71:191–197
OECD (2013) Test No. 236: Fish embryo acute toxicity (FET) test. OECD Publishing, Paris
Osterauer R,Köhler H-R (2008) Temperature-dependent effects of the pesticides thiacloprid and diazinon on the embryonic development of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat Toxicol 86:485–494
Roex EWM, De Vries E, Van Gestel CaM (2002) Sensitivity of the zebrafish (Danio rerio) early life stage test for compounds with different modes of action. Environ Pollut 120:355–362
Scheil V, Kienle C, Osterauer R, Gerhardt A,Köhler H-R (2009) Effects of 3,4-dichloroaniline and diazinon on different biological organisation levels of zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos and larvae. Ecotoxicology 18:355–363
Shi X, Du Y, Lam PKS, Wu RSS, Zhou B (2008) Developmental toxicity and alteration of gene expression in zebrafish embryos exposed to PFOS. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 230:23–32
Thellmann P, Köhler H-R, Rößler A, Scheurer M, Schwarz S, Vogel H-J, Triebskorn R (2014) Fish embryo tests with Danio rerio as a tool to evaluate surface water and sediment quality in rivers influenced by wastewater treatment plants using different treatment technologies. Environ Sci Pollut Res.1–12
Thorarensen H, Gallaugher PE, Farrell AP (1996) The limitations of heart rate as a predictor of metabolic rate in fish. J Fish Biol 49:226–236
Xiong X, Luo S, Wu B, Wang J (2017) Comparative developmental toxicity and stress protein responses of dimethyl sulfoxide to rare minnow and zebrafish embryos/larvae. Zebrafish 14:60–68
Yozzo KL, Isales GM, Raftery TD, Volz DC (2013) High-content screening assay for identification of chemicals impacting cardiovascular function in zebrafish embryos. Environ Sci Technol 47:11302–11310
Acknowledgements
We thank C. Hepper, A. Meral, V. Baur, F. Gammerdinger and J. Leibßle for the maintenance of the D. rerio culture.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schweizer, M., Dieterich, A., Triebskorn, R. et al. Drifting Away of a FET Endpoint: The Heart Rate in Danio rerio Embryos is Extremely Sensitive to Variation in Ambient Temperature. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 99, 684–689 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-017-2196-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-017-2196-1