Abstract
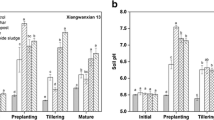
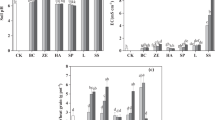
This study assessed the effectiveness of limestone-montmorillonite-rapeseed residue-Si fertilizer compound amendment on the bioavailability and crop uptake of cadmium (Cd) and enzyme activities in acidic paddy soils. Applying the compound amendment at ratios of 1%–3% increased soil pH by 0.1–1.9 units, decreased leaching ratios of soil Cd 4.0%–22%, and decreased exchangeable and carbonated Cd 42%–55% and 27%–49%, respectively. Organic matter-bound Cd increased 47%–62% (p < 0.05). Cadmium concentrations decreased in the roots, culms, leaves, and grains of rice grown in the Cd-contaminated soils by 37%–81%, 18%–73%, 29%–64% and 27%–63%, respectively, (p < 0.05). Catalase and urease activities increased 2.5%–63% and 3.9%–36%, (p < 0.05), respectively. Applying this compound amendment may significantly mitigate soil acidification and decrease the bioavailability and crop uptake of Cd in acidic Cd-contaminated paddy soils.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abad-Valle P, Iglesias-Jiménez E, Álvarez-Ayuso E (2017) A comparative study on the influence of different organic amendments on trace element mobility and microbial functionality of a polluted mine soil. J Environ Manag 188:287–296
Bandick AK, Dick RP (1999) Field management effects on soil enzyme activities. Soil Biol Biochem 31:1471–1479
Chavez E, He ZL, Stoffella PJ, Mylavarapu RS, Li YC, Baligar VC (2016) Chemical speciation of cadmium: an approach to evaluate plant-available cadmium in Ecuadorian soils under cacao production. Chemosphere 150:57–62
Cheng SF, Hseu ZY (2002) In-situ immobilization of cadmium and lead by different amendments in two contaminated soils. Water Air Soil Pollut 140:73–84
Dermont G, Bergeron M, Mercier G, Richer-Laflèche M (2008) Soil washing for metal removal: a review of physical/chemical technologies and field applications. J Hazard Mater 152:1–31
Dresler S, Wojcik M, Bednarek W, Hanaka A, Tukiendorf A (2015) The effect of silicon on maize growth under cadmium stress. Russ J Plant Physiol 62:86–92
Du H, Chen W, Cai P, Rong X, Dai K, Peacock CL, Huang Q (2016) Cd(II) Sorption on montmorillonite-humic acid-bacteria composites. Sci Rep 6:19499
Farooq MA, Detterbeck A, Clemens S, Dietz KJ (2016) Silicon-induced reversibility of cadmium toxicity in rice. J Exp Bot 67:3573–3585
Gao Y, Zhou P, Mao L, Zhi Y, Zhang C, Shi W (2010) Effects of plant species coexistence on soil enzyme activities and soil microbial community structure under Cd and Pb combined pollution. J Environ Sci 22:1040–1048
Garau G, Castaldi P, Santona L, Deiana P, Melis P (2007) Influence of red mud, zeolite and lime on heavy metal immobilization, culturable heterotrophic microbial populations and enzyme activities in a contaminated soil. Geoderma 14:47–57
Gu Y, Wang P, Kong CH (2009) Urease, invertase, dehydrogenase and polyphenoloxidase activities in paddy soil influenced by allelopathic rice variety. Eur J Soil Biol 45:436–441
Guo G, Zhou Q, Ma LQ (2006) Availability and assessment of fixing additives for the in situ remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils: a review. Environ Monit Assess 116:513–528
Hamidpour M, Kalbasi M, Afyuni M, Shariatmadari H, Holm PE, Hansen HC (2010) Sorption hysteresis of Cd(II) and Pb(II) on natural zeolite and bentonite. J Hazard Mater 181:686–691
He YB, Huang DY, Zhu QH, Wang S, Liu SL, He HB, Zhu HH, Xu C (2017) A three-season field study on the in-situ remediation of Cd-contaminated paddy soil using lime, two industrial by-products, and a low-Cd-accumulation rice cultivar. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 136:135–141
Hu Y, Cheng H, Tao S (2016) The challenges and solutions for cadmium-contaminated rice in china: a critical review. Environ Int 92–93:515–532
Huang SH, Yang Y, Li Q, Su Z, Yuang CY, Yang KO (2017) Evaluation of the effects of lime–bassanite–charcoal amendment on the immobilization of cadmium in contaminated soil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 98:433–438
Kirchmann H, Mattsson L, Eriksson J (2009) Trace element concentration in wheat grain: results from the Swedish long-term soil fertility experiments and national monitoring program. Environ Geochem Health 31:561–571
Kumpiene J, Lagerkvist A, Maurice C (2008) Stabilization of As, Cr, Cu, Pb and Zn in soil using amendments—a review. Waste Manag 28:215–225
Lee SH, Lee JS, Choi YJ, Kim JG (2009) In situ stabilization of cadmium-, lead-, and zinc-contaminated soil using various amendments. Chemosphere 77:1069–1075
Lee SS, Lim JE, El-Azeem SA, Choi B, Oh SE, Moon DH, Ok YS (2013) Heavy metal immobilization in soil near abandoned mines using eggshell waste and rapeseed residue. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 20:1719–1726
Lestan D, Grcman H, Zupan M, Bacac N (2003) Relationship of soil properties to fractionation of Pb and Zn in soil and their uptake into Plantago lanceolata. Soil Sediment Contam 12:507–522
Li H, Luo N, Li YW, Cai QY, Li HY, Mo CH, Wong MH (2017a) Cadmium in rice: transport mechanisms, influencing factors, and minimizing measures. Environ Pollut 224:622–630
Li Y, Pang HD, He LY, Wang Q, Sheng XF (2017b) Cd immobilization and reduced tissue Cd accumulation of rice (Oryza sativa wuyun-23) in the presence of heavy metal-resistant bacteria. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 138:56–63
Liu L, Li W, Song W, Guo M (2018) Remediation techniques for heavy metal-contaminated soils: principles and applicability. Sci Total Environ 633:206–219
Madejón E, de Mora AP, Felipe E, Burgos P, Cabrera F (2006) Soil amendments reduce trace element solubility in a contaminated soil and allow regrowth of natural vegetation. Environ Pollut 139:40–52
Querol X, Alastury A, Moreno N, Alvarez-ayuso E, Garía-Sánchez A, Cama J, Ayora C, Simón M (2006) Immobilization of heavy metals in polluted soils by the addition of zeolitic material synthesized from coal fly ash. Chemosphere 62:171–180
Rizwan M, Ali S, Adrees M, Ibrahim M, Tsang DCW, Zia-Ur-Rehman M, Zahir ZA, Rinklebe J, Tack FMG, Ok YS (2017) A critical review on effects, tolerance mechanisms and management of cadmium in vegetables. Chemosphere 182:90–105
Shakir SK, Azizullah A, Murad W, Daud MK, Nabeela F, Rahman H, Ur Rehman S, Häder DP (2017) Toxic metal pollution in Pakistan and its possible risks to public health. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 242:1–60
Shao JF, Che J, Yamaji N, Shen RF, Ma JF (2017) Silicon reduces cadmium accumulation by suppressing expression of transporter genes involved in cadmium uptake and translocation in rice. J Exp Bot 68:5641–5651
Shen GQ, Cao LK, Lu YT, Hong JB (2005) Influence of phenanthrene on cadmium toxicity to soil enzymes and microbial growth. Environ Sci Pollut Res 12:259–263
Stepniewska Z, Wolińska A, Ziomek J (2009) Response of soil catalase activity to chromium contamination. J Environ Sci 21:1142–1147
Sun Y, Sun G, Xu Y, Wang L, Liang X, Lin D, Hu F (2013) Assessment of natural sepiolite on cadmium stabilization, microbial communities, and enzyme activities in acidic soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 20:3290–3299
Sun YB, Li Y, Xu YM, Liang XF, Wang L (2015) In situ stabilization remediation of cadmium (Cd) and lead (Pb) co-contaminated paddy soil using bentonite. Appl Clay Sci 105–106:200–206
Tang W, Zhong h, Xiao L, Tan Q, Zeng Q, Wei Z (2017) Inhibitory effects of rice residues amendment on Cd phytoavailability: a matter of Cd-organic matter interactions? Chemosphere 186:227–234
Tica D, Udovic M, Lestan D (2011) Immobilization of potentially toxic metals using different soil amendments. Chemosphere 85(4):577–583
Wu PX, Zhang Q, Dai YP, Zhu NW, Dang Z, Li P, Wu JH, Wang XD (2011) Adsorption of Cu(II), Cd(II) and Cr(III) ions from aqueous solutions on humic acid modified Ca-montmorillonite. Geoderma 164:215–219
Wu YJ, Zhou H, Zou ZJ, Zhu W, Yang WT, Peng PQ, Zeng M, Liao BH (2016) A three-year in-situ study on the persistence of a combined amendment (limestone + sepiolite) for remedying paddy soil polluted with heavy metals. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 130:163–170
Xia Q, Peng C, Lamb D, Mallavarapu M, Naidu R, Ng JC (2016) Bioaccessibility of arsenic and cadmium assessed for in vitro bioaccessibility in spiked soils and their interaction during the Unified BARGE Method (UBM) extraction. Chemosphere 147:444–450
Yang WT, Gu JF, Zou JL, Zhou H, Zeng QR, Liao BH (2016) Impacts of rapeseed dregs on Cd availability in contaminated acid soil and Cd translocation and accumulation in rice plants. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23:20853–20861
Zare AA, Khoshgoftarmanesh AH, Malakouti MJ, Bahrami HA, Chaney RL (2017) Root uptake and shoot accumulation of cadmium by lettuce at various Cd:Zn ratios in nutrient solution. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 148:441–446
Zeng F, Ali S, Zhang H, Ouyang Y, Qiu B, Wu F, Zhang G (2011) The influence of pH and organic matter content in paddy soil on heavy metal availability and their uptake by rice plants. Environ Pollut 159:84–91
Zhang C, Wang L, Nie Q, Zhang W, Zhang F (2008) Long-term effects of exogenous silicon on cadmium translocation and toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environ Exp Bot 62:300–307
Zhong H, Wang WX (2006) Influences of aging on the bioavailability of sediment-bound Cd and Zn to deposit-feeding sipunculans and soldier crabs. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:2775–2780
Zhou YF, Haynes RJ, Naidu R (2012) Use of inorganic and organic wastes for in situ immobilisation of Pb and Zn in a contaminated alkaline soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 19:1260–1270
Zhou G, Xia X, Wang H, Li LQ, Wang GJ, Zheng SX, Liao SJ (2016) Immobilization of lead by Alishewanella sp. WH16-1 in pot experiments of Pb-contaminated paddy soil. Water Air Soil Pollut 227:339
Zhu H, Chen C, Xu C, Zhu Q, Huang D (2016) Effects of soil acidification and liming on the phytoavailability of cadmium in paddy soils of central subtropical China. Environ Pollut 219:99–106
Acknowledgements
This project was financially supported by the Science Research Project of the Science and Technology Department in Hunan Province (2017NK2144 and 2016NK2036), Changsha Municipal Science and Technology Major Project (kq1703010), Opening Foundation of the Hunan Engineering Research Center of Safe and Efficient Utilization of Heavy Metal Contaminated Arable Land, Changsha, 410083, China (TGOP-001) and Hunan Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Alliance Project (2017LM0305).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shan, S., Guo, Z., Lei, P. et al. Impacts of a Compound Amendment on Cd Immobilization, Enzyme Activities and Crop Uptake in Acidic Cd-Contaminated Paddy Soils. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 101, 243–249 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-018-2379-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-018-2379-4