Abstract
Rationale
Low capacity of the central serotonergic system has been associated with impulsive behaviour. Both low platelet monoamine oxidase (MAO) activity and the short (S) allele of the serotonin transporter gene promoter region polymorphism (5-HTTLPR) are proposed to be markers of less efficient serotonergic functioning.
Objectives
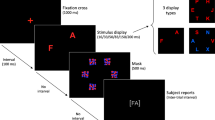
The effect of the two markers for serotonin system efficiency on performance in a visual comparison task (VCT) and self-reported impulsiveness (Barratt Impulsiveness Scale, BIS-11) were investigated in healthy adolescents participating in the Estonian Children Personality Behaviour and Health Study. Possible confounding effect of general cognitive abilities on the performance in VCT was controlled for.
Results
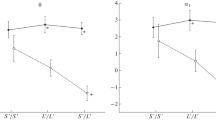
Low platelet MAO activity and carrying of the S allele of 5-HTTLPR were both associated with higher error-rate and more impulsive performance in VCT. Platelet MAO activity and 5-HTTLPR S allele had a significant interactive effect on self-reported impulsivity (BIS-11). The effect of platelet MAO activity on both self-reported and performance impulsivity was significant only in the S allele carriers. The effect of 5-HTTLPR S allele on impulsive performance remained significant after controlling for general cognitive abilities.
Conclusions
The two markers of lower serotonergic capacity, 5-HTTLPR S allele and low platelet MAO activity, have a similar and partly synergistic influence on self-reported as well as performance measures of impulsivity.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
af Klinteberg B, Levander SE, Oreland L, Asberg M, Schalling D (1987) Neuropsychological correlates of platelet monoamine oxidase (MAO) activity in female and male subjects. Biol Psychol 24:237–252
af Klinteberg B, Oreland L, Hallman J, Wirsen A, Levander SE, Schalling D (1990) Exploring the connections between platelet monoamine oxidase activity and behaviour: relationships with performance in neuropsychological tasks. Neuropsychobiology 23:188–196
Amador-Campus J, Kirchner-Nebot T (2001) Childrens embedded figures test and matching familiar figures test-20: factorial structure for boys and girls from 6 to 11 years old. Percept Mot Skills 93:709–712
Baca-Garcia E, Salgadoa BR, Segala HD, Lorenzo CV, Acosta MN, Romeroa MA, Hernandez MD, Ruiza JS, Piqueras JF, de Leonc J (2005) A pilot genetic study of the continuum between compulsivity and impulsivity in females: The serotonin transporter promoter polymorphism. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 29:713–717
Barratt ES (1993) Impulsivity: integrating cognitive, behavioral, biological and environmental data. In: McCown WB, Johnson JL, Shure MB (eds) The impulsive client: theory, research and treatment. American Psychological Association, Washington, DC, pp 39–56
Bernfeld GA, Peters RV (1986) Social reasoning and social behaviour reflective and impulsive children. J Clin Child Psychol 15:221–227
Botvinick M, Nystrom LE, Fissell K, Carter CS, Cohen JD (1999) Conflict monitoring versus selection-for-action in anterior cingulate cortex. Nature 402:179–181
Brannigan GG, Ass T, Margolis H (1980) Impulsivity-relfectivity and children’s intellectual performances. J Pers Assess 44:41–43
Brázdil M, Roman R, Daniel P, Rektor I (2005) Intracerebral error-related negativity in a simple Go/No-go task. J Psychophysiol 19:244–255
Brotman MA, Schmajuk M, Rich BA, Dickstein DP, Guyer AE, Costello EJ, Egger HL, Angold A, Pine DS, Leibenluft E (2006) Prevalence, clinical correlates, and longitudinal course of severe mood dysregulation in children. Biol Psychiatry 60:991–997
Brown GI, Ebert M, Goyer PF, Jimerson DC, Klwin WJ, Bunney WE, Goodwin FK (1982) Aggression, suicide, and serotonin: relationships to CSF amine metabolites. Am J Psychiatryyiatry 139:741–746
Caspi A, Sugden K, Moffitt TE, Taylor A, Craig IW, Harrington H, McClay J, Mill J, Martin J, Braithwaite A, Poulton R (2003) Influence of life stress on depression: moderation by a polymorphism in the 5-HTT. Science 301:386–389
Cherek DR, Lane SD (1999) Effects of d,l-fenfluramine on aggressive and impulsive responding in adult males with a history of conduct disorder. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 146:473–481
Clark L, Roiser JP, Cools R, Rubinsztein DC, Sahakian BJ, Robbins TW (2005) Stop signal response inhibition is not modulated by tryptophan depletion or the serotonin transporter polymorphism in healthy volunteers: implications for the 5-HT theory of impulsivity. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 182:570–578
Costa PT, McCrae RR (1989) The NEO-PI/NEO-FFI manual supplement. Psychological Assessment Resources, Odessa, FL
Dickman SJ (1990) Functional and dysfunctional impulsivity: personality and cognitive correlates. J Pers Soc Psychol 58:95–102
Dickman J (1993) Impulsivity and information processing. In: McCown WB, Johnson JL, Shure MB (eds) The impulsive client: theory, research and treatment. American Psychological Association, Washington, DC, pp 39–56
Dickman S, Meyer DE (1988) Impulsivity and speed–accuracy tradeoffs in information processing. J Pers Soc Psychol 54:274–290
Ebstein RP (2006) The molecular genetic architecture of human personality: beyond self-report questionnaires. Mol Psychiatry 11:427–445
Evenden JL (1999) Varieties of impulsivity. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 146:348–361
Fairbanks LA, Melega WP, Jorgensen MJ, Kaplan KR, McGuire MT (2001) Social impulsivity inversely associated with CSF 5-HIAA and fluoxetine exposure in vervet monkeys. Neuropsychopharmacology 24:370–378
Fallgatter AJ, Jatzke S, Bartsch AJ, Hamelbeck B, Lesch KP (1999) Serotonin transporter promoter polymorphism influences topography of inhibitory motor control. Int J Neuropsychopharmacology 2:115–120
Frankle WG, Lombardo I, New AS, Goodman M, Talbot PS, Huang YH, Hwang DR, Slifstein M, Curry S, Abi-Dargham A, Laruelle M, Siever LJ (2005) Brain serotonin transporter distribution in subjects with impulsive aggressivity: a positron emission study with [11c]mcn 5652. Am J Psychiatryyiatry 5:915–923
Galvan A, Hare TA, Parra CE, Penn J, Voss H, Glover G, Casey BJ (2006) Earlier development of the accumbens relative to orbitofrontal cortex might underlie risk-taking behavior in adolescents. J Neurosci 26:6885–6892
Gerra G, Garofano L, Santoro G, Bosari S, Pellegrini C, Zaimovic A, Moi G, Bussandri M, Moi A, Brambilla F, Donnini C (2004) Association between low-activity serotonin transporter genotype and heroin dependence: behavioral and personality correlates. Am J Med Genet 126B:37–42
Hallikainen T, Saito T, Lachman HM, Volavka J, Pojhanen T, Ryynänen OP, Kauhanen J, Syvälahti E, Hietala J, Tiihonen J (1999) Association between low activity serotonin transporter promoter genotype and early onset alcoholism with habitual impulsive violent behavior. Mol Psychiatry 4:385–388
Hallman J, Oreland L, Edman G, Schalling D (1987) Thrombocyte monoamine oxidase activity and personality traits in women with severe premenstrual syndrome. Acta Psychiatr Scand 76:225–234
Harrison BJ, Olver JS, Norman TR, Nathan PJ (2002) Brain monoamines and early visual information-processing speed. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 5:295–300
Harro M, Eensoo D, Kiive E, Merenäkk L, Alep J, Oreland L, Harro J (2001) Platelet monoamine oxidase in healthy 9- and 15-years old children: the effect of gender, smoking and puberty. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 25:1497–1511
Harro J, Fischer K, Vansteelandt S, Harro M (2004) Both low and high activity of platelet monoamine oxidase increase the probability of becoming a smoker. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 14:65–69
Hu XZ, Lipsky RH, Zhu G, Akhtar LA, Taubman J, Greenberg BD, Xu K, Arnold PD, Richter MA, Kennedy JL, Murphy DL, Goldman D (2006) Serotonin transporter promoter gain-of-function genotypes are linked to obsessive-compulsive disorder. Am J Hum Genet 78:815–826
Jensen AR (1998) The g factor. Praeger, Westport, CT
Kagan J, Rosman B, Day D, Albert J, Phillips W (1964) Information processing in the child: Significance of analytic and reflective attitudes. Psychol Monogr, 78 (1, Whole no. 578)
Kiive E, Merenäkk L, Harro M, Harro J (2005) Changes in platelet monoamine oxidase activity, cholesterol levels and hyperactive behaviour in adolescents over a period of three years. Neurosci Lett 384:310–315
Lesch KP (2005) Alcohol dependence and gene x environment interaction in emotion regulation: Is serotonin the link? Eur J Pharmacol 526:113–124
Lesch KP, Gutknecht L (2005) Pharmacogenetics of the serotonin transporter. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 29:1062–1073
Lesch KP, Bengel D, Heils A, Sabol SZ, Greenberg BD, Petri S, Benjamin J, Müller CR, Hamer DH, Murphy DL (1996) Association of anxiety-related traits with a polymorphism in the serotonin transporter gene regulatory region. Science 274:1527–1531
Lynn J, Allik J, Pullmann H, Laidra K (2002) A study of intelligence in Estonia. Psychol Rep 91:1022–1026
Messer SB, Brodzinsky DM (1981) Three-year stability of reflection-impulsivity in young adolescents. Dev Psychol 17:848–850
Milich R, Kramer J (1984) Reflections on impulsivity: An empirical investigation of impulsivity as a construct. Adv Learn Beh Disabil 3:57–94
Morgan MJ (1998) Recreational use of ecstasy (MDMA) is associated with elevated impulsivity. Neuropsychopharmacology 19:252–264
Murphy FC, Smith KA, Cowen PJ, Robbins TW, Sahakian BJ (2002) The effects of tryptophan depletion on cognitive and affective processing in healthy volunteers. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 163:42–53
Nelson RJ (2005) Biology of aggression. Oxford University Press, Cary, NC, USA, pp 79–84
Oreland L (2004) Platelet monoamine oxidase, personality and alcoholism: the rise, fall and resurrection. Neurotoxicology 25:79–89
Paaver M, Eensoo D, Pulver A, Harro J (2006a) Adaptive and maladaptive impulsivity, platelet monoamine oxidase (MAO) activity and risk-admitting in different types of risky drivers. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 186:32–40
Paaver M, Kreegipuu K, Tamm M, Harro M, Harro J (2006b) Platelet MAO activity is associated with vulnerability to fatigue and accuracy and speed of information processing in the tasks of visual cognition. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 9:S200
Patton JH, Stanford MS, Barratt ES (1995) Factor structure of the Barratt Impulsiveness Scale. J Clin Psychol 51:768–774
Pezawas L, Meyer-Lindenberg A, Drabant EM, Verchinski BA, Munoz KE, Kolachana BS, Egan MF, Mattay VS, Hariri, AR, Weinberger DR (2005) 5-HTTLPR polymorphism impacts human cingulate-amygdala interactions: a genetic susceptibility mechanism for depression. Nat Neurosci 8:828–834
Preuss UW, Soyka M, Bahlmann M, Wenzel K, Behrens S, Jonge S, Kruger M, Bondy B (2000) Serotonin transporter gene regulatory region polymorphism (5-HTTLPR), [3H] paroxetine binding in healthy control subjects and alcohol-dependent patients and their relationships to impulsivity. Psychiatry Res 96:51–61
Raven J (1981) Manual for Raven’s Progressive Matrices and Mill Hill vocabulary scales. Oxford Psychologists Press, Oxford
Reynolds B, Ortengren A, Richards JB, de Wit H (2006) Dimensions of impulsive behavior in personality and behavioral measures. Person Indiv Diff 40:305–315
Ruchkin VV, Koposov RA, af Klinteberg B, Oreland L, Grigorenko EL (2005) Platelet MAO-B, personality, and psychopathology. J Abnorm Psychol 114:477–482
Schalling D, Asberg M, Edman G, Oreland L (1987) Markers for vulnerability to psychopathology: temperament traits associated with platelet MAO activity. Acta Psychiatr Scand 176:172–182
Schalling D, Edman G, Asberg M, Oreland L (1988) Platelet MAO activity associated with impulsivity and aggressivity. Person Indiv Diff 9:597–605
Schmitt J, Jorissen B, Sobczak S, van Boxtel MPJ, Hogervorst E, Deutz NEP, Riedel W (2000) Tryptophan depletion impairs memory consolidation but improves focussed attention in healthy young volunteers. J Psychopharmacol 14:21–30
Shekim WO, Hodges K, Horwitz E, Glaser RD, Davis L, Bylund DB (1984) Psychoeducational and impulsivity correlates of platelet MAO in normal children. Psychiatry Res 11:99–106
Smeraldi E, Zanardi R, Benedetti F, DiBella D, Perez J, Catalano M (1998) Polymorphism within the promoter of the serotonin transporter gene and antidepressant efficacy of fluvoxamine. Mol Psychiatry 3:508–511
Swann AC, Bjork JM Moeller FG, Dougherty DM (2002) Two models of impulsivity: relationship to personality traits and psychopathology. Biol Psychiatry 51:988–994
Talpos JC, Wilkinson LS, Robbins TW (2006) A comparison of multiple 5-HT receptors in two tasks measuring impulsivity. J Psychopharmacol 20:47–58
Taylor SE, Way BM, Welch WT, Hilmert CJ, Lehman BJ, Eisenberger NI (2006) Early family environment, current adversity, the serotonin transporter promoter polymorphism, and depressive symptomatology. Biol Psychiatry 60:671–676
Vigil-Colet A, Morales-Vives F (2005) How impulsivity is related to intelligence and academic achievement. Spanish J Psychol 8:199–204
von Knorring L, Oreland L, Winblad B (1984) Personality traits related to monoamine oxidase activity in platelets. Psychiatry Res 12:11–26
Walderhaug E, Lunde H, Nordvik JE, Landro NI, Refsum H, Magnusson A (2002) Lowering of serotonin by rapid tryptophan depletion increases impulsiveness in normal individuals. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 164:385–391
Wengland JR, Martin BJ, Kruse MR, Lesch KP, Murphy DL (2006) Simultaneous genotyping of four functional loci of human SLC6A4, with a reappraisal of 5-HTTLPR and rs25531. Mol Psychiatry 11:224–226
Yamamoto S, Ouchi Y, Onoe H, Yoshikawa E, Tsukada H, Takahashi H, Iwase M, Yamaguti K, Kuratsune H, Watanabe Y (2004) Reduction of serotonin transporters of patients with chronic fatigue syndrome. Neuroreport 15:2571–2574
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from the Estonian Ministry of Education and Science (No 0182643 and 0942706) and the Estonian Science Foundation (No 6932 and 6788), the Swedish Science Foundation (VR) and the AFA insurance company. The skilful technical assistance by Ms Erika Comasco is gratefully acknowledged. We are grateful to the participants of the ECPBHS and to the whole ECPBHS Study Team.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paaver, M., Nordquist, N., Parik, J. et al. Platelet MAO activity and the 5-HTT gene promoter polymorphism are associated with impulsivity and cognitive style in visual information processing. Psychopharmacology 194, 545–554 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-007-0867-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-007-0867-z