Abstract
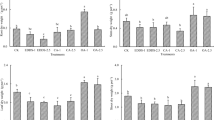
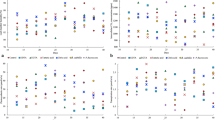
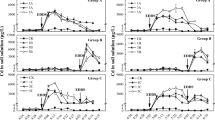
The leaching behavior of five additives, including citric acid (CA), wood vinegar (WV), 1-hydroxyethylidene-1,1-diphosphonic acid (HEDP), polyaspartic acid (PASP) and FeCl3, was investigated to evaluate the possibility of enhanced phytoextraction of Pennisetum sp. from cadmium-contaminated soil. FeCl3 and CA have the highest leaching potential due to the ability that could convert large amounts of mobile fractions of Cd. The pot experiment showed that HEDP, WV, and PASP treatments could not only significantly increase the biomass of Pennisetum sp., but also maintain high uptake capacity of Cd by activating the stable fractions. HEDP has the highest Cd extraction efficiency and metal extraction ratio (MER) value. The phytoremediation efficiency could be improved mainly by increasing the biomass of the tolerant shoots, and Pennisetum sp. seems to have the maximum potential of phytoextraction to Cd with HEDP which could achieve a higher phytoextraction effect than Cd-hyperaccumulator.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afshan S, Ali S, Bharwana SA, Rizwan M, Farid M (2015) Citric acid enhances the phytoextraction of chromium, plant growth, and photosynthesis by alleviating the oxidative damages in Brassica napus L. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:11679–11689
Alkorta I, Allica J, Beccerril JM, Amezaga I, Albizu I, Garbisu C (2004) Recent findings on the phytoremediation of soils contaminated with environmentally toxic heavy metals and metalloids such as zinc, cadmium, lead and arsenic. Rev Environ Health 3:71–90
Allica JH, Becerrili JM, Garbisu C (2008) Assessment of the phytoextraction potential of high biomass crop plants. Environ Pollut 152:32–40
Baker AJM, Mcgrath SP, Sidoli C, Reeves RD (1994) The possibility of in situ heavy metal decontamination of polluted soils using crops of metal-accumulating plants. Resour Conserv Recycl 11:41–49
Begum ZA, Rahman IM, Sawai H, Mizutani S, Maki T, Hasegawa H (2013) Effect of extraction variables on the biodegradable chelant-assisted removal of toxic metals from artificially contaminated European reference soils. Water Air Soil Pollut 224:1–21
Bluskov S, Arocena JM, Omotoso OO, Young JP (2005) Uptake, distribution, and speciation of chromium in Brassica juncea. Int J Phytoremediat 7:153–165
Cui HB, Fan YC, Yang J, Xu L, Zhou J, Zhu ZQ (2016) In situ phytoextraction of copper and cadmium and its biological impacts in acidic soil. Chemosphere 161:233–241
Evangelou MWH, Ebel M, Schaeffer A (2007) Chelate assisted phytoextraction of heavy metals from soil. Effect, mechanism, toxicity, and fate of chelating agents. Chemosphere 68:989–1003
Garcia G, Faz A, Cunha M (2004) Performance of Piptatherum miliaceum (Smilo grass) in edaphic Pb and Zn phytoremediation over a short growth period. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 54:245–250
He S, Yang X, He Z, Baligar VC (2017) Morphological and physiological responses of plants to cadmium toxicity: a review. Pedosphere 27:421–438
Huang FYC, Brady PV, Lindgren ER, Guerra P (1998) Biodegradation of uranium-citrate complexes: implications for extraction of uranium from soils. Environ Sci Technol 32:379–382
Kennedy VH, Sanchez AL, Oughton DH, Rowland AP (1997) Use of single and sequential chemical extractants to assess radionuclide and heavy metal availability from soils for root uptake. Analyst 122:89–100
Khan I, Ahmad A, Iqbal M (2009) Modulation of antioxidant defence system for arsenic detoxification in Indian mustard. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:626–634
Makino T, Sugahara K, Sakurai Y, Takano H, Kamiya T, Sasaki K, Itou T, Sekiya N (2006) Remediation of cadmium contamination in paddy soils by washing with chemicals: selection of washing chemicals. Environ Pollut 144:2–10
Makino T, Takano H, Kamiya T, Itou T, Sekiya N, Inahara M, Sakurai Y (2008) Restoration of cadmium-contaminated paddy soils by washing with ferric chloride: Cd extraction mechanism and bench-scale verification. Chemosphere 70:1035–1043
Mertens J, Luyssaert S, Verheyen K (2005) Use and abuse of trace metal concentrations in plant tissue for biomonitoring and phytoextraction. Environ Pollut 138:1–4
Nemati K, Abu Bakar NK, Sobhanzadeh E, Abas MR (2009) A modification of the BCR sequential extraction procedure to investigate the potential mobility of copper and zinc in shrimp aquaculture sludge. Microchem J 92:165–169
Nowack B (2003) Environmental chemistry of phosphonates. Water Res 37:2533–2546
Qin F, Shan XQ, Wei B (2004) Effects of low-molecular-weight organic acids and residence time on desorption of Cu, Cd, and Pb from soils. Chemosphere 57:253–263
Quartacci MF, Cosi E, Meneguzzo S, Sgherri C, Navari-Izzo F (2003) Uptake and translocation of copper in brassicaceae. J Plant Nutr 26:1065–1083
Roque J, Molera J, Vendrell-Saz M, Salvado N (2004) Crystal size distributions of induced calcium carbonate crystals in polyaspartic acid and Mytilus edulis acidic organic proteins aqueous solutions. J Cryst Growth 262:543–553
Solis-Dominguez FA, Gonzalez-Chavez MC, Carrillo-Gonzalez R, Rodriguez-Vazquez R (2007) Accumulation and localization of cadmium in Echinochloa polystachya grown within a hydroponic system. J Hazard Mater 141:630–636
Steber J, Wierich P (1986) Properties of hydroxyethane diphosphonate affecting its environmental fate-degradability, sludge adsorption, mobility in soils, and bioconcentration. Chemosphere 15:929–945
Sun YB, Zhou QX, Diao CY (2008) Effects of cadmium and arsenic on growth and metal accumulation of Cd-hyperaccumulator Solanum nigrum L. Bioresour Technol 99:1103–1110
Sun YB, Zhou QX, Wang L, Liu WT (2009) The influence of different growth stages and dosage of EDTA on Cd uptake and accumulation in Cd-hyperaccumulator (Solanum nigrum L.). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 82:348–353
Trotta A, Falaschi P, Cornara L, Minganti V, Fusconi A, Drava G, Berta G (2006) Arbuscular mycorrhizae increase the arsenic translocation factor in the as hyperaccumulating fern Pteris vittata L. Chemosphere 65:74–81
Tu C, Ma LQ, Bondada B (2002) Arsenic accumulation in the hyperaccumulator Chinese brake and its utilization potential for phytoremediation. J Environ Qual 31:1671–1675
Wang X, Bai Y, Luo Q, Liu Z (2013) Study on ATMP and HEDP water treatment agent synergistic effect. Appl Chem Ind 1:4–7
Wang GY, Zhang SR, Xu XX, Zhong QM, Zhang CE, Jia YX, Li T, Deng OP, Li Y (2016) Heavy metal removal by GLDA washing: optimization, redistribution, recycling, and changes in soil fertility. Sci Total Environ 569:557–568
Wu Q, Cui YR, Li QL, Sun JH (2015) Effective removal of heavy metals from industrial sludge with the aid of a biodegradable chelating ligand GLDA. J Hazard Mater 283:748–754
Zalewska M (2012) Response of perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) to soil contamination with zinc. J Elementol 17:329–343
Zayed A, Gowthaman S, Terry N (1998) Phytoaccumulation of trace elements by wetland plants: I. Duckweed. J Environ Qual 27:715–721
Zhang WH, Cai Y, Tu C, Ma LQ (2002) Arsenic speciation and distribution in an arsenic hyperaccumulating plant. Sci Total Environ 300:167–177
Zhang X, Zhang S, Xu X, Li T, Gong G, Jia Y (2010) Tolerance and accumulation characteristics of cadmium in Amaranthus hybridus L. J Hazard Mater 180:303–308
Zhang Y, Ge SJ, Jiang MY, Jiang Z, Wang ZG, Ma BB (2014) Combined bioremediation of atrazine-contaminated soil by Pennisetum and Arthrobacter sp. strain DNS10. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:6234–6238
Zhang JR, Li HZ, Zhou YZ, Dou L, Cai LM, Mo LP, You J (2018) Bioavailability and soil-to-crop transfer of heavy metals in farmland soils: a case study in the Pearl River Delta, South China. Environ Pollut 235:710–719
Zu YQ, Li Y, Chen JJ, Chen HY, Qin L, Schvartz C (2005) Hyperaccumulation of Pb, Zn and Cd in herbaceous grown on lead-zinc mining area in Yunnan, China. Environ Int 31:755–762
Zvobgo G, Lwalaba JLW, Sehar S, Mapodzeke JM, Shamsi IH, Zhang GP (2018) The tolerance index and translocation factor were used to identify the barley genotypes with high arsenic stress tolerance. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 49:50–62
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Key R&D Plan (2018YFD0800304) and Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. BK20171075).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, F., Zhang, Y., Hao, S. et al. Leaching Behaviour and Enhanced Phytoextraction of Additives for Cadmium-Contaminated Soil by Pennisetum sp.. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 104, 658–667 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-020-02851-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-020-02851-8