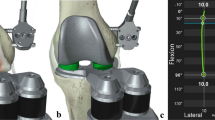
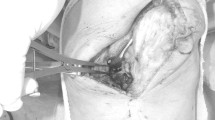
Abstract
Equalized rectangular extension and flexion gaps are considered desirable to ensure proper kinematics in total knee arthroplasty (TKA). We compared soft tissue balancing in TKAs performed using navigation-assisted gap-balancing (60 knees) and conventional measured resection (56 knees). The outlier of soft tissue balancing was defined as a gap difference >3 mm between the medial and lateral sides in 90° flexion and extension. Medial or lateral outliers in extension or flexion were observed in 12% (7 of 60) navigation TKAs and 25% (14 of 56) conventional TKAs (p = 0.028). There were more outliers in flexion–extension gap difference on the medial side in the conventional (23%) than in the navigation-assisted (5%) group (p = 0.025). However, the proportion of flexion gap difference, extension gap difference, and lateral gap difference outliers did not differ significantly between the two groups (n.s.). Additionally, clinicoradiologic outcomes were similar for the two groups except for the postoperative mechanical axis outlier (p = 0.012). Navigation-assisted soft tissue balancing in TKA reduced not only the postoperative alignment outlier, but also the medial gap difference and achieved a more rectangular flexion and extension gap compared with conventional TKA.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
D’Lima DD, Chen PC, Colwell CW Jr (2001) Polyethylene contact stresses, articular congruity, and knee alignment. Clin Orthop Relat Res 392:232–238
D’Lima DJ, Patil S, Steklov N, Colwell CW (2007) An ABJS best paper: dynamic intraoperative ligament balancing for total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 463:208–212
Gamada K, Jayasekera N, Kashif F, Fennema P, Schmotzer H, Banks SA (2008) Does ligament balancing technique affect kinematics in rotating platform, PCL retaining knee arthroplasties? A prospective randomized study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 16:160–166
Griffin FM, Insall JN, Scuderi GR (2000) Accuracy of soft tissue balancing in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 15:970–973
Hanada H, Whiteside LA, Steiger J, Dyer P, Naito M (2007) Bone landmarks are more reliable than tensioned gaps in TKA component alignment. Clin Orthop Relat Res 462:137–142
Insall JN, Binazzi R, Soudry M, Mestriner LA (1985) Total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 192:13–22
Jenny J-Y, Boeri C (2004) Low reproducibility of the intra-operative measurement of the transepicondylar axis during total knee replacement. Acta Orthop Scand 75:74–77
Jerosch J, Peuker E, Philipps B, Filler T (2002) Interindividual reproducibility in perioperative rotational alignment of femoral components in knee prosthetic surgery using the transepicondylar axis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 10:194–197
Lotke PA, Ecker ML (1977) Influence of positioning of prosthesis in total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am 59:77–79
Mason JB, Fehring TK, Estok R, Banel D, Fahrbach K (2007) Meta-analysis of alignment outcomes in computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty surgery. J Arthroplasty 22:1097–1106
Matsumoto T, Mizuno K, Muratsu H, Tsumura N, Fukase N, Kubo S, Yoshiya S, Kurosaka M, Kuroda R (2007) Influence of intra-operative joint gap on post-operative flexion angle in osteoarthritis patients undergoing posterior-stabilized total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 15:1013–1018
Picard F, Deakin AH, Clarke JV, Dillon JM, Gregori A (2007) Using navigation intraoperative measurements narrows range of outcomes in TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res 463:50–57
Seon JK, Song EK, Yoon TR, Bae BH, Park SJ, Cho SG (2007) In vivo stability of total knee arthroplasty using a navigation system. Int Orthop 31:45–48
Siston RA, Goodman SB, Delp SL, Giori NJ (2007) Coronal plane stability before and after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 463:43–49
Sugama R, Kadoya Y, Kobayashi A, Takaoka K (2005) Preparation of the flexion gap affects the extension gap in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 20:602–607
Tanaka K, Muratsu H, Mizuno K, Kuroda R, Yoshiya S, Kurosaka M (2007) Soft tissue balance measurement in anterior cruciate ligament-resected knee joint: cadaveric study as a model for cruciate-retaining total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Sci 12:149–153
Tingart M, Lüring C, Bäthis H, Beckmann J, Grifka J, Perlick L (2008) Computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty versus the conventional technique: how precise is navigation in clinical routine? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 16:44–50
Unitt L, Sambatakakis A, Johnstone D, Briggs TW (2008) Short-term outcome in total knee replacement after soft-tissue release and balancing. J Bone Joint Surg Br 90:159–165
Viskontas DG, Skrinskas TV, Johnson JA, King GJ, Winemaker MJ, Chess DG (2007) Computer-assisted gap equalization in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 22:334–342
Windsor RE, Scuderi GR, Moran MC, Insall JN (1989) Mechanisms of failure of the femoral and tibial components in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 248:15–19
Winemaker MJ (2002) Perfect balance in total knee arthroplasty: the elusive compromise. J Arthroplasty 17:2–10
Yagishita K, Muneta T, Ikeda H (2003) Step-by-step measurements of soft tissue balancing during total knee arthroplasty for patients with varus knees. J Arthroplasty 18:313–320
Yau WP, Chiu KY, Zuo JL, Tang WM, Ng TP (2008) Computer navigation did not improve alignment in a lower-volume total knee practice. Clin Orthop Relat Res 466:935–945
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Research of this case was performed at Korea University Anam Hospital.
No benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article, nor have any funds been received in support of this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, DH., Park, JH., Song, DI. et al. Accuracy of soft tissue balancing in TKA: comparison between navigation-assisted gap balancing and conventional measured resection. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 18, 381–387 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-009-0983-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-009-0983-x