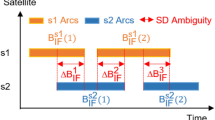
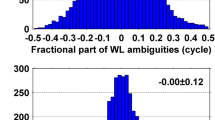
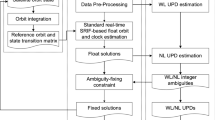
Abstract
Ambiguity resolution (AR) is an effective approach to improve the orbit accuracy of the low Earth orbit satellites using the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS). The most commonly used single-difference (SD) AR requires prior knowledge of the GNSS hardware biases, while the potential unavailability of the bias products may hinder the AR process for users. The track-to-track (T2T) AR can work as an alternative without the GNSS bias products, but the performance may be degraded by the receiver hardware biases. To provide a better alternative in this condition, a new AR method called SD T2T (SDT2T) is proposed in this study, where the GNSS and receiver biases can be greatly eliminated without external knowledge. The performance of the SD AR, SDT2T AR, and T2T AR methods are assessed based on the gravity recovery and climate experiment follow on and SWARM data. The results show that the improvements contributed by the SDT2T AR are comparable to the SD AR. The multiple iterations required by the T2T AR can be avoided by the SDT2T AR, and the accuracy of the T2T AR can be further improved with the preprocessed ambiguities of the SDT2T AR. Considering the efficiency and stable performance, the SDT2T AR is recommended as the preferred alternative single-receiver AR method in the absence of the GNSS hardware bias products.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All original data in this article are publicly available. The CODE precise orbit and clock products can be found on the website of the IGS data center of Wuhan University via ftp://igs.gnsswhu.cn/pub/gnss/products/. The GRACE-FO data can be provided by JPL at https://podaac.jpl.nasa.gov/GRACE-FO or GFZ via ftp://rz-vm152.gfz-potsdam.de/. The SWARM data are from ftp://swarm-diss.eo.esa.int/Level1b/Latest_baselines/. The SLR tracking data are obtained from ftp://cddis.gsfc.nasa.gov/pub/slr/data/, and the F10.7 data and geomagnetic data are from ftp://ftp.swpc.noaa.gov/. The antenna file is obtained from ftp://garner.ucsd.edu/archive/garner/gamit/tables.
References
Arnold D, Montenbruck O, Hackel S, Sośnica K (2019a) Satellite laser ranging to low Earth orbiters: orbit and network validation. J Geod 93:2315–2334. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-018-1140-4
Arnold D, Schaer S, Villiger A, Dach R, Jäggi A (2019b) Single-receiver ambiguity fixing for GPS-based precise orbit determination of low Earth orbiters using CODE’s new clock and phase bias products. Geophys Res Abstracts 21:1
Bertiger W, Desai SD, Haines B, Harvey N, Moore AW, Owen S, Weiss JP (2010) Single receiver phase ambiguity resolution with GPS data. J Geod 84(5):327–337. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-010-0371-9
Blewitt G (1989) Carrier phase ambiguity resolution for the global positioning system applied to geodetic baselines up to 2,000 km. J Geophys Res 94(B8):10187–10203. https://doi.org/10.1029/JB094iB08p10187
Cohen H (1993) A course in computational algebraic number theory. Springer, Berlin. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-02945-9
Collins P, Bisnath S, Lahaye F, Héroux P (2010) Undifferenced GPS ambiguity resolution using the decoupled clock model and ambiguity datum fixing. Navigation 57(2):123–135. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.2161-4296.2010.tb01772.x
Collins P, Lahaye F, Heroux P, Bisnath S (2008) Precise point positioning with ambiguity resolution using the decoupled clock model. In: Proceedings of the 21st international technical meeting of the satellite division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS 2008), pp 1315–1322
Dach R, Schaer S, Arnold D, Kalarus M, Prange L, Stebler P, Villiger A, Jäggi A (2020) CODE final product series for the IGS. Published by Astronomical Institute, University of Bern. http://www.aiub.unibe.ch/download/CODE. https://doi.org/10.7892/boris.75876.4
Dong D, Bock Y (1989) Global positioning system network analysis with phase ambiguity resolution applied to crustal deformation studies in California. J Geophys Res 94(B4):3949–3966. https://doi.org/10.1029/JB094iB04p03949
Duan B, Hugentobler U (2019) Precise orbit determination of Sentinel satellites using zero-difference ambiguity resolution approach. Living planet symposium, Milan, Italy
Duan B, Hugentobler U (2021) Comparisons of CODE and CNES/CLS GPS satellite bias products and applications in Sentinel-3 satellite precise orbit determination. GPS Solut 25(4):128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-021-01164-5
Folkner WM, Williams JG, Boggs DH (2009) The planetary and lunar ephemeris DE 421. IPN Prog Rep 42(178):1–34
Förste C, Bruinsma SL, Flechtner F, Marty J, Lemoine JM, Dahle C et al (2012) A preliminary update of the Direct approach GOCE Processing and a new release of EIGEN-6C. In: AGU Fall meeting abstracts, vol 2012, pp G31B-0923
Ge M, Gendt G, Rothacher M, Shi C, Liu J (2008) Resolution of GPS carrier-phase ambiguities in precise point positioning (PPP) with daily observations. J Geod 82:389–399. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-007-0187-4
Geng J, Chen X, Pan Y, Zhao Q (2019) A modified phase clock/bias model to improve PPP ambiguity resolution at Wuhan University. J Geod 93:2053–2067. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-019-01301-6
Geng J, Meng X, Dodson AH, Teferle FN (2010) Integer ambiguity resolution in precise point positioning: method comparison. J Geod 84(9):569–581. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-010-0399-x
Guo X, Geng J, Chen X et al (2020) Enhanced orbit determination for formation-flying satellites through integrated single- and double-difference GPS ambiguity resolution. GPS Solut 24(1):14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-019-0932-1
Hatch R (1982) The synergism of GPS code and carrier measurements. In: Proceedings of the third international symposium on satellite doppler positioning at physical sciences laboratory of New Mexico State University, 8–12 Feb 1982, vol 2, pp 1213–1231
ILRS (2017) SLRF2014 station coordinates. Retrieved from ftp://ftp.cddis.eosdis.nasa.gov/pub/slr/products/resource/SLRF2014_POS+VEL_2030.0_170605.snx
Jäggi A, Dahle C, Arnold D, Bock H, Meyer U, Beutler G, van den Ijssel J (2016) SWARM kinematic orbits and gravity fields from 18 months of GPS data. Adv Space Res 57(1):218–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2015.10.035
Jäggi A, Dach R, Montenbruck O, Hugentobler U, Bock H, Beutler G (2009) Phase center modeling for LEO GPS receiver antennas and its impact on precise orbit determination. J Geod 83(12):1145–1162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-009-0333-2
Jäggi A, Hugentobler U, Bock H, Beutler G (2007) Precise orbit determination for GRACE using undifferenced or doubly differenced GPS data. Adv Space Res 39(10):1612–1619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2007.03.012
Kang Z, Bettadpur S, Nagel P, Save H, Poole S, Pie N (2020) GRACE-FO precise orbit determination and gravity recovery. J Geod 94(9):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-020-01414-3
Knocke P, Ries J, Tapley B (1988) Earth radiation pressure effects on satellites. In: Proceedings of the AIAA/AAS astrodynamics conference, Minneapolis, USA, pp 577–586
Kornfeld RP, Arnold BW, Gross MA, Dahya NT, Klipstein WM, Gath PF, Bettadpur S (2019) GRACE-FO: the gravity recovery and climate experiment follow-on mission. J Spacecr Rocket 56(3):931–951. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.A34326
Kouba J (2015) A guide to using international GNSS service (IGS) products, September 2015 update. Retrieved from http://kb.igs.org/hc/enus/articles/201271873-A-Guide-to-Using-the-IGS-Products
Kroes R, Montenbruck O, Bertiger W, Visser P (2005) Precise GRACE baseline determination using GPS. GPS Solut 9(1):21–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-004-0123-5
Landerer FW, Flechtner FM, Save H, Webb FH, Bandikova T, Bertiger WI et al (2020) Extending the global mass change data record: GRACE follow-on instrument and science data performance. Geophys Res Lett 47:e2020GL088306. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020GL088306
Laurichesse D, Mercier F, Berthias J, Broca P, Cerri L (2009) Integer ambiguity resolution on undifferenced GPS phase measurements and its application to PPP and satellite precise orbit determination. Navigation 56(2):135–149. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.2161-4296.2009.tb01750.x
Li P, Zhang X, Ren X, Zuo X, Pan Y (2016) Generating GPS satellite fractional cycle bias for ambiguity-fixed precise point positioning. GPS Solut 20(4):771–782. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-015-0483-z
Li X, Han X, Li X, Liu G, Zheng H (2021) GREAT-UPD: an open-source software for uncalibrated phase delay estimation based on multi-GNSS and multi-frequency observations. GPS Solut 25:66. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-020-01070-2
Li X, Li X, Yuan Y, Zhang K, Zhang X, Wickert J (2018) Multi-GNSS phase delay estimation and PPP ambiguity resolution: GPS, BDS, GLONASS, Galileo. J Geod 92:579–608. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-017-1081-3
Li X, Wu J, Zhang K, Li X, Xiong Y, Zhang Q (2019) Real-time kinematic precise orbit determination for LEO satellites using zero-differenced ambiguity resolution. Remote Sens 11:2815. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11232815
Loyer S, Perosanz F, Mercier F, Capdeville H, Marty JC (2012) Zero-difference GPS ambiguity resolution at CNES-CLS IGS analysis center. J Geod 86(11):991. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-012-0559-2
Lyard F, Lefevre F, Letellier T, Francis O (2006) Modelling the global ocean tides: modern insights from FES2004. Ocean Dyn 56(5–6):394–415. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10236-006-0086-x
Malys S, Jensen PA (1990) Geodetic point positioning with GPS carrier beat phase data from the CASA UNO experiment. Geophys Res Lett 17(5):651–654. https://doi.org/10.1029/GL017i005p00651
Mao X, Arnold D, Girardin V, Villiger A, Jäggi A (2021) Dynamic GPS-based LEO orbit determination with 1 cm precision using the Bernese GNSS Software. Adv Space Res 67(2):788–805. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2020.10.012
Melbourne W (1985) The case for ranging in GPS-based geodetic systems. Rockville: first international symposium on precise positioning with the global positioning system
Michalak G, König R (2016) Satellite baseline determination with phase cycle slip fixing over long data gaps. IAG 2016. Held 4–7 Sept 2016, Wroclaw
Michalak G, König R, Dahle C (2017) GPS-based LEO orbit determination with carrier phase cycle slip fixing over long data gaps. IGS workshop 2017
Milani A, Nobili AM, Farinella P (1987) Non-gravitational perturbations and satellite geodesy. Adam Hilger, Bristol
Montenbruck O, André H, Langley R, Siemes C (2019) CASSIOPE orbit and attitude determination using commercial off-the-shelf GPS receivers. GPS Solut 23(4):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-019-0907-2
Montenbruck O, Gill E (2012) Satellite orbits: models, methods and applications. Springer, Berlin. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.1451162
Montenbruck O, Hackel S, Ijssel J, Arnold D (2018a) Reduced dynamic and kinematic precise orbit determination for the SWARM mission from 4 years of GPS tracking. GPS Solut 22(3):79. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-018-0746-6
Montenbruck O, Hackel S, Jaggi A (2018b) Precise orbit determination of the Sentinel-3A altimetry satellite using ambiguity-fixed GPS carrier phase observations. J Geod 92(7):711–726. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-017-1090-2
Montenbruck O, Wermuth M, Kahle R (2011) GPS based relative navigation for the TanDEM-X mission-first flight results. Navigation 58(4):293–304
Pearlman M, Degnan J, Bosworth J (2002) The international laser ranging service. Adv Space Res 30(2):135–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0273-1177(02)00277-6
Pearlman M, Noll C, Pavlis E, Lemoine F, Combrink L, Degnan J, Kirchner G, Schreiber U (2019) The ILRS: approaching 20 years and planning for the future. J Geod 93(11):2161–2180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-019-01241-1
Petit G, Luzum B (2010) IERS conventions (2010). Bureau International des Poids et mesures sevres (France)
Picone J, Hedin A, Drob DP, Aikin A (2002) NRLMSISE-00 empirical model of the atmosphere: statistical comparisons and scientific issues. J Geophys Res Space Phys 107(A12):SIA-15. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002JA009430
Rebischung P, Schmid R, Herring T (2016) Upcoming switch to IGS14/igs14.atx. IGSMAIL-7399. Retrieved from https://lists.igs.org/pipermail/igsmail/2016/001233.html
Schaer S, Villiger A, Arnold D, Dach R, Prange L, Jäggi A (2021) The CODE ambiguity-fixed clock and phase bias analysis products: generation, properties, and performance. J Geod 95:81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-021-01521-9
Schaer S, Villiger A, Dach R, Prange L, Jäggi A, Arnold D (2018) New ambiguity-fixed IGS clock analysis products at CODE. In: International GNSS service workshop 2018, vol 29
Schreiner P, König R, Michalak G (2021) Precise orbit determination of low Earth orbiters using carrier phase cycle slip fixing over long data gaps-an alternative to GNSS phase bias products based ambiguity resolution. 43rd COSPAR Scientific Assembly. Held 28 January–4 February, 43, 2342
Siemes C (2019) Swarm instrument positions related to GPS receiver data processing. Technical report, RHEA for ESA, ESA-EOPSM-SWRM-TN-3559
Švehla D (2018) Track-to-track ambiguity resolution for zero-differences—integer phase clocks. Springer theses (recognizing outstanding Ph.D. research): geometrical theory of satellite orbits and gravity field, Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-76873-1_20
Švehla D, Rothacher M (2003) Kinematic and reduced-dynamic precise orbit determination of low earth orbiters. Adv Geosci 1:47–56. https://doi.org/10.5194/adgeo-1-47-2003
van den Ijssel J, Encarnação J, Doornbos E, Visser P (2015) Precise science orbits for the Swarm satellite constellation. Adv Space Res 56(6):1042–1055. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2015.06.002
Wen H, Gerhard K, Meegyeong P, Felix L, William B, Carly S, Tamara B, Christopher MM (2019) Gravity recovery and climate experiment follow-on (GRACE-FO) level-1 data product user handbook. Technical report JPL D-56935, NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory/California Institute of Technology
Weinbach U, Schön S (2013) Improved GRACE kinematic orbit determination using GPS receiver clock modeling. GPS Solut 17:511–520. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-012-0297-1
Wermuth M, Montenbruck O, van Helleputte T (2010) GPS high precision orbit determination software tools (GHOST). In: 4th international conference on astrodynamics tools and techniques, 3–6 May 2010, Madrid
Wielicki BA, Barkstrom BR, Harrison EF, Lee RB III, Louis SG, Cooper JE (1996) Clouds and the Earth’s radiant energy system (CERES): an earth observing system experiment. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 77(5):853–868. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0477(1996)077%3c0853:CATERE%3e2.0.CO;2
Wu S, Yunck T, Thornton C (1988) Reduced-dynamic technique for precise orbit determination of low earth satellites. J Guid Control Dyn 14(1):2143–2153. https://doi.org/10.2514/3.20600
Wübbena G (1985) Software developments for geodetic positioning with GPS using TI-4100 code and carrier measurements.In: First international symposium on precise positioning with the global positioning system, Rockville, US, pp 403–412
Xu P, Shi C, Liu J (2012) Integer estimation methods for GPS ambiguity resolution: an applications oriented review and improvement. Surv Rev 44(324):59–71. https://doi.org/10.1179/1752270611Y.0000000004
Yunck T, Bertiger W, Wu S et al (1994) First assessment of GPS-based reduced dynamic orbit determination on TOPEX/Poseidon. Geophys Res Lett 21(7):541–544. https://doi.org/10.1029/94GL00010
Yunck T, Wu S, Wu J, Thornton C (1990) Precise tracking of remote sensing satellites with the Global Positioning System. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 28(1):108–116. https://doi.org/10.1109/36.45753
Zhang K, Li X, Wu J, Yuan Y, Li X, Zhang X, Zhang W (2021) Precise orbit determination for LEO satellites with ambiguity resolution: improvement and comparison. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 126(9):e2021JB022491. https://doi.org/10.1029/2021JB022491
Zhou X, Chen H, Fan W, Zhou X, Chen Q, Jiang W (2021) Assessment of single-difference and track-to-track ambiguity resolution in LEO precise orbit determination. GPS Solut 25:62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-021-01103-4
Zhou X, Jiang W, Chen H, Li Z, Liu X (2019) Improving the GRACE kinematic precise orbit determination through modified clock estimating. Sensors 19(19):4347. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19194347
Zumberge J, Heflin M, Jefferson D, Watkins M, Webb F (1997) Precise point positioning for the efficient and robust analysis of GPS data from large networks. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 102(B3):5005–5017. https://doi.org/10.1029/96JB03860
Acknowledgements
This study is supported by the Natural Science Innovation Group Foundation of China (No. 41721003), the National Science Foundation of China (41704030), and the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFC1503601). Thanks to IGS, CODE, and ILRS for providing GNSS data, precise products, and SLR data. Thanks to JPL and GFZ for providing GRACE-FO data. Thanks to ESA for providing SWARM data. Thanks to SWPC/NOAA for the F10.7 data and geomagnetic data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XZ, HC, and WJ devised the project and the main conceptual ideas. XZ and HC worked out most technical details and performed the calculations for the experiments; YC, TJ and TL helped analyze the data. XZ and HC wrote the paper; WJ and YG modified the paper. All authors provided critical feedback and helped to shape the research, analysis, and manuscript.
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, X., Chen, H., Jiang, W. et al. A new ambiguity resolution method for LEO precise orbit determination. J Geod 96, 49 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-022-01629-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-022-01629-6