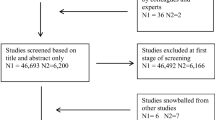
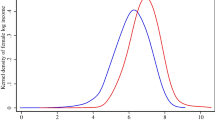
Abstract
Previous research has shown adverse effects of growing up under unilateral divorce laws on long-term outcomes of children. It remains an open question of whether these effects of early childhood conditions arise due to divorce laws raising the likelihood of parental marital disruption or whether unilateral divorce laws also affect children in intact marriages by changing intra-household bargaining. Using recently available data from SHARELIFE for 11 Western European countries, we address this question employing a difference-in-differences approach and controlling for childhood family structure and socioeconomic status. Like previous research, we find adverse effects of growing up under unilateral divorce laws on the well-being of children. This effect remains even when controlling for childhood variables. We conclude that unilateral divorce laws affect children by changing family bargaining in intact marriages.

Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
In principle, we have information on some measures from two waves of SHARE (wave 1 and 2) which would allow us to separately identify age and cohort effects. However, we refrain from doing so because in most measures there is not much variation between waves since educational attainment and the demographic variables do not change much for individuals older than 50 years.
Notice that there is a second interpretation of this variable, as it implicitly is also a control for the age of the individual when unilateral divorce laws were introduced. In our data set we cannot distinguish between those opportunities.
References
Amato PR (2001) Children of divorce in the 1990s: an update of the Amato and Keith (1991) meta-analysis. J Fam Psychol 15(3):355–370
Amato PR, Keith B (1991) Parental divorce and the well-being of children: a meta-analysis. Psychol Bull 110(1):26–46
Becker GS (1993). A treatise on the family. Harvard University Press, Cambridge
Braver SL, Whitley M, Ng C (1993) Who divorced whom? Methodological and theoretical issues. J Divorce Remarriage 20:1–19
Brown M, Flinn CJ (2011) Family law effects on divorce, fertility and child investment. Working Paper, New York University
Browning M, Chiappori PA (1998) Efficient intra-household allocations: a general characterization and empirical tests. Econometrica 66(6):1241–1278
Cáceres-Delpiano J, Giolito E (2008) How unilateral divorce affects children. IZA Discussion Paper 3342
Cáceres-Delpiano J, Giolito E (2012) The impact of unilateral divorce on crime. J Labor Econ 30(1):215–248
Chase-Lansdale PL, Cherlin AJ, Kiernan KE (1995) The long-term effects of parental divorce on the mental health of young adults: a developmental perspective. Child Dev 66(6):1614–1634
Cherlin AJ, Kiernan KE, Chase-Lansdale PL (1995) Parental divorce in childhood and demographic outcomes in young adulthood. Demography 32(3):299–318
Cherlin AJ, Chase-Lansdale PL, McRae C (1998) Effects of parental divorce on mental health throughout the life course. Am Sociol Rev 63(2):239–249
Cigno A (2012) Marriage as a commitment device. Rev Econ Househ. doi:10.1007/s11150–012–9141–1
Dawson DA (1991) Family structure and children’s health and well-being: data from the 1988 National Health Interview Survey on child health. J Marriage Fam 53(3):573–584
Del Boca D, Flinn CJ (2012) Endogenous household interaction. J Econom 166:49–65
Flinn CJ (2000) Modes of interaction between divorced parents. Int Econ Rev 41:545–578
Friedberg L (1998) Did unilateral divorce raise divorce rates? Evidence from panel data. Am Econ Rev 88:608–627
González L, Viitanen TK (2009) The effect of divorce laws on divorce rates in Europe. Eur Econ Rev 53:127–138
González L, Viitanen T (2008) The long term effects of legalizing divorce on children. IZA Discussion Paper 3789
Goode WJ (1993) World changes in divorce patterns. Yale University Press, New Haven
Gruber J (2004) Is making divorce easier bad for children? The long-run implications of unilateral divorce. J Labor Econ 22(4):799–833
Heckman JJ, Layne-Farrar A, Todd P (1996) Does measured school quality really matter? An examination of the earnings quality relationship. In: Burtless G (ed) Does money matter? Brookings Institution, Washington, pp 192–289
Johnson JH, Mazingo CJ (2000) The economic consequences of unilateral divorce for children. Working Paper, University of Illinois
Jürges H, Reinhold S, Salm M (2011) Does schooling affect health behavior? Evidence from the educational expansion in Western Germany. Econ Educ Rev 30:862–872
Keith VM, Finlay B (1988) The impact of parental divorce on children’s educational attainment, marital timing, and the likelihood of divorce. J Marriage Fam 50(3):797–809
Kemptner D, Jürges H, Reinhold S (2011) Changes in compulsory schooling and the causal effect of education on health. J Health Econ 30(2):340–354
Kiernan KE, Cherlin AJ (1999) Parental divorce and partnership dissolution in adulthood: evidence from a British cohort study. Pop Stud-J Demogr 53(1):39–48
Kneip T, Bauer G (2009) Did unilateral divorce laws raise divorce rates in Western Europe? J Marriage Fam 71:592–607
Kneip T, Bauer G, Reinhold S (2011) Direct and indirect effects of unilateral divorce law on marital stability. MEA Discussion Paper 248–11
Lampard R, Peggs K (1999) Repartnering: the relevance of parenthood and gender to cohabitation and remarriage among the formerly married. Br J Sociol 50(3):443–465
Lundberg S, Pollak RA (1993) Separate spheres bargaining and the marriage market. J Polit Econ 101(6):988–1010
Manser M, Brown M (1980) Marriage and household decision making: a bargaining analysis. Int Econ Rev 21:31–44
McElroy MB, Horney MJ (1981) Nash-bargained household decisions: towards a generalization of the theory of demand. Int Econ Rev 22:333–349
Parkman AM (1992) Unilateral divorce and the labor-force participation rate of married women, revisited. Am Econ Rev 82(3):671–678
Parkman AM (2000) Good intentions gone awry. No-fault divorce and the American family. Rowman and Littlefield, Lanham
Paxson C, Waldfogel J (2002) Work, welfare, and child maltreatment. J Labor Econ 20(3):435–474
Peters HE (1986) Marriage and divorce: informational constraints and private contracting. Am Econ Rev 76:437–454
Pischke JS, von Wachter T (2008) Zero returns to compulsory schooling in Germany. Rev Econ Stat 90(3):592–598
Prince M, Reischies F, Beekman ATF et al (1999) Development of the EURO–D scale—a European Union initiative to compare symptoms of depression in 14 European centres. Br J Psychiatr 174:330–338
Rasul I (2005) Marriage markets and divorce laws. J Law Econ Organ 22(1):30–68
Stevenson B (2008) Divorce law and women’s labor supply. J Empir Legal Stud 5(4):853–873
Stevenson B, Wolfers J (2006) Bargaining in the shadow of the law: divorce laws and family distress. Q J Econ 121(1):267–288
Wolfers J (2006) Did unilateral divorce raise divorce rates? A reconciliation and new results. Am Econ Rev 96(5):1802–1820
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Alessandro Cigno
This paper uses data from SHARELIFE release 1, as of November 24, 2010 or SHARE release 2.4.0, as of March 17 2011. The SHARE data collection has been primarily funded by the European Commission through the fifth framework program (project QLK6-CT-2001–00360 in the thematic program Quality of Life), through the sixth framework program (projects SHARE-I3, RII-CT-2006–062193, COMPARE, CIT5-CT-2005–028857, and SHARELIFE, CIT4-CT-2006–028812) and through the seventh framework program (SHARE-PREP, 211909 and SHARE-LEAP, 227822). Additional funding from the US National Institute on Aging (U01 AG09740–13S2, P01 AG005842, P01 AG08291, P30 AG12815, Y1-AG-4553–01 and OGHA 04–064, IAG BSR06–11, and R21 AG025169) as well as from various national sources is gratefully acknowledged (see www.share-project.org for a full list of funding institutions). We would like to thank Alessandro Cigno and two anonymous referees for helpful suggestions.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reinhold, S., Kneip, T. & Bauer, G. The long run consequences of unilateral divorce laws on children—evidence from SHARELIFE. J Popul Econ 26, 1035–1056 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00148-012-0435-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00148-012-0435-7
Keywords
- Unilateral divorce
- Childhood conditions
- Difference-in-differences
- Intra-household bargaining
- Children’s human capital formation