Abstract
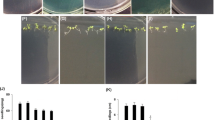
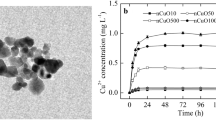
The widespread application of copper oxide nanoparticles (nCuO) results in ecological risk when nanoparticles enter the environment. This study clarifies the mechanism of nCuO toxicity in Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings via comparison with copper (Cu) ion bioeffects. Under the same culture conditions, Cu2+ ion exposure exerted a stronger inhibitory effect on plant fresh weight and growth and caused stronger oxidative disruption (measured by malondialdehyde, MDA) than nCuO exposure. The Cu2+ ions also showed a stronger induction effect than did nCuO on the activity of antioxidant enzymes and the transcription of antioxidant-related genes. Dissolved Cu2+ ions contributed a minority of the toxicity of nCuO, implying that nCuO itself showed relative strong phytotoxicity. The work presented here will help increase our understanding of the toxicity of metal nanoparticles in plants.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aderemi TA, Adenuga AA, Oyekunle JAO, Ogunfowokan AO (2017) High level leaching of heavy metals from colorful ceramic foodwares: a potential risk to human. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24(20):17116–17126
Chen S, Li XX, Lavoie M, Jin YJ, Xu JH, Fu ZW, Qian HF (2017) Diclofop-methyl affects microbial rhizosphere community and induces systemic acquired resistance in rice. J Environ Sci 51:352–360
Deng F, Wang SL, Xin H (2016) Toxicity of CuO nanoparticles to structure and metabolic activity of Allium cepa root tips. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 97:702–708
Griffitt RJ, Weil R, Hyndman KA, Denslow ND, Powers K, Taylor D, Barber DS (2007) Exposure to copper nanoparticles causes gill injury and acute lethality in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ Sci Technol 41:8178–8186
Gupta SD, Datta S (2003) Antioxidant enzyme activities during in vitro morphogenesis of gladiolus and the effect of application of antioxidant on plant regeneration. Biol Plant 47:179–183
Jin Y, Fan X, Li X, Zhang Z, Sun L, Fu Z, Lavoie M, Pan X, Qian H (2017) Distinct physiological and molecular responses in Arabidopsis thaliana exposed to aluminum oxide nanoparticles and ionic aluminum. Environ Pollut 228:517–527
Kaweeteerawat C, Chang CH, Roy KR, Liu R, Li RB, Toso D, Fischer H, Ivask A, Ji ZX, Zink JI, Zhou ZH, Chanfreau GF, Telesca D, Cohen Y, Holden PA, Nel AE, Godwin HA (2015) Cu nanoparticles have different impacts in Escherichia coli and Lactobacillus brevis than their microsized and ionic analogues. ACS Nano 9:7215–7225
Kim S, Lee S, Lee I (2012) Alteration of phytotoxicity and oxidant stress potential by metal oxide nanoparticles in cucumis sativus. Water Air Soil Pollut 223:2799–2806
Ma CX, Chhikara S, Xing BS, Musante C, White JC, Dhankher OP (2013) Physiological and molecular response of Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) to nanoparticle cerium and indium oxide exposure. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 1:768–778
Nair PMG, Chung IM (2014) Physiological and molecular level effects of silver nanoparticles exposure in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings. Chemosphere 112:105–113
Nair PMG, Chung IM (2017) Regulation of morphological, molecular and nutrient status in Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings in response to ZnO nanoparticles and Zn ion exposure. Sci Total Environ 575:187–198
Qian HF, Lu T, Peng XF, Han X, Fu ZW, Liu WP (2011) Enantioselective phytotoxicity of the herbicide imazethapyr on the response of the antioxidant system and starch metabolism in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS ONE 6:e19451
Qian HF, Han X, Zhang QN, Sun ZQ, Sun LW, Fu ZW (2013) Imazethapyr enantioselectively affects chlorophyll synthesis and photosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Agric Food Chem 61:1172–1178
Qian HF, Zhu K, Lu H, Lavoie M, Chen S, Zhou Z, Deng Z, Chen J, Fu Z (2016) Contrasting silver nanoparticle toxicity and detoxification strategies in Microcystis aeruginosa and Chlorella vulgaris: new insights from proteomic and physiological analyses. Sci Total Environ 572:1213–1221
Salah SM, Guan YJ, Cao DD, Li J, Aamir N, Hu QJ, Hu WM, Ning MY, Hu J (2015) Seed priming with polyethylene glycol regulating the physiological and molecular mechanism in rice (Oryza sativa L.) under nano-ZnO stress. Sci Rep 5:14278
Shaw AK, Hossain Z (2013) Impact of nano-CuO stress on rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings. Chemosphere 93:906–915
Stampoulis D, Sinha SK, White JC (2009) Assay-dependent phytotoxicity of nanoparticles to plants. Environ Sci Technol 43:9473–9479
Sun CC, Chen S, Jin YJ, Song H, Ruan SL, Fu ZW, Asad MAU, Qian HF (2016) Effects of the herbicide imazethapyr on photosynthesis in PGR5-and NDH-deficient Arabidopsis thaliana at the biochemical, transcriptomic, and proteomic Levels. J Agric Food Chem 64:4497–4504
Wang LY, Wang M, Peng CS, Pan JF (2013) Toxic effects of nano-CuO, microCuO and Cu2+ on chlorella sp. J Environ Prot 4:86–91
Wang ZY, Xu LN, Zhao J, Wang XK, White JC, Xing BS (2016) CuO nanoparticle interaction with Arabidopsis thaliana: toxicity, parent-progeny transfer, and gene expression. Environ Sci Technol 50:6008–6016
Xiao YL, Peijnenburg WJGM, Chen GC, Vijver MG (2016) Toxicity of copper nanoparticles to Daphnia magna under different exposure conditions. Sci Total Environ 563:81–88
Yang JG, Okamoto T, Ichino R, Bessho T, Satake S, Okido M (2006) A simple way for preparing antioxidation nano-copper powders. Chem Lett 35:648–649
Yuan J, He A, Huang S, Hua J, Sheng GD (2016) Internalization and phytotoxic effects of CuO nanoparticles in as revealed by fatty acid profiles. Environ Sci Technol 50(19):10437–10447
Zhao LJ, Peng B, Hernandez-Viezcas JA, Rico C, Sun YP, Peralta-Videa JR, Tang XL, Niu GH, Jin LX, Varela-Ramirez A, Zhang JY, Gardea-Torresdey JL (2012) Stress response and tolerance of Zea mays to CeO2 nanoparticles: cross talk among H2O2, heat shock protein, and lipid peroxidation. ACS Nano 6:9615–9622
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21577128), and a One Hundred Talents Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences grant to H.F. Qian, and Xingjiang Uighur Autonomous Region Talent Project to H.F. Qian.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ke, M., Zhu, Y., Zhang, M. et al. Physiological and Molecular Response of Arabidopsis thaliana to CuO Nanoparticle (nCuO) Exposure. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 99, 713–718 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-017-2205-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-017-2205-4