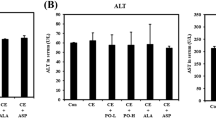
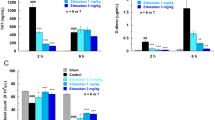
Abstract
Celecoxib, a selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, produces thrombotic events in patients predisposed to cardiovascular risk factors. One theory reported an increase in endothelial expression of tissue factor (TF) as a predisposing factor. This work explored the effect of evening primrose oil (EPO), a source of prostaglandin E1, and forskolin (a cyclic adenosine monophosphate stimulator) against the prothrombotic effect of celecoxib in mice. Lipopolysaccharide mouse model of endotoxemia was used to induce an upregulation of TF activity. Male mice received celecoxib (25 mg/kg), celecoxib plus EPO, or celecoxib plus forskolin for 4 weeks and then subjected to a prothrombotic challenge in the form of an intraperitoneal injection of lipopolysaccharide. Results showed an increase in plasma TF activity, endothelial TF expression, and thrombin–antithrombin (TAT) but lower antithrombin III (ATIII) level in mice that received celecoxib in comparison to those that received the vehicle. Adding EPO or forskolin to celecoxib regimen significantly decreased the prothrombotic effect of celecoxib. A positive correlation (r = 0.8501) was found between TF activity and TAT. Co-administration of EPO or forskolin decreased the activity of TF and mitigated the prothrombotic effect of celecoxib. Therefore, these combinations may have the utility to abrogate the prothrombotic adverse effect of celecoxib in clinical setting.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AC:
-
Adenylyl cyclase
- cAMP:
-
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate
- ATIII:
-
Antithrombin III
- CMC:
-
Carboxymethyl cellulose
- COX-2:
-
Cyclooxygenase-2
- DMSO:
-
Dimethylsulfoxide
- EPO:
-
Evening primrose oil
- FSK:
-
Forskolin
- GLA:
-
Gamma linolenic acid
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- PGE1:
-
Prostaglandin E1
- TAT:
-
Thrombin–antithrombin
- TF:
-
Tissue factor
References
Archipoff G, Beretz A, Bartha K, Brisson C, Salle C, Froget-Léon C, Klein-Soyer C, Cazenave JP (1993) Role of cyclic AMP in promoting the thromboresistance of human endothelial cells by enhancing thrombomodulin and decreasing tissue factor activities. Br J Pharmacol 109(1):18–28
Blatt PM, White GC, Goldsmith JC, Roberts HR (1978) Antithrombin-III transfusion in disseminated intravascular coagulation. Lancet 1:1212
Bick RL, Arun B, Frenkel EP (1999) Disseminated intravascular coagulation clinical and pathophysiological mechanisms and manifestations. Hemostasis 29(2–3):111–134
Bick RL, Bick MD, Fekete LF (1980) Antithrombin III patterns in disseminated intravascular coagulation. Am J Clin Pathol 73:577–583
Brzeski M, Madhok R, Capell HA (1991) Evening primrose oil in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and side-effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Br J Rheumatol 30(5):370–372
Butenas S, Mann KG (2004) Active tissue factor in blood? Nat Med 10(11):1155–1156
Camici GG, Steffel J, Akhmedov A, Schafer N, Baldinger J, Schulz U, Shojaati K, Matter CM, Yang Z, Lüscher TF, Tanner FC (2006) Dimethyl sulfoxide inhibits tissue factor expression, thrombus formation, and vascular smooth muscle cell activation a potential treatment strategy for drug-eluting stents. Circulation 114(14):1512–1521
Catella-Lawson F, Reilly MP, Kapoor SC, Cucchiara AJ, DeMarco S, Tournier B, Vyas SN, FitzGerald GA (2001) Cyclooxygenase inhibitors and the antiplatelet effects of aspirin. N Engl J Med 345(25):1809–1817
Cheng Y, Wang M, Yu Y, Lawson J, Funk CD, FitzGerald GA (2006) Cyclooxygenases, microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1, and cardiovascular function. J Clin Invest 116(5):1391–1399
Chu AJ (2006) Tissue factor upregulation drives a thrombosis–inflammation circuit in relation to cardiovascular complications. Cell Biochem Funct 24(2):173–192
Crutchley DJ, Hirsh MJ (1991) The stable prostacyclin analog, iloprost, and prostaglandin E1 inhibit monocyte procoagulant activity in vitro. Blood 78(2):382–386
Dutta-Roy AK, Kahn NN, Sinha AK (1989) Prostaglandin E1: the endogenous physiological regulator of platelet mediated blood coagulation. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 35(4):189–195
El-Sayed RM, Moustafa YM, El-Azab MF (2014) Evening primrose oil and celecoxib inhibited pathological angiogenesis, inflammation, and oxidative stress in adjuvant-induced arthritis: novel role of angiopoietin-1. Inflammopharmacology 22(5):305–317
Fink MP, Heard SO (1990) Laboratory models of sepsis and septic shock. J Surg Res 49(2):186–196
FitzGerald GA, Patrono C (2001) The coxibs, selective inhibitors of cyclooxygenase-2. N Engl J Med 345(6):433–442
FitzGerald GA (2004) Coxibs and cardiovascular disease. N Engl J Med 351(17):1709–1711
Ghosh M, Wang H, Ai Y, Romeo E, Luyendyk JP, Peters JM, Mackman N, Dey SK, Hla T (2007) COX-2 suppresses tissue factor expression via endocannabinoid-directed PPARδ activation. J Exp Med 204(9):2053–2061
Haak HL, Stolk JC, Gratama JW et al (1982) Use of antithrombin concentrate in stable diffuse intravascular coagulation. A case report. Acta Haematol 68:28–33
Hayashida N, Chihara S, Tayama E, Takaseya T, Enomoto N, Kawara T, Aoyagi S (2001) Antiinflammatory effects of colforsin daropate hydrochloride, a novel water-soluble forskolin derivative. Ann Thorac Surg 71(6):1931–1938
Hrachovinová I, Cambien B, Hafezi-Moghadam A, Kappelmayer J, Camphausen RT, Widom A, Xia L, Kazazian HH, Schaub RG, McEver RP, Wagner DD (2003) Interaction of P-selectin and PSGL-1 generates microparticles that correct hemostasis in a mouse model of hemophilia A. Nat Med 9(8):1020–1025
Hudson BJ (1984) Evening primrose (Oenothera spp.) oil and seed. J Am Oil Chem Soc 61(3):540–543
Kaplan GB, Leite-Morris KA, Sethi RK, McClelland EG (1998) Regulation of G protein-mediated adenylyl cyclase in striatum and cortex of opiate-dependent and opiate withdrawing mice. Brain Res 788(1):104–110
Koyama K, Madoiwa S, Nunomiya S, Koinuma T, Wada M, Sakata A, Ohmori T, Mimuro J, Sakata Y (2014) Combination of thrombin-antithrombin complex, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, and protein C activity for early identification of severe coagulopathy in initial phase of sepsis: a prospective observational study. Crit Care 18:R13
Kirchhofer D, Moran P, Bullens S, Peale F, Bunting S (2005) A monoclonal antibody that inhibits mouse tissue factor function. J Thromb Haemost 3(5):1098–1099
Léon C, Freund M, Ravanat C, Baurand A, Cazenave JP, Gachet C (2001) Key role of the P2Y1 receptor in tissue factor-induced thrombin-dependent acute thromboembolism studies in P2Y1-knockout mice and mice treated with a P2Y1 antagonist. Circulation 103(5):718–723
Lorente JA, García-Frade LJ, Landín L, de Pablo R, Torrado C, Renes E, Garcia-Avello A (1993) Time course of hemostatic abnormalities in sepsis and its relation to outcome. Chest 103:1536–1542
Mackman N, Sawdey MS, Keeton MR, Loskutoff DJ (1993) Murine tissue factor gene expression in vivo. Tissue and cell specificity and regulation by lipopolysaccharide. Am J Pathol 143(1):76–84
Mackman N (2004) Role of tissue factor in hemostasis, thrombosis, and vascular development. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 24(6):1015–1022
Manolopoulos VG, Samet MM, Lelkes PI (1995) Regulation of the adenylyl cyclase signaling system in various types of cultured endothelial cells. J Cell Biochem 57(4):590–598
Matsuo N, Osada K, Kodama T, Lim BO, Nakao A, Yamada K, Sugano M (1996) Effects of γ-linolenic acid and its positional isomer pinolenic acid on immune parameters of brown-Norway rats. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 55(4):223–229
McAdam BF, Catella-Lawson F, Mardini IA, Kapoor S, Lawson JA, FitzGerald GA (1999) Systemic biosynthesis of prostacyclin by cyclooxygenase (COX)-2: the human pharmacology of a selective inhibitor of COX-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96(1):272–277
Morrissey JH, Macik BG, Neuenschwander PF (1993) Quantitation of activated factor VII levels in plasma using a tissue factor mutant selectively deficient in promoting factor VII activation. Blood 81(3):734–744
Paillusson S, Tasselli M, Lebouvier T, Mahé MM, Chevalier J, Biraud M, Cario-Toumaniantz C, Neunlist M, Derkinderen P (2010) α-Synuclein expression is induced by depolarization and cyclic AMP in enteric neurons. J Neurochem 115(3):694–706
Palayoor ST, Molykutty J, Aryankalayil A, Makinde Y, Cerna D, Falduto MT, Magnuson SR, Coleman CN (2012) Gene expression profile of coronary artery cells treated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs reveals off-target effects. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 59(6):487–499
Pawlinski R, Pedersen B, Schabbauer G, Tencati M, Holscher T, Boisvert W, Andrade-Gordon P, Frank RD, Mackman N (2004) Role of tissue factor and protease-activated receptors in a mouse model of endotoxemia. Blood 103(4):1342–1347
Petersen LC, Nørby PL, Branner S, Sørensen BB, Elm T, Stennicke HR, Persson E, Bjørn SE (2005) Characterization of recombinant murine factor VIIa and recombinant murine tissue factor: a human–murine species compatibility study. Thromb Res 116(1):75–85
Rabausch K, Bretschneider E, Sarbia M, Meyer-Kirchrath J, Censarek P, Pape R, Fischer JW, Schrör K, Weber AA (2005) Regulation of thrombomodulin expression in human vascular smooth muscle cells by COX-2-derived prostaglandins. Circ Res 96(1):e1–e6
Saetre T, Lindgaard AK, Lyberg T (2000) Systemic activation of coagulation and fibrynolysis in a porcine model of serogroup A streptococcal shock. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 11:433–438
Saini SS, Gessell-Lee DL, Peterson JW (2003) The cox-2-specific inhibitor celecoxib inhibits adenylyl cyclase. Inflammation 27(2):79–88
Senanayake SN, Shahidi F (2004) Incorporation of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) into evening primrose (Oenothera biennis L.) oil via lipase-catalyzed transesterification. Food Chem 85(4):489–496
Solovey A, Kollander R, Shet A, Milbauer LC, Choong S, Panoskaltsis-Mortari A, Blazar BR, Kelm RJ, Hebbel RP (2004) Endothelial cell expression of tissue factor in sickle mice is augmented by hypoxia/reoxygenation and inhibited by lovastatin. Blood 104(3):840–846
Steffel J, Akhmedov A, Fähndrich C, Ruschitzka F, Lüscher TF, Tanner FC (2006) Differential effect of celecoxib on tissue factor expression in human endothelial and vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 349(2):597–603
Steffel J, Hermann M, Greutert H, Gay S, Lüscher TF, Ruschitzka F, Tanner FC (2005) Celecoxib decreases endothelial tissue factor expression through inhibition of c-Jun terminal NH2 kinase phosphorylation. Circulation 111(13):1685–1689
Taylor FB Jr, Chang A, Ruf W, Morrissey JH, Hinshaw L, Catlett R, Blick K, Edgington TS (1991) Lethal E. coli septic shock is prevented by blocking tissue factor with monoclonal antibody. Circ Shock 33(3):127–134
Unruh M, Grunow A, Gottstein C (2005) Systemic coagulation parameters in mice after treatment with vascular targeting agents. Thromb J 3(1):21
Walsh PN (1978) Different requirements for intrinsic factor-Xa forming activity and platelet factor 3 activity and their relationship to platelet aggregation and secretion. Br J Haematol 40(2):311–331
Wang G, Manly D, Kirchhofer D, Pawlinski R, Mackman N (2009a) Levels of microparticle tissue factor activity correlate with coagulation activation in endotoxemic mice. J Thromb Haemost 7(7):1092–1098
Wang L, Miller C, Swarthout RF, Rao M, Mackman N, Taubman MB (2009b) Vascular smooth muscle–derived tissue factor is critical for arterial thrombosis after ferric chloride–induced injury. Blood 113(3):705–713
Willis AL, Smith DL (1989) Dihomo-gamma-linolenic and gamma-linolenic acids in health and disease. In: Spiller GA, Scala J (eds) New protective roles for selected nutrients, current topics in nutrition and disease. Alan Liss, Inc., New York, pp 39–108
Zaitone SA, Moustafa YM, Mosaad SM, El-Orabi NF (2011) Effect of evening primrose oil and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on the cardiovascular risk of celecoxib in rats. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 58(1):72–79
Acknowledgements
Authors thank Amoun Pharmaceutical Company for the generous gift of celecoxib. Authors wish to acknowledge Dr. Daniel Kirchhofer for kindly providing tissue factor antibody 1H1 and Dr. Lars Petersen for the generous gift of mouse factor VIIa.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This work did not receive funding from any organization.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mosaad, S.M., Zaitone, S.A., Ahmed, A.A.M. et al. Evening primrose oil or forskolin ameliorates celecoxib-enhanced upregulation of tissue factor expression in mice subjected to lipopolysaccharide-induced endotoxemia. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 390, 483–492 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-017-1342-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-017-1342-y