Abstract
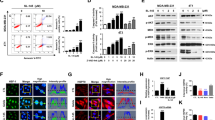
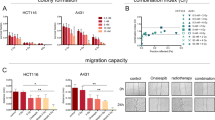
Heat shock protein 90 (HSP90) inhibitors are considered as new radiosensitizing agents. PU-H71, a novel HSP90 inhibitor, is under evaluation for the treatment of advanced cancer. It is however not known whether PU-H71 alters radiosensitivity of metastatic breast cancer. Hence, we here evaluated mechanisms of possible anti-tumoral and radiosensitizing effects of PU-H71 on breast carcinoma cells metastasized to vital organs such as the liver and brain. The effect of PU-H71 on proliferation of breast carcinoma cells was determined using 4T1 cells and its brain (4TBM), liver (4TLM), and heart (4THM) metastatic subsets as well as non-metastatic 67NR cells. Changes in radiation sensitivity were determined by clonogenic assays. Changes in client proteins and levels of angiogenic and inflammatory mediators from these cancer cell cultures and ex vivo cultures were detected. PU-H71 alone inhibited ERK1/2, p38, and Akt activation and reduced N-cadherin and HER2 which further documented the anti-tumoral effects of PU-H71. The combination of PU-H71 and radiotherapy induced cytotoxic effect than PU-H71 alone, and PU-H71 showed a radiosensitizing effect in vitro. On the other hand, PU-H71 and radiation co-treatment increased p38 phosphorylation which is one of the hallmarks of inflammatory response. Accordingly, IL-6 secretion was increased following PU-H71 and radiotherapy co-treatment ex vivo. Levels of angiogenic and inflammatory factors such as MIP-2, SDF-1, and VEGF were increased under in vitro conditions but not under ex vivo conditions. These results demonstrated for the first time that PU-H71 enhances therapeutic effects of radiotherapy especially in highly metastatic breast carcinoma but a possible increase in inflammatory response should also be considered.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HSP90:
-
Heat shock protein 90
- SDF-1:
-
Stromal-derived factor-1
- MIP-2:
-
Macrophage inflammatory protein-2
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin 6
- RT:
-
Radiotherapy
- 4THM:
-
4T1 heart metastasis
- 4TLM:
-
4T1 liver metastasis
- 4TBM:
-
4T1 brain metastasis
References
Adachi S et al (2010) HSP90 inhibitors induce desensitization of EGF receptor via p38 MAPK-mediated phosphorylation at Ser1046/1047 in human pancreatic cancer cells. Oncol Rep 23:1709–1714
Akmansu M, Unsal D, Bora H, Elbeg S (2005) Influence of locoregional radiation treatment on tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6 in the serum of patients with head and neck cancer. Cytokine 31:41–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2005.02.009
Ambati SR et al (2014) Pre-clinical efficacy of PU-H71, a novel HSP90 inhibitor, alone and in combination with bortezomib in Ewing sarcoma. Mol Oncol 8:323–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molonc.2013.12.005
Aslakson CJ, Miller FR (1992) Selective events in the metastatic process defined by analysis of the sequential dissemination of subpopulations of a mouse mammary tumor. Cancer res 52:1399–1405
Bao L, Haque A, Jackson K, Hazari S, Moroz K, Jetly R, Dash S (2011) Increased expression of P-glycoprotein is associated with doxorubicin chemoresistance in the metastatic 4T1 breast cancer model. Am J Pathol 178:838–852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2010.10.029
Barbero S et al (2003) Stromal cell-derived factor 1alpha stimulates human glioblastoma cell growth through the activation of both extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2 and Akt. Cancer Res 63:1969–1974
Bhagwat N et al (2014) Improved targeting of JAK2 leads to increased therapeutic efficacy in myeloproliferative neoplasms. Blood, 123:2075–2083. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2014-01-547760
Butler LM, Ferraldeschi R, Armstrong HK, Centenera MM, Workman P (2015) Maximizing the therapeutic potential of HSP90 inhibitors. Mol cancer res 13:1445–1451. https://doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-15-0234
Caldas-Lopes E et al (2009) Hsp90 inhibitor PU-H71, a multimodal inhibitor of malignancy, induces complete responses in triple-negative breast cancer models. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:8368–8373. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0903392106
Charafe-Jauffret E et al (2009) Breast cancer cell lines contain functional cancer stem cells with metastatic capacity and a distinct molecular signature. Cancer Res 69:1302–1313. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2741
Chin AR, Wang SE (2014) Cytokines driving breast cancer stemness. Mol Cell Endocrinol 382:598–602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2013.03.024
Erin N, Boyer PJ, Bonneau RH, Clawson GA, Welch DR (2004) Capsaicin-mediated denervation of sensory neurons promotes mammary tumor metastasis to lung and heart. Anticancer Res 24:1003–1009
Erin N, Kale S, Tanriover G, Koksoy S, Duymus O, Korcum AF (2013) Differential characteristics of heart, liver, and brain metastatic subsets of murine breast carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res Treat 139:677–689. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-013-2584-0
Erin N, Nizam E, Tanriover G, Koksoy S (2015a) Autocrine control of MIP-2 secretion from metastatic breast cancer cells is mediated by CXCR2: a mechanism for possible resistance to CXCR2 antagonists. Breast Cancer Res Treat 150:57–69. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-015-3297-3
Erin N, Podnos A, Tanriover G, Duymus O, Cote E, Khatri I, Gorczynski RM (2015b) Bidirectional effect of CD200 on breast cancer development and metastasis, with ultimate outcome determined by tumor aggressiveness and a cancer-induced inflammatory response. Oncogene 34:3860–3870. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.317
Erin N et al (2009) Altered gene expression in breast cancer liver metastases. Int J Cancer 124:1503–1516. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.24131
Erin N, Zhao W, Bylander J, Chase G, Clawson G (2006) Capsaicin-induced inactivation of sensory neurons promotes a more aggressive gene expression phenotype in breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 99:351–364. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-006-9219-7
Erin N, Bronson SK, Billingsley ML (2003) Calcium-dependent interaction of calcineurin with Bcl-2 in neuronal tissue. Neurosci. 117:541–555
Franken NA, Rodermond HM, Stap J, Haveman J, van Bree C (2006) Clonogenic assay of cells in vitro. Nat Protoc 1:2315–2319. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.339
Gandhi N et al (2013) Novel Hsp90 inhibitor NVP-AUY922 radiosensitizes prostate cancer cells. Cancer biol ther 14:347–356. https://doi.org/10.4161/cbt.23626
Gao X et al (2015) Anti-VEGF treatment improves neurological function and augments radiation response in NF2 schwannoma model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112:14676–14681. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1512570112
Giulino-Roth L et al (2017) Inhibition of Hsp90 suppresses PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling and has antitumor activity in Burkitt lymphoma. Mol Cancer Ther 16:1779–1790. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-16-0848
Goldstein RL et al (2015) Pharmacoproteomics identifies combinatorial therapy targets for diffuse large B cell lymphoma. J Clin Invest 125:4559–4571. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI80714
Guo A, Lu P, Lee J, Zhen C, Chiosis G, Wang YL (2017) HSP90 stabilizes B-cell receptor kinases in a multi-client interactome: PU-H71 induces CLL apoptosis in a cytoprotective microenvironment. Oncogene 36:3441–3449. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.494
Gupta J, Nebreda AR (2015) Roles of p38alpha mitogen-activated protein kinase in mouse models of inflammatory diseases and cancer. FEBS J 282:1841–1857. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.13250
Ha K, Fiskus W, Rao R, Balusu R, Venkannagari S, Nalabothula NR, Bhalla KN (2011) Hsp90 inhibitor-mediated disruption of chaperone association of ATR with hsp90 sensitizes cancer cells to DNA damage. Mol Cancer Ther 10:1194–1206. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0094
Hashida S et al (2015) Hsp90 inhibitor NVP-AUY922 enhances the radiation sensitivity of lung cancer cell lines with acquired resistance to EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Oncol Rep 33:1499–1504. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2015.3735
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D (2011) Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 61:69–90. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.20107
Kamal A, Thao L, Sensintaffar J, Zhang L, Boehm MF, Fritz LC, Burrows FJ (2003) A high-affinity conformation of Hsp90 confers tumour selectivity on Hsp90 inhibitors. Nature 425:407–410. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01913
Knupfer H, Preiss R (2007) Significance of interleukin-6 (IL-6) in breast cancer (review). Breast Cancer Res Treat 102:129–135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-006-9328-3
Kollmar O, Menger MD, Schilling MK (2006) Macrophage inflammatory protein-2 contributes to liver resection-induced acceleration of hepatic metastatic tumor growth. World J Gastroenterol 12:858–867
Kwon Y et al (2015) MicroRNA-26a/-26b-COX-2-MIP-2 loop regulates allergic inflammation and allergic inflammation-promoted enhanced tumorigenic and metastatic potential of cancer cells. J Biol Chem 290:14245–14266. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.645580
Lee J, Cacalano G, Camerato T, Toy K, Moore MW, Wood WI (1995) Chemokine binding and activities mediated by the mouse IL-8 receptor. J Immunol 155:2158–2164
Lee Y et al (2016) The purine scaffold Hsp90 inhibitor PU-H71 sensitizes cancer cells to heavy ion radiation by inhibiting DNA repair by homologous recombination and non-homologous end joining. Radiother Oncol 121:162–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2016.08.029
Li HK, Matsumoto Y, Furusawa Y, Kamada T (2016) PU-H71, a novel Hsp90 inhibitor, as a potential cancer-specific sensitizer to carbon-ion beam therapy. J Radiat Res 57:572–575. https://doi.org/10.1093/jrr/rrw054
Liu Y et al (2017) STK33 participates to HSP90-supported angiogenic program in hypoxic tumors by regulating HIF-1alpha/VEGF signaling pathway. Oncotarget 8:77474–77488. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.20535
Lushchak VI (2014) Dissection of the hormetic curve: analysis of components and mechanisms. Dose Response 12:466–479. https://doi.org/10.2203/dose-response.13-051.Lushchak
Mao AW, Jiang TH, Sun XJ, Peng J (2015) Application of chemokine receptor antagonist with stents reduces local inflammation and suppresses cancer growth. Tumour biology : the journal of the International Society for Oncodevelopmental Biology and Medicine 36:8637–8643. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3557-1
McMahon G (2000) VEGF receptor signaling in tumor angiogenesis. The oncologist 5(Suppl 1):3–10
Mimnaugh EG, Chavany C, Neckers L (1996) Polyubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of the p185c-erbB-2 receptor protein-tyrosine kinase induced by geldanamycin. The Journal of biological chemistry 271:22796–22801
Miyamoto Y et al (2001) Interleukin-6 inhibits radiation induced apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells. Anticancer research 21:2449–2456
Morimoto RI, Kline MP, Bimston DN, Cotto JJ (1997) The heat-shock response: regulation and function of heat-shock proteins and molecular chaperones. Essays Biochem 32:17–29
Moulick K et al (2011) Affinity-based proteomics reveal cancer-specific networks coordinated by Hsp90. Nature chemical biology 7:818–826. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.670
Nagaraju GP et al (2013) Antiangiogenic effects of ganetespib in colorectal cancer mediated through inhibition of HIF-1alpha and STAT-3. Angiogenesis 16:903–917. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-013-9364-7
Neckers L (2007) Heat shock protein 90: the cancer chaperone. J Biosci 32:517–530
Pathak S et al (2015) Radiation and SN38 treatments modulate the expression of microRNAs, cytokines and chemokines in colon cancer cells in a p53-directed manner. Oncotarget. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.5815
Provencio M, Sanchez A (2014) Therapeutic integration of new molecule-targeted therapies with radiotherapy in lung cancer. Translational lung cancer research 3:89–94. https://doi.org/10.3978/j.issn.2218-6751.2014.03.06
Qu Z, Wang S, Teng R, Yi X (2014) PU-H71 effectively induces degradation of IkappaB kinase beta in the presence of TNF-alpha. Mol Cell Biochem 386:135–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1852-y
Rae C, Mairs RJ (2017) Evaluation of the radiosensitizing potency of chemotherapeutic agents in prostate cancer cells. Int J Radiat Biol 93:194–203. https://doi.org/10.1080/09553002.2017.1231946
Rezaei M, Friedrich K, Wielockx B, Kuzmanov A, Kettelhake A, Labelle M, Schnittler H, Baretton G, Breier G (2012) Interplay between neural-cadherin and vascular endothelial-cadherin in breast cancer progression. Breast cancer res 14:R154. https://doi.org/10.1186/bcr3367
Seaton A, Maxwell PJ, Hill A, Gallagher R, Pettigrew J, Wilson RH, Waugh DJ (2009) Inhibition of constitutive and cxc-chemokine-induced NF-kappaB activity potentiates ansamycin-based HSP90-inhibitor cytotoxicity in castrate-resistant prostate cancer cells. Br j cancer 101:1620–1629. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6605356
Segawa T, Fujii Y, Tanaka A, Bando S, Okayasu R, Ohnishi K, Kubota N (2014) Radiosensitization of human lung cancer cells by the novel purine-scaffold Hsp90 inhibitor, PU-H71. Int j mol med 33:559–564. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2013.1594
Shen XY, Wang SH, Liang ML, Wang HB, Xiao L, Wang ZH (2008) The role and mechanism of CXCR4 and its ligand SDF-1 in the development of cervical cancer metastasis Ai zheng = Aizheng = Chinese journal of cancer 27:1044-1049
Singh JK, Simoes BM, Howell SJ, Farnie G, Clarke RB (2013) Recent advances reveal IL-8 signaling as a potential key to targeting breast cancer stem cells. Breast cancer res 15:210. https://doi.org/10.1186/bcr3436
Terwisscha van Scheltinga AG et al (2014) Visualising dual downregulation of insulin-like growth factor receptor-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor-A by heat shock protein 90 inhibition effect in triple negative breast cancer. Eur j cancer 50:2508–2516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2014.06.008
Valastyan S, Weinberg RA (2011) Tumor metastasis: molecular insights and evolving paradigms. Cell 147:275–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.09.024
Wagner M, Bjerkvig R, Wiig H, Melero-Martin JM, Lin RZ, Klagsbrun M, Dudley AC (2012) Inflamed tumor-associated adipose tissue is a depot for macrophages that stimulate tumor growth and angiogenesis. Angiogenesis 15:481–495. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-012-9276-y
Weigelt B, Peterse JL, van’t Veer LJ (2005) Breast cancer metastasis: markers and models. Nat Rev Cancer 5:591–602. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc1670
Wu CT, Chen MF, Chen WC, Hsieh CC (2013) The role of IL-6 in the radiation response of prostate cancer. Radiat oncol 8:159. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-717X-8-159
Xiang L et al (2014) Ganetespib blocks HIF-1 activity and inhibits tumor growth, vascularization, stem cell maintenance, invasion, and metastasis in orthotopic mouse models of triple-negative breast cancer. J mol med 92:151–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-013-1102-5
Xu C, Zhao H, Chen H, Yao Q (2015) CXCR4 in breast cancer: oncogenic role and therapeutic targeting. Drug des devel ther 9:4953–4964. https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S84932
Xu Y, Zhang C, Chen D, Zhao J, Shen Z, Wu Y, Zhu Y (2013) Effect of HSP90 inhibitor in pheochromocytoma PC12 cells: an experimental investigation. Tumour biology : the journal of the International Society for Oncodevelopmental Biology and Medicine 34:4065–4071. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-013-0996-4
Yoshida S et al (2011) Low-dose Hsp90 inhibitors tumor-selectively sensitize bladder cancer cells to chemoradiotherapy. Cell cycle 10:4291–4299. https://doi.org/10.4161/cc.10.24.18616
Zong H et al (2015) A hyperactive signalosome in acute myeloid leukemia drives addiction to a tumor-specific Hsp90 species. Cell Rep 13:2159–2173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2015.10.073
Zuehlke A, Johnson JL (2010) Hsp90 and co-chaperones twist the functions of diverse client proteins. Biopolymers 93:211–217. https://doi.org/10.1002/bip.21292
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Akdeniz University Research Unit, Grant No: 2014.03.0122.005.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ŞK conducted the experiments; ŞK and NE were involved in planning and analyzing the experiments as well as writing the manuscript; AK and ED are involved in planning and conducting of the radiotherapy experiments.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 541 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kale, Ş., Korcum, A.F., Dündar, E. et al. HSP90 inhibitor PU-H71 increases radiosensitivity of breast cancer cells metastasized to visceral organs and alters the levels of inflammatory mediators. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 393, 253–262 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-019-01725-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-019-01725-z