Abstract
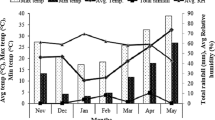
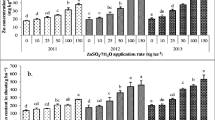
Nutritional status of people can be improved by enhancing zinc (Zn) and iron (Fe) content in cereals used as staple mainly in poor resource countries. Zinc and Fe were applied through soil and foliage in a study to biofortify wheat grains. Foliar application of both micronutrients increased the growth and grain vigor as compared to soil application and control. Also, foliar application significantly enhanced Zn and Fe concentration in grain pre-dominantly localized in aleurone layer. Exogeneous application of Fe and Zn was found beneficial for plant growth and enhanced Fe and Zn concentrations in grain, however aleurone layer and embryonic region of the grain showed higher accumulations than that in endosperm. Therefore, understanding of physiological and molecular pathways for uptake and localization of Fe and Zn in wheat grains need to be critically examined to improve their concentration in grain to achieve the biofortification targets.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
AACC International (2000) AACC International approved methods of analysis. AACC International, Saint Paul
AOAC (2016) Official methods of analysis of AOAC INTERNATIONAL, 20th edn. AOAC International, Rockville
Balk J, Connorton JM, Wan Y, Lovegrove A, Moore KL, Uauy C, Sharp PA, Shewry PR (2019) Improving wheat as a source of iron and zinc for global nutrition. Nutr Bull 44:53–59
Borrill P, Connorton JM, Balk J, Miller AJ, Sanders D, Uauy C (2014) Biofortification of wheat grain with iron and zinc: integrating novel genomic resources and knowledge from model crops. Front Plant Sci 5:53
Cakmak I, Kutman UB (2018) Agronomic biofortification of cereals with zinc: a review. Eur J Soil Sci 69:172–180
Cakmak I, Pfeiffer WH, McClafferty B (2010) REVIEW: biofortification of durum wheat with zinc and iron. Cereal Chem J 87:10–20
Ciccolini V, Pellegrino E, Coccina A, Fiaschi AI, Cerretani D, Sgherri C, Quartacci MF, Ercoli L (2017) J Agric Food Chem 65:5443–5452
Fox J, Leanage A (2016) J Stat Softw 73:1–13
Garcia-Oliveira AL, Chander S, Ortiz R, Menkir A, Gedil M (2018) Genetic basis and breeding perspectives of grain iron and zinc enrichment in cereals. Front Plant Sci 9:937
Habib M (2012) Effect of supplementary nutrition with Fe, Zn chelates and urea on wheat quality and quantity. Afr J Biotechnol 11:2661–2665
Jeong J, Lou GM (2009) Homing in on iron homeostasis in plants. Trends Plant Sci 14:280–285
Kyriacou B, Moore KL, Paterson D, De Jonge MD, Howard DL, Stangoulis J, Tester M, Lombi E, Johnson AAT (2014) Localization of iron in rice grain using synchrotron X-ray fluorescence microscopy and high resolution secondary ion mass spectrometry. J Cereal Sci 59:173–180
Naz S, Tahir MA, Qadir A (2015) Iron and zinc biofortification strategies in wheat crop by exogenous application of micronutrients. Food Sci Q Manag 35:49–55
Nowack B, Schwyzer I, Schulin R (2008) Uptake of Zn and Fe by wheat (Triticum aestivum var. Greina) and transfer to the grains in the presence of chelating agents (ethylenediaminedisuccinic acid and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid). J Agric Food Chem 56:4643–4649
Olsen LI, Palmgren MG (2014) Many rivers to cross: the journey of zinc from soil to seed. Front Plant Sci 5:1–6
Ozturk L, Yazici MA, Yucel C, Torun A, Cekic C, Bagci A, Ozkan H, Braun H-J, Sayers Z, Cakmak I (2006) Concentration and localization of zinc during seed development and germination in wheat. Physiol Plant 128:144–152
Ru K, Hl S, Kunjadia BB (2018) Effect of zinc and iron application on leaf chlorophyll, carotenoid, grain yield and quality of wheat in calcareous soil of Saurashtra region. Int J Chem Stud 6:2092–2096
Sultana S, Naser HM, Quddus MA, Shil NCA, Hossain MA (2018) Effect of foliar application of iron and zinc on nutrient uptake and grain yield of wheat under different irrigation regimes. Bangladesh J Agric Res 2:395–406
Sumanta N, Imranul Haque C, Nishika J, Suprakash R (2014) Spectrophotometric analysis of chlorophylls and carotenoids from commonly grown fern species by using various extracting solvents. Res J Chem Sci 4:63–69
Velu G, Ortiz-Monasterio I, Cakmak I, Hao Y, Singh RP (2014) Biofortification strategies to increase grain zinc and iron concentrations in wheat. J Cereal Sci 59:365–372
Wakeel A, Farooq M, Bashir K, Ozturk L (2018) Micronutrient malnutrition and biofortification: recent advances and future perspectives. In: Hossain SD et al (eds) Plant micronutrition use efficiency. Academic Press, London, pp 225–243
Walker CF, Kordas K, Stoltzfus RJ, Black RE (2005) Interactive effects of iron and zinc on biochemical and functional outcomes in supplementation trials. Am J Clin Nutr 82:5–12
Welch RM, Graham RD (2004) Breeding for micronutrients in staple food crops from a human nutrition perspective. J Exp Bot 55:353–364
Zayed BA, Salem AKM, El Sharkawy HM (2011) Effect of different micronutrient treatments on rice (Oriza sativa L.) growth and yield under saline soil conditions. World J Agric Sci 7:179–184
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kiran, A., Wakeel, A., Sultana, R. et al. Concentration and Localization of Fe and Zn in Wheat Grain as Affected by Its Application to Soil and Foliage. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 106, 852–858 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03183-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03183-x