Abstract
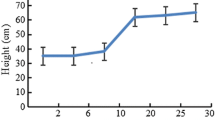
A long term experiment was conducted to verify the phytoremediation effect of large biomass plants and to seek the balance between remediation effect and economy. Eucalyptus globulus were planted with rotation periods of respectively 3, 6 and 9 years to examine the effect on soil remediation. Biomass and concentrations of Cd, Pb and Cu in E. globulus were measured after each harvest. The economic value of the plant was estimated. Results showed E3 (9th year uprooted) had the best soil remediation effect and economic benefit. Therefore, soil remediation and economy were best balanced when E. globulus were not cut.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali H, Khan E, Sajad MA (2013) Phytoremediation of heavy metals—concepts and applications. Chemosphere 91:869–881
An HM, Liu Y, Zhao XF, Huang Q, Yuan SH, Yang XY, Dong JY (2015) Characterization of cadmium-resistant endophytic fungi from Salix variegata Franch. in three gorges reservoir region China. Microbiol Res 176:29–37
Andreazza R, Bortolon L, Pieniz S, Camargo FAO (2013) Use of high-yielding bioenergy plant castor bean (Ricinus communis L.) as a potential phytoremediator for copper-contaminated soils. Pedosphere 23:651–661
Bachir Raho G, Benali M (2012) Antibacterial activity of the essential oils from the leaves of Eucalyptus globulus against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 2:739–742
Bueno PCP, Groppo M, Bastos JK (2014) A GC-FID validated method for the quality control of Eucalyptus globulus raw material and its pharmaceutical products, and GC-MS fingerprinting of 12 Eucalyptus species. Nat Prod Commun 9:1787–1790
Di Lonardo S, Capuana M, Arnetoli M, Gabbrielli R, Gonnelli C (2011) Exploring the metal phytoremediation potential of three Populus alba L. clones using an in vitro screening. Environ Sci Pollut Res 18:82–90
Eufrade HJ, de Melo RX, Sartori MMP, Guerra SPS, Ballarin AW (2016) Sustainable use of Eucalypt biomass grown on short rotation coppice for bioenergy. Biomass Bioenerg 90:15–21
Garcia C, Montero G, Coronado MA, Valdez B, Stoytcheva M, Rosas N, Torres R, Sagaste CA (2017) Valorization of Eucalyptus leaves by essential oil extraction as an added value product in Mexico. Waste Biomass Valoriz 8:1187–1197
Hou XL, Han H, Meng FR, Cai LP, Liu AQ (2019) Intermittent lead induced stress on antioxidant enzyme activity and subcellular distribution of Pb in Pogonatherum crinitum seedlings. Plant Biol (Stuttg). https://doi.org/10.1111/plb.12962
Huang HL, Wu JX, Xu SH, Wang XM, Cao H (2007) Evaluation of investment economic revenue and confirmation of the best economic cutting cycle of industrial raw material forest Eucalyptus. Sci Silva Sin 43:128–133
Jun R, Ling T (2012) Increase of Cd accumulation in five poplar (Populus L.) with different supply levels of Cd. Int J Phytorem 14:101–113
Kuklin AP, Matafonov PV (2014) Background concentrations of heavy metals in benthos from transboundary rivers of the transbaikalia region, Russia. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 92:137–142
Li JH, Duan HB, Shi PX (2011) Heavy metal contamination of surface soil in electronic waste dismantling area: site investigation and source-apportionment analysis. Waste Manage Res 29:727–738
Liu J, Chen X, Shu HY, Lin XR, Zhou QX, Bramryd T, Shu WS, Huang LN (2018) Microbial community structure and function in sediments from e-waste contaminated rivers at Guiyu area of China. Environ Pollut 235:171–179
Luo J, Qi SH, Peng L, Xie XM (2015) Phytoremediation potential of cadmium-contaminated soil by Eucalyptus globulus under different coppice systems. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 94:321–325
Luo J, Qi SH, Peng L, Wang JJ (2016) Phytoremediation efficiency of Cd by Eucalyptus globulus transplanted from polluted and unpolluted sites. Int J Phytorem 18:308–314
Luo J, He M, Qi SH, Wu J, Gu XS (2018) Effect of planting density and harvest protocol on field-scale phytoremediation efficiency by Eucalyptus globulus. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:11343–11350
Ma C, Zhang WH, Zhou RY, Wu M, Xue YQ, Ma LW (2014) Fine root architecture, morphology, and biomass response to cutting in a Chinese cork oak (Quercus variabilis Blume) forest. Turk J Agric For 38:668–675
Mahdieh M, Yazdani M, Mahdieh S (2013) The high potential of Pelargonium roseum plant for phytoremediation of heavy metals. Environ Monit Assess 185:7877–7881
Mota VD, Turrini RNT, Poveda VD (2015) Antimicrobial activity of Eucalyptus globulus oil, xylitol and papain: a pilot study. Rev Esc Enferm USP 49:215–219
Pilon-Smits E (2005) Phytoremediation. Annu Rev Plant Biol 56:15–39
Pirralho M, Flores D, Sousa VB, Quilho T, Knapic S, Pereira H (2014) Evaluation on paper making potential of nine Eucalyptus species based on wood anatomical features. Ind Crop Prod 54:327–334
Qu GZ, Tong YA, Gao PC, Zhao ZP, Song XY, Ji PH (2013) Phytoremediation potential of Solanum nigrum L. under different cultivation protocols. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 91:306–309
Raj A, Singh N (2015) Phytoremediation of arsenic contaminated soil by arsenic accumulators: a three year study. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 94:308–313
Rance SJ, Mendham DS, Cameron DM, Grove TS (2012) An evaluation of the conical approximation as a generic model for estimating stem volume, biomass and nutrient content in young Eucalyptus plantations. New For 43:109–128
Schwegman K, Little KM, McEwan A, Ackerman SA (2018) Harvesting and extraction impacts on Eucalyptus grandis × E. urophylla coppicing potential and rotation-end volume in Zululand South Africa. South For 80:51–57
Sheoran V, Sheoran AS, Poonia P (2011) Role of hyperaccumulators in phytoextraction of metals from contaminated mining sites: a review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 41:168–214
Vieira M, Bessa LJ, Martins MR, Arantes S, Teixeira APS, Mendes A, da Costa PM, Belo ADF (2017) Chemical composition, antibacterial, antibiofilm and synergistic properties of essential oils from Eucalyptus globulus Labill. and seven mediterranean aromatic plants. Chem Biodivers 14(6):e1700006
Wang Y, Yan A, Wu T, Zhang X (2012) Accumulation and remediation of cadmium-polluted soil by a potential cadmium-hyperaccumulator Chlorophytum comosum. Energ Source Part A 34:1523–1533
Wang F, Zhao WJ, Chen YY (2018) Spatial variations of soil heavy metal potential ecological risks in typical Moso bamboo forests of southeast China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 102:224–230
Wang X, Bai JY, Wang J, Le SX, Wang ML, Zhao Y (2019) Variations in cadmium accumulation and distribution among different oilseed rape cultivars in Chengdu Plain in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:3415–3427
Wrobel-Tobiszewska A, Boersma M, Sargison J, Adams P, Jarick S (2015) An economic analysis of biochar production using residues from Eucalypt plantations. Biomass Bioenerg 81:177–182
Yekeen TA, Xu XJ, Zhang YL, Wu YS, Kim S, Reponen T, Dietrich KN, Ho SM, Chen AM, Huo X (2016) Assessment of health risk of trace metal pollution in surface soil and road dust from e-waste recycling area in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:17511–17524
Zhang X, Li M, Yang HH, Li XX, Cui ZJ (2018) Physiological responses of Suaeda glauca and Arabidopsis thaliana in phytoremediation of heavy metals. J Environ Manag 223:132–139
Zheng H, Zhang ZZ, Xing XL, Hu TP, Qu CK, Chen W, Zhang JQ (2018) Potentially toxic metals in soil and dominant plants from Tonglushan Cu–Fe deposit, central China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 102:92–97
Acknowledgments
Authors thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project Nos. 21876014 and 41872144) for financial support of this study. We also thank the Key Laboratory of Exploration Technologies for Oil and Gas Resources for experimental resources for the present study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Research Involving Human Participants and/or Animals
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xing, Y., Wang, Z., Zhang, C. et al. Balance Between Soil Remediation and Economic Benefits of Eucalyptus globulus. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 102, 887–891 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-019-02606-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-019-02606-0