Abstract
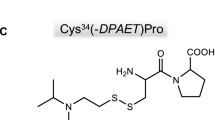
The organophosphorus nerve agents sarin, soman, cyclosarin and tabun phosphylate a tyrosine residue on albumin in human blood. These adducts may offer relatively long-lived biological markers of nerve agent exposure that do not ‘age’ rapidly, and which are not degraded by therapy with oximes. Sensitive methods for the detection of these adducts have been developed using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Adducts of all four nerve agents were detected in the blood of exposed guinea pigs being used in studies to improve medical countermeasures. The tyrosine adducts with soman and tabun were detected in guinea pigs receiving therapy 7 days following subcutaneous administration of five times the LD50 dose of the respective nerve agent. VX also forms a tyrosine adduct in human blood in vitro but only at high concentrations.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams TK, Capacio BR, Smith JR, Whalley CED, Korte WD (2004) The application of the fluoride reactivation process to the detection of sarin and soman nerve agent exposures in biological samples. Drug Chem Toxicol 27:77–91
Bechtold WE, Willis JK, Sun JD, Griffith WC, Reddy TV (1992) Biological markers of exposure to benzene: S-phenylcysteine in albumin. Carcinogenesis 13:1217–1220
Black RM, Noort D (2005) Methods for the retrospective detection of exposure toxic scheduled chemicals. Part A: analysis of free metabolites. In: Mesilaakso M (ed) Chemical weapons convention chemicals analysis (Sample collection, preparation and analytical methods). Wiley, Chichester, pp 403–431
Black RM, Clarke RJ, Read RW, Reid MTJ (1994) Application of gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry to the analysis of chemical warfare samples, found to contain residues of the nerve agent sarin, sulphur mustard and their degradation products. J Chromatogr A 662:301–321
Black RM, Harrison JM, Read RW (1999) The interaction of sarin and soman with plasma proteins: the identification of a novel phosphonylation site. Arch Toxicol 73:123–126
Briseno-Roa L, Hill J, Notman S, Sellars D, Smith AP, Timperley CM, Wetherell J, Williams NH, Williams GR, Fersht AR, Griffiths AD (2006) Analogues with fluorescent leaving groups for screening and selection of enzymes that efficiently hydrolyze organophosphorus nerve agents. J Med Chem 49:246–255
Bryant PJR, Ford-Moore AH, Perry BJ, Wardrop AWH, Watkins TF (1960) The preparation and physical properties of isopropyl methylphosphonofluoridate (sarin). J Chem Soc 1553–1555
Degenhardt CEAM, Pleijsier K, Van der Schans MJ, Langenberg JP, Preston KE, Solano MI, Maggio VL, Barr JR (2004) Improvements of the fluoride reactivation method for the verification of nerve agent exposure. J Anal Toxicol 28:364–371
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Anders V, Featherstone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorometric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95
Fidder A, Noort D, Hulst AG, De Ruiter R, Van der Schans MJ, Benschop HP, Langenberg JP (2002) Retrospective detection of exposure to organophosphorus anti-cholinesterases: mass spectrometric analysis of phosphylated human butyrylcholinesterase. Chem Res Toxicol 15:582–590
Jakubowski EM, Heykamp LS, Durst HD, Thomson SA (2001) Preliminary studies in the formation of ethyl methylphosphonofluoridate from rat and human serum exposed to VX and treated with fluoride ion. Anal Lett 34:727–737
Jakubowski EM, McGuire JM, Evans RA, Edwards JL, Hulet SW, Benton BJ, Forster JS, Burnett DC, Muse WT, Matson K, Crouse CL, Mioduszewski RJ, Thomson SA (2004) Quantitation of fluoride ion released sarin in red blood cell samples by gas chromatography-chemical ionization mass spectrometry using isotope dilution and large-volume injection. J Anal Toxicol 28:357–363
Kitas EA, Perich JW, Tregear GW, Johns RB (1990) Synthesis of phosphotyrosine-containing peptides. 3. Synthesis of H-Pro-Tyr(P)-Val-OH via dimethylphosphate protection and the use of improved deprotection procedures. J Org Chem 55:4181–4187
Means GE, Wu HL (1979) The reactive tyrosine residue of human serum albumin: characterization of its reaction with diisopropylfluorophosphate. Arch Biochem Biophys 194:526–530
Murachi T (1963) A general reaction of diisopropylphosphofluoridate with proteins without direct effect on enzymic activities. Biochim Biophys Acta 71:239–241
Nagao M, Takatori T, Matsuda Y, Nakajima M, Iwase H, Iwadate K (1997) Definitive evidence for the acute sarin poisoning diagnosis in the Tokyo subway. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 144:198–203
Nigg HN, Knaak JB (2000) Blood cholinesterases as biomarkers of organophosphorus pesticide exposure. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 163:29–112
Noort D, Black RM (2005) Methods for the retrospective detection of exposure toxic scheduled chemicals. Part B: mass spectrometric and immunochemical analysis of covalent adducts to proteins and DNA. In: Mesilaakso M (ed) Chemical weapons convention chemicals analysis (sample collection, preparation and analytical methods). Wiley, Chichester, pp 433–451
Noort D, Hulst AG, Platenburg DHJM, Polhuijs M, Benschop HP (1998) Quantitative analysis of O-isopropyl methylphosphonic acid in serum samples of Japanese citizens allegedly exposed to sarin: estimation of internal dosage. Arch Toxicol 72:671–675
Noort D, Benschop HP, Black RM (2002) Biomonitoring of exposure to chemical warfare agents: a review. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 184:116–126
Noort D, Fidder A, Hulst AG, Woolfit AR, Ash D, Barr JR (2004) Retrospective detection of exposure to sulfur mustard: improvements on an assay for liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis of albumin/sulfur mustard adducts. J Anal Toxicol 28:333–338
Peeples ES, Schopfer LM, Duysen EG, Spaulding R, Voelker T, Thompson CM, Lockridge O (2005) Albumin, a new biomarker of organophosphorus toxicant exposure, identified by mass spectrometry. Toxicol Sci 83:303–312
Polhuijs M, Langenberg JP, Benschop HP (1997) New method for retrospective detection of exposure to organophosphorus anticholinesterases: application to alleged victims of Japanese terrorists. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 146:156–161
Riches J, Morton I, Read RW, Black RM (2005) The trace analysis of alkyl alkylphosphonic acids in urine using gas chromatography-ion trap negative ion tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 816:251–258
Schopfer LM, Champion MC, Tamblyn N, Thompson CM, Lockridge O (2005) Characteristic mass spectral fragments of the organophosphorus agent FP-biotin and FP-biotinylated peptides from trypsin and bovine albumin (Tyr410). Anal Biochem 345:122–132
Tsuchihashi H, Katagi M, Nishikawa M, Tatsuno M (1998) Identification of metabolites of nerve agent VX in serum collected from a victim. J Anal Toxicol 22:383–388
United Nations (1984) Report of the specialists appointed by the Secretary-General to investigate allegations by the Islamic Republic of Iran concerning the use of chemical weapons. Report number S/16433
Van Helden HPM, Trap HC, Oostdijk JP, Kuijpers WC, Langenberg JP, Benschop HP (2003) Long-term, low-level exposure of guinea pigs and marmosets to sarin vapor in air: lowest observable effect level. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 189:170–179
Worek F, Thiermann H, Szinicz L, Eyer P (2004) Kinetic analysis of interactions between human acetylcholinesterase, structurally different organophosphorus compounds and oximes. Biochem Pharmacol 68:2237–2248
Acknowledgments
Biomedical Sciences Department, Dstl, Porton Down for guinea pig samples and to N. Bailey and E. Gosden, Dstl, Porton Down for cholinesterase determinations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Williams, N.H., Harrison, J.M., Read, R.W. et al. Phosphylated tyrosine in albumin as a biomarker of exposure to organophosphorus nerve agents. Arch Toxicol 81, 627–639 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-007-0191-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-007-0191-8