Abstract
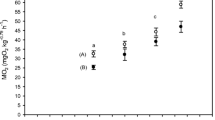
Lesser sandeel (Ammodytes tobianus) is abundant in near-shore areas where it is a key prey. It exhibits the behaviour of alternating between swimming in schools and lying buried in the sediment. We first determined the species’ standard metabolic rate (SMR), critical partial pressure of oxygen \((P_{{\rm O}_{2{\rm crit}}})\) and maximal oxygen uptake \((M_{{\rm O}_{2{\rm max}}}).\) The sandeel were then exposed to an acute stepwise decline in water oxygen pressure (18.4, 13.8, 9.8, 7.5, 5.8, 4.0, and 3.1 kPa \(P_{{\rm O}_{2}}\)). Swimming speed and routine- and post-experimental blood lactate levels were measured, in addition to levels associated with strenuous exercise. The SMR was 69.0 ± 8.4 mg O2 kg−1 h−1 and the \(M_{{\rm O}_{2{\rm max}}}\) about seven times as high. The \(P_{{\rm O}_{2{\rm crit}}}\) was found to be 4.1 kPa. A rapid decrease (within 1 h) in \(P_{{\rm O}_{2}}\) from 18.4 to 3.1 kPa had no significant effect on routine swimming speed (0.9 ± 0.06 bl s−1), but steady levels at the lowest \(P_{{\rm O}_{2}}\) (3.1 kPa) gradually reduced the swimming speed by 95% after 40 min. The routine blood lactate levels were 2.2 ± 0.6 mmol l−1, while the levels in the strenuously exercised groups were significantly higher with 5.4 ± 1.6 and 5.8 ± 1.3 mmol l−1. The highest levels were observed in post-experimental fish with 7.5 ± 2.7 mmol l−1. We argue that, as sandeel showed no decrease in swimming speed (to offset stress) nor an increased speed to escape the hypoxia, the fish either rely on a low SMR and being a reasonable strong oxygen regulator \((\hbox{low}\;P_{{\rm O}_{2{\rm crit}}})\) as a mean to cope when exposed to acute hypoxia, or that the hypoxia simply developed too fast for the fish to decide on an appropriate strategy. Not showing a behavioural response may in the present case be maladaptive, as the consequence was major physiological stress which the fish however appears tolerant towards. The high routine blood lactate levels suggest that anaerobic metabolism is associated with swimming in sandeel, which may be related to the specific lifestyle of the fish where they regularly bury in the sediment.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(P_{{\rm O}_{2{\rm crit}}}\) :
-
Critical partial pressure of oxygen
- \(M_{{\rm O}_{2{\rm max}}}\) :
-
maximal oxygen uptake
- MS:
-
metabolic scope
- \(P_{{\rm O}_{2}}\) :
-
partial pressure of oxygen
- SMR:
-
Standard metabolic rate
References
Anderson L, Rydberg L (1993) Exchange of water and nutrients between the Skagerrak and the Kattegat. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 36:159–181
Baker DW, Wood AM, Litvak MK, Kieffer JD (2005) Haematology of juvenile Acipenser onyrinchus and Acipenser brevirostrum at rest and following forced activity. J Fish Biol 66:208–221
Behrens JW, Præbel K, Steffensen JF (2006) Swimming energetics of the Barents Sea capelin (Mallotus villosus) during the spawning migration period. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 331(2):208–216
Bejda AJ, Studholme AL, Olla BL (1987) Behavioural responses of red hake, Urophycis chuss, to decreasing concentrations of dissolved oxygen. Environ Biol Fish 19:261–268
Brett JR (1964) The respiratory metabolism and swimming performance of young sockeye salmon. J Fish Res Bd Can 21(5):1183–1226
Cech JJ, Crocker CE (2002) Physiology of sturgeon: effects of hypoxia and hypercapnia. J Appl Ichthyol 18:320–324
Claireaux G, Webber DM, Kerr SR, Boutilier RG (1995) Physiology and behaviour of free swimming Atlantic cod, Gadus morhua, facing fluctuating salinity and oxygen conditions. J Exp Biol 198:61–69
Claireaux G, Webber DM, Lagardère J-P, Kerr SR (2000) Influence of water temperature and oxygenation on the aerobic metabolic scope of Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua). J Sea Res 44:257–265
Clarke A, Johnston NM (1999) Scaling of metabolic rate with body mass and temperature in teleost fish. J Animal Ecol 68:893–905
Conley DJ, Kaas H, Møhlenberg B, Rasmussen B, Windolf J (2000) Characteristics of Danish estuaries. Estuaries 23:820–837
Conley DJ, Carstensen J, Ærtebjerg G, Christensen PB, Dalsgaard T, Hansen JLS, Josefson AB (in press) Long-term changes and impacts of hypoxia in Danish coastal waters. Ecol Appl Sp issue Coast Eutrophs: accepted
Dalla Via J, van den Thillart G, Cattani O, Cortesi P (1998) Behavioral responses and biochemical correlates in Solea solea to gradual hypoxic exposure. Can J Zool 76:2108–2113
Domenici P, Steffensen JF, Batty RS (2000) The effect of progressive hypoxia on swimming activity and schooling in Atlantic herring. J Fish Biol 57:1526–1538
Driedzic WR, Hochachka PW (1978) Metabolism in fish during exercise. In: Hoar WS, Randall DJ (Eds) Fish physiology, vol VII. Academic, New York
Fischer P, Rademacher K, Kils U (1992) In situ investigations on the respiration and behaviour of the eelpout Zoarces viviparous under short-term hypoxia. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 88:181–184
Fry FEJ (1971) The effect of environmental factors on the physiology of fish. In: Hoar WS and Randall DJ (Eds) Fish physiology, vol VI. Academic , New York, pp 1–98
Gauld A (1990) Movements of lesser sandeels (Ammodytes marius Raitt) tagged in the northwestern North Sea. Journal du Conseil. Int Council Explor Sea 46:229–231
Gillis GB (1998) Neuromuscular control of anguilliform locomotion: patterns of red and white muscle activity during swimming in the American ell Anguilla rostrata. J Exp Biol 201:3245–3256
Gislason H, Kirkegaard E (1998) Is the industrial fishery in the North Sea sustainable? In: Symes D (Ed) Northern waters: management issues and practice. Fishing news books. Blackwell, Oxford, pp 195–208
HELCOM (2003) The 2002 oxygen depletion event in the Kattegat, Belt Sea and Western Baltic. Baltic Sea Environment Proceeding No: 90
Herbert NA, Steffensen JF (2005) The response of Atlantic cod, Gadus morhua, to progressive hypoxia: fish swimming speed and physiological stress. Mar Biol 147:1403–1412
Hoffmann E (2000) Fisk og fiskebestande I Limfjorden 1984–1999. DFU-rapport 75-00. In Danish
Holland GJ, Greenstreet SPR, Gibb IM, Fraser HM, Robertson MR (2005) Identifying sandeel Ammodytes marinus sediment habitat preferences in the marine environment. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 303:269–282
Johansen JL, Herbert NA, Steffensen JF (2006) The behavioural and physiological response of Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.) to short-term acute hypoxia. J Fish Biol 68:1918–1924
Lefrançois C, Claireaux G (2003) Influence of ambient oxygenation and temperature on metabolic scope and heart rate in the common sole Solea solea. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 259:273–284
Le François NR, Lamarre SG, Blier PU (2005) Is white anaerobic glycolysis capacity indicative of competitive ability in Arctic charr. J Fish Biol 66:1167–1176
Lutz PL (1989) Interaction between hypometabolism and acid-base balance. Can J Zool 67:3018–3023
Lutz PL, Nilsson GE (1997) Contrasting strategies for anoxic brain survival—glycolysis up or down. J Exp Biol 200:411–419
Møhlenberg F (1999) Effect of meterology and nutrient load on oxygen depletion in a Danish micro-tidal estuary. Aquatic Ecol 33:55–64
Macer CT (1966) Sand eels (Ammodytidae) in the southwestern North Sea; their biology and fishery. Fishery Investigations, Series 2, Great Britain Minist Agric, Fish Food 24:1–55
Martínez M, Guderley H, Dutil J-D, Winger PD, He P, Walsh SJ (2003) Condition, prolonged swimming performance and muscle metabolic capacities of cod Gadus morhua. J Exp Biol 206:503–511
Metcalfe JD, Butler PJ (1984) Changes in activity and ventilation in response to hypoxia in unrestrained, unoperated dogfish (Scyliorhinus canicula L.). J Exp Biol 108:411–418
Meyer TL, Cooper RA, Langton RW (1979) Relative abundance, behaviour, and food habits of the American sand lance, Ammodytes americanus, from the Gulf of Maine. Fish Bul (Washington DC) 77:243–253
Milligan CL, Wood CM (1987) Regulation of blood oxygen transport and red cell pHi after exhaustive activity in rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) and starry flounder (Platichthys stellatus). J Exp Biol 133:263–282
Munch-Pedersen S (2004) Fiskebestande og fiskeri i 2003. DFU-Rapport 95-01. In Danish
Muus BJ, Nielsen JG (1997) Havfisk og fiskeri I Nordvesteuropa. 5. udgave, Gads Forlag pp 214–216. In Danish
Neuenfeldt S (2002) The influence of oxygen saturation on the distributional overlap of predator (cod, Gadus morhua) and prey (herring, Clupea harengus) in the Bornholm Basin of the Baltic Sea. Fish Oceangr 11:11–17
Nilsson GE, Rosen P, Johannson D (1993) Anoxic depression of spontaneous locomotor activity in crucian carp quantified by a computer imagine technique. J Exp Biol 180:153–162
Petersen JK, Pihl L (1995) Responses to hypoxia of plaice, Pleuronectes platessa, and dab, Limanda limanda, in the south-east Kattegat: distribution and growth. Environ Biol Fish 43:311–321
Pinto JM, Pearson WH, Anderson JW (1984) Sediment preferences and oil contamination in the Pacific sand lance Ammodytes hexapterus. Mar Biol 83:193–204
Popp Madsen K (1994) Sandeel or not sandeel. An important question for the Danish fishery. (In Danish) Fish og Hav 45:27–34
Pörtner H-O, Branco LGS, Malvin GM, Wood SC (1994) A new function for lactate in the toad Bufo marinus. J Appl Physiol 76:2405–2410
Quinn T, Schneider DE (1991) Respiration of the teleost fish Ammodytes hexapterus in relation to its burrowing behaviour. Comp Biochem Physiol 98A:71–75
Randall DJ, Burrgren WW, Farrell AP, Haswell MS (1981) The evolution of air-breathing vertebrates. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Rasmussen B, Gustafsson BG, Ærtebjerg G, Lundsgaard C (2003) Oxygen concentration at the entrance to the Baltic Sea from 1975 to 2000. J Mar Systems 42:13–30
Schaarschmidt T, Jürss K (2003) Locomotor capacity of Baltic Sea and freshwater populations of the threespine stickleback (Gasterosteus aculeatus). Comp Biochem Physiol A 135:411–424
Schurmann H, Steffensen JF (1997) Effect of temperature, hypoxia and activity on the metabolism of juvenile cod. J Fish Biol 50:1166–1180
Scott JS (1968) Morphometrics, distribution, growth, and maturity of offshore sand lance (Ammodytes dubius) on the Nova Scotia Banks. J Fish Res Bd Canada 25:1775–1785
Steffensen JF (1989) Some errors in respirometry of aquatic breathers: how to avoid and correct them. Fish Physiol Biochem 6:49–59
Steinhausen MF, Steffensen JF, Andersen NG (2005) Tail beat frequency as a predictor of swimming speed and oxygen consumption of saithe (Pollachius virens) and whiting (Merlangius merlangus) during forced swimming. Accepted by Mar Biol 148:197–204
Stigebrandt A, Gustafsson BG (2003) Response of the Baltic Sea to climate change-theory and observations. J Sea Res 49:243–251
van den Thillart G, Dalla Via J, Vitali G, Cortesi P (1994) Influence of long-term hypoxia on the energy metabolism of Solea solea. I. Critical O2 levels for aerobic and anaerobic metabolism. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 104: 109–117
Van Raaij MTM, Pitt DSS, Balm PHM, Steffens AB, van den Thillart G (1996) Behavioural strategy and the physiological stress response in rainbow trout exposed to severe hypoxia. Horm Behav 30:85–92
Videler JJ (1993) Fish swimming. Chapman & Hall, London
Watcher De B, Sartoris F-J, Pörtner H-O (1997) The anaerobic endproduct lactate has a behavioural and metabolic signalling function in the shore crab Carcinuc maenas. J Exp Biol 200:1015–1024
Winslade P (1974a) Behavioural studies on lesser sandeel Ammodytes marius (Raitt) I. The effect of food availability on activity and the role of olfaction in food detection. J Fish Biol 6:565–576
Winslade P (1974b) Behavioural studies on lesser sandeel Ammodytes marius (Raitt) II. The effect of light intensity on activity. J Fish Biol 6:577–586
Winslade P (1974c) Behavioural studies on lesser sandeel Ammodytes marius (Raitt) III. The effect of temperature on activity and the environmental control of the annual cycle of activity. J Fish Biol 6:587–599
Wright PJ, Pedersen PA, Donald L, Anderson C, Lewy P, Proctor R (1998) The influence of physical factors on the distribution of lesser sandeel and its relevance to fishing pressure in the North Sea. CM-Int Counc Explor Sea (1998/AA:3)
Wright PJ, Jensen H, Tuck I (2000) The influence of sediment type on the distribution of lesser sandeel, Ammodytes marius. J Sea Res 44:243–256
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Neill Herbert, University of Glasgow, for assistance with the experimental design. The study was financially supported by a Ph.D. stipend from the Copenhagen Global Change Initiative (COGCI) Ph.D. School to Jane W. Behrens. The experiments comply with the Danish laws on animal ethics.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by M. Kühl, Helsingør.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Behrens, J.W., Steffensen, J.F. The effect of hypoxia on behavioural and physiological aspects of lesser sandeel, Ammodytes tobianus (Linnaeus, 1785). Mar Biol 150, 1365–1377 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-006-0456-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-006-0456-4