Abstract
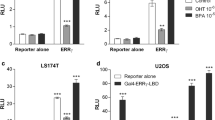
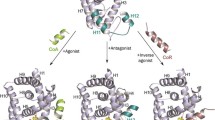
As a potential endocrine disruptor, tris(2,3-dibromopropyl) isocyanurate (TBC) has previously been demonstrated to reduce expression of estrogen-dependent vitellogenin (vtg) mRNA in adult zebrafish. However, the underlying toxicity pathways and molecular mechanisms involved in TBC-induced endocrine disruption remain elusive. In the current study, E-Screen and MVLN assays were employed to explore the potential anti-estrogenic effects of TBC via the estrogen receptor α (ERα)-mediated signaling pathway. Within a dose range between 1 × 10− 9 and 1 × 10− 7 M, TBC significantly inhibited 17β-estradiol (E2)-induced cell proliferation in a breast cancer cell line. The luciferase activity induced by E2 was also significantly inhibited by TBC in a dose-dependent manner. Moreover, neither TBC nor E2 affected proliferation of the ERα-negative breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231. These experimental results confirmed that TBC has anti-estrogenic effects by affecting the ERα-mediated signaling pathway. By comparing TBC with known antagonists of ERα, we found that TBC has similar molecular structure as certain co-activator binding inhibitors. Therefore, using molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations, TBC was further predicted to competitively occupy the surface site of ERα rather than the canonical E2-binding pocket of ERα, thus disrupt subsequent co-activator recruitment and transcription activation. Our findings elucidate the anti-estrogenic mechanism of TBC at the atomic level and highlight the biological importance of surface sites of nuclear receptors for a risk assessment of potential environmental pollutants.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anandakrishnan R, Aguilar B, Onufriev AV (2012) H++ 3.0: automating pK prediction and the preparation of biomolecular structures for atomistic molecular modeling and simulations. Nucleic Acids Res 40(W1):W537-W541
Belorusova AY, Eberhardt J, Potier N, Stote RH, Dejaegere A, Rochel N (2014) Structural insights into the molecular mechanism of vitamin D receptor activation by lithocholic acid involving a new mode of ligand recognition. J Med Chem 57(11):4710–4719
Bernardes A, Souza PC, Muniz JR, Ricci CG, Ayers SD, Parekh NM, Godoy AS, Trivella DB, Reinach P, Webb P (2013) Molecular mechanism of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α activation by WY14643: a new mode of ligand recognition and receptor stabilization. J Mol Biol 425(16):2878–2893
Cao H, Sun Y, Wang L, Zhao C, Fu J, Zhang A (2017a) Understanding the microscopic binding mechanism of hydroxylated and sulfated polybrominated diphenyl ethers with transthyretin by molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulations and binding free energy calculations. Mol BioSyst 13(4):736–749
Cao H, Wang F, Liang Y, Wang H, Zhang A, Song M (2017b) Experimental and computational insights on the recognition mechanism between the estrogen receptor α with bisphenol compounds. Arch Toxicol 91(12):3897–3912
Cuzzolin A, Sturlese M, Deganutti G, Salmaso V, Sabbadin D, Ciancetta A, Moro S (2016) Deciphering the complexity of ligand–protein recognition pathways using supervised molecular dynamics (SuMD) simulations. J Chem Inf Model 56(4):687–705
Darden T, York D, Pedersen L (1993) Particle mesh Ewald: An N⋅log (N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J Chem Phys 98:10089–10092
Estébanezperpiñá E, Arnold LA, Nguyen P, Rodrigues ED, Mar E, Bateman R, Pallai P, Shokat KM, Baxter JD, Guy RK (2007) A surface on the androgen receptor that allosterically regulates coactivator binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(41):16074–16079
Freyberger A, Schmuck G (2005) Screening for estrogenicity and anti-estrogenicity: a critical evaluation of an MVLN cell-based transactivation assay. Toxicol Lett 155(1):1–13
Hale RC, La Guardia MJ, Harvey E, Gaylor MO, Mainor TM (2006) Brominated flame retardant concentrations and trends in abiotic media. Chemosphere 64(2):181–186
Hamers T, Kamstra JH, Sonneveld E, Murk AJ, Kester MHA, Andersson PL, Legler J, Brouwer A (2006) In vitro profiling of the endocrine-disrupting potency of brominated flame retardants. Toxicol Sci 92(1):157–173
Han C, Fang S, Cao H, Lu Y, Ma Y, Wei D, Xie X, Liu X, Li X, Fei D (2013) Molecular interaction of PCB153 to human serum albumin: insights from spectroscopic and molecular modeling studies. J Hazard Mater 248:313–321
Hou T, Wang J, Li Y, Wang W (2010) Assessing the performance of the MM/PBSA and MM/GBSA methods. 1. The accuracy of binding free energy calculations based on molecular dynamics simulations. J Chem Inf Model 51(1):69–82
Huang H, Du G, Zhang W, Hu J, Wu D, Song L, Xia Y, Wang X (2014) The in vitro estrogenic activities of triclosan and triclocarban. J Appl Toxicol 34(9):1060–1067
Jain AN (2007) Surflex-Dock 2.1: robust performance from ligand energetic modeling, ring flexibility, and knowledge-based search. J Comput Aided Mol Des 21(5):281–306
Jorgensen WL, Chandrasekhar J, Madura JD, Impey RW, Klein ML (1983) Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J Chem Phys 79:926–935
Legler J, Brouwer A (2003) Are brominated flame retardants endocrine disruptors? Environ Int 29(6):879–885
Li J, Liang Y, Zhang X et al (2011) Impaired gas bladder inflation in zebrafish exposed to a novel heterocyclic brominated flame retardant tris(2,3-dibromopropyl) isocyanurate. Environ Sci Technol 45(22):9750–9757
Li H, Leung K-S, Ballester PJ, Wong M-H (2014) istar: A web platform for large-scale protein-ligand docking. Plos One 9(1):e85678
Li J, Zhang X, Bao J et al (2015) Toxicity of new emerging pollutant tris-(2,3-dibromopropyl) isocyanurate on BALB/c mice. J Appl Toxicol 35(4):375–382
Li X, Pan Y, Wang C, Chen M, Liu Y, Li J, Zhou Z, Xu J, Liang Y, Song M (2016) Effects of tris(2,3-dibromopropyl) isocyanurate on steroidogenesis in H295R cells. Environ Earth Sci 75(20):1339
Liu Q, Sun Y, Qu G, Long Y, Zhao X, Zhang A, Zhou Q, Hu L, Jiang G (2017) Structure-dependent hematological effects of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances on activation of plasma kallikrein–kinin system cascade. Environ Sci Technol 51(17):10173–10183
Maier JA, Martinez C, Kasavajhala K, Wickstrom L, Hauser KE, Simmerling C (2015) ff14SB: improving the accuracy of protein side chain and backbone parameters from ff99SB. J Chem Theory Comput 11(8):3696–3713
Miller IIIBR., McGee TD Jr, Swails JM, Homeyer N, Gohlke H, Roitberg AE (2012) MMPBSA. py: an efficient program for end-state free energy calculations. J Chem Theory Comput 8(9):3314–3321
Minerva MF, Bigsby RM (2008) Hydroxylated metabolites of the polybrominated diphenyl ether mixture DE-71 are weak estrogen receptor-α ligands. Environ Health Perspect 116(10):1315–1321
Morris GM, Huey R, Lindstrom W, Sanner MF, Belew RK, Goodsell DS, Olson AJ (2009) AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J Comput Chem 30(16):2785–2791
Onufriev A, Bashford D, Case DA (2004) Exploring protein native states and large-scale conformational changes with a modified generalized born model. Proteins Struct Funct Bioinf 55(2):383–394
Parent AA, Gunther JR, Katzenellenbogen JA (2008) Blocking estrogen signaling after the hormone: pyrimidine-core inhibitors of estrogen receptor-coactivator binding. J Med Chem 51(20):6512–6530
Pendse SN, Maertens A, Rosenberg M, Roy D, Fasani RA, Vantangoli MM, Madnick SJ, Boekelheide K, Fornace AJ, Odwin SA (2017) Information-dependent enrichment analysis reveals time-dependent transcriptional regulation of the estrogen pathway of toxicity. Arch Toxicol 91(4):1749–1762
Qu GB, Shi JB, Li ZN, Ruan T, Fu JJ, Wang P, Wang T, Jiang GB (2011) Detection of tris-(2, 3-dibromopropyl) isocyanurate as a neuronal toxicant in environmental samples using neuronal toxicity-directed analysis. Sci China Chem 54(10):1651–1658
Reistad T, Fonnum F, Mariussen E (2006) Neurotoxicity of the pentabrominated diphenyl ether mixture, DE-71, and hexabromocyclododecane (HBCD) in rat cerebellar granule cells in vitro. Arch Toxicol 80(11):785–796
Ren XM, Zhang YF, Guo LH, Qin ZF, Lv QY, Zhang LY (2015) Structure-activity relations in binding of perfluoroalkyl compounds to human thyroid hormone T3 receptor. Arch Toxicol 89(2):233–242
Roe DR, Cheatham TE III (2013) Ptraj and cpptraj: software for processing and analysis of molecular dynamics trajectory data. J Chem Theory Comput 9(7):3084–3095
Romkes M, Piskorska-Pliszczynska J, Safe S (1987) Effects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin on hepatic and uterine estrogen receptor levels in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 87(2):306–314
Ruan T, Wang Y, Wang C, Wang P, Fu J, Yin Y, Qu G, Wang T, Jiang G (2009) Identification and evaluation of a novel heterocyclic brominated flame retardant tris(2,3-dibromopropyl) isocyanurate in environmental matrices near a manufacturing plant in southern China. Environ Sci Technol 43(9):3080–3086
Ryckaert J-P, Ciccotti G, Berendsen HJ (1977) Numerical integration of the cartesian equations of motion of a system with constraints: molecular dynamics of n-alkanes. J Comput Phys 23(3):327–341
Scheepstra M, Leysen S, Almen GCV, Miller JR, Piesvaux J, Kutilek V, Eenennaam HV, Zhang H, Barr K, Nagpal S (2015) Identification of an allosteric binding site for RORγt inhibition. Nat Commun 6(5):8833
Schultz DJ, Wickramasinghe NS, Ivanova MM, Isaacs SM, Dougherty SM, Imbertfernandez Y, Cunningham AR, Chen C, Klinge CM (2010) Anacardic acid inhibits estrogen receptor alpha-DNA binding and reduces target gene transcription and breast cancer cell proliferation. Mol Cancer Ther 9(3):594–605
Shao J, Tanner SW, Thompson N, CheathamTE (2007) Clustering molecular dynamics trajectories: 1. characterizing the performance of different clustering algorithms. J Chem Theory Comput 3(6):2312–2334
Sheng N, Li J, Liu H, Zhang A, Dai J (2016) Interaction of perfluoroalkyl acids with human liver fatty acid-binding protein. Arch Toxicol 90(1):217–227
Shiau AK, Barstad D, Loria PM, Cheng L, Kushner PJ, Agard DA, Greene GL (1998) The structural basis of estrogen receptor/coactivator recognition and the antagonism of this interaction by tamoxifen. Cell 95(7):927–937
Song M, Liang D, Liang Y, Chen M, Wang F, Wang H, Jiang G (2014) Assessing developmental toxicity and estrogenic activity of halogenated bisphenol A on zebrafish (Danio rerio). Chemosphere 112(1):275–281
Soto AM, Sonnenschein C, Chung KL, Fernandez MF, Olea N, Serrano FO (1995) The E-SCREEN assay as a tool to identify estrogens: an update on estrogenic environmental pollutants. Enviro Health Perspect 103(Suppl 7):113–122
Souza PC, Puhl AC, Martínez L, Aparício R, Nascimento AS, Figueira AC, Nguyen P, Webb P, Skaf MS, Polikarpov I (2014) Identification of a new hormone-binding site on the surface of thyroid hormone receptor. Mol Endocrinol 28(4):534–545
Trott O, Olson AJ (2010) AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J Comput Chem 31(2):455–461
Wang J, Wolf RM, Caldwell JW, Kollman PA, Case DA (2004) Development and testing of a general amber force field. J Comput Chem 25(9):1157–1174
Wang Y, Chirgadze NY, Briggs SL, Khan S, Jensen EV, Burris TP (2006) A second binding site for hydroxytamoxifen within the coactivator-binding groove of estrogen receptor β. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(26):9908–9911
Wang C, Wang T, Liu W, Ruan T, Zhou Q, Liu J, Zhang A, Zhao B, Jiang G (2012) The in vitro estrogenic activities of polyfluorinated iodine alkanes. Enviro Health Perspect 120(1):119–125
Wang T, Han S, Ruan T, Wang Y, Feng J, Jiang G (2013) Spatial distribution and inter-year variation of hexabromocyclododecane (HBCD) and tris-(2,3-dibromopropyl) isocyanurate (TBC) in farm soils at a peri-urban region. Chemosphere 90(2):182–187
Wang L, Zhao Q, Zhao Y, Lou Y, Zheng M, Yu Y, Zhang M (2016) Determination of heterocyclic brominated flame retardants tris-(2, 3-dibromopropyl) isocyanurate and hexabromocyclododecane in sediment from Jiaozhou Bay wetland. Mar Pollut Bull 2016 113(1):509–512
Wärnmark A, Treuter E, Gustafsson JA, Hubbard RE, Brzozowski AM, Pike AC (2002) Interaction of transcriptional intermediary factor 2 nuclear receptor box peptides with the coactivator binding site of estrogen receptor alpha. J Biol Chem 277(24):21862–21868
Weiser J, Shenkin PS, Still WC (1999) Approximate atomic surfaces from linear combinations of pairwise overlaps (LCPO). J Comput Chem 20(2):217–230
Xu J, Li Q (2003) Review of the in vivo functions of the p160 steroid receptor coactivator family. Mol Endocrinol 17(9):1681–1692
Yang Y, Lv QY, Guo LH, Wan B, Ren XM, Shi YL, Cai YQ (2017) Identification of protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2 as a new target of perfluoroalkyl acids in HepG2 cells. Arch Toxicol 91(4):1697–1707
Ye L, Hu Z, Wang H, Zhu H, Dong Z, Jiang W, Zhao H, Li N, Mi W, Wang W, Hu X (2015) Tris-(2,3-Dibromopropyl) isocyanurate, a new emerging pollutant, impairs cognition and provokes depression-like behaviors in adult rats. Plos One 10(10):e0140281
Zhang X, Li J, Chen MJ, Wu L, Zhang C, Zhang J, Zhou QF, Liang Y (2011) Toxicity of the brominated flame retardant tris-(2,3-dibromopropyl) isocyanurate in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Chin Sci Bull 56(15):1548–1555
Zhu N, Li A, Wang T, Wang P, Qu G, Ruan T, Fu J, Yuan B, Zeng L (2012) Tris(2,3-dibromopropyl) isocyanurate, hexabromocyclododecanes, and polybrominated diphenyl ethers in mollusks from Chinese Bohai Sea. Environ Sci Technol 46(13):7174–7181
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDB14030501), the National Nature Science Foundation of China (21277062, 21477049) and the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (2017CFB368).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, H., Li, X., Zhang, W. et al. Anti-estrogenic activity of tris(2,3-dibromopropyl) isocyanurate through disruption of co-activator recruitment: experimental and computational studies. Arch Toxicol 92, 1471–1482 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-018-2159-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-018-2159-2