Abstract
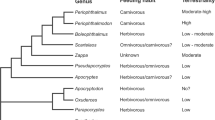
Mudskippers (Gobiidae: Oxudercinae) are amphibious gobies. The occurrence and habitats of seven sympatric species of Malayan mudskippers were recorded: Boleophthalmus boddarti, Boleophthalmus pectinirostris, Periophthalmodon schlosseri, Periophthalmus chrysospilos, Periophthalmus gracilis, Periophthalmus variabilis and Scartelaos histophorus. A total of 14 surveys were made at six localities along 120 km of the west coast of the Malay Peninsula in August 1996 and September 2006. A multivariate set of ordinal parameters were used to measure the quantity of environmental water in mudskippers’ habitats, and three guilds of species were discriminated. The resulting pattern mirrored the adaptive scenario depicted by physiological and anatomical studies of mudskippers’ terrestriality, although in one case a terminal taxon was less terrestrial than other more basal ones. Differentiation of trophic niches may also play a role in habitat selection by the herbivorous Boleophthalmus spp., which were only found in unvegetated, illuminated areas and on wet mud at low tide. With the more terrestrial guild, a significant negative co-occurrence suggested direct interspecific competition.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilar NM (2000) Comparative physiology of air-breathing gobies. PhD dissertation in Marine Biology, University of California, San Diego
Bellinger BJ, Abdullahi AS, Gretz MR, Underwood GJC (2005) Biofilm polymers: relationship between carbohydrate biopolymers from estuarine mudflats and unialgal cultures of benthic diatoms. Aquat Microb Ecol 38:169–180. doi:https://doi.org/10.3354/ame038169
Berry AJ (1972) The natural history of west Malaysian mangrove faunas. Malay Nat J 25:135–162
Blaber SM, Brewer DT (1989) Species composition and biomasses of fishes in different habitats of a tropical northern Australian estuary: their occurrence in the adjoining sea and estuarine dependence. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 29:509–531. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/0272-7714(89)90008-5
Cantor T (1849) Catalog of Malayan fishes. J Asiat Soc Bengal 18:983–1443
Chew SF, Hong LN, Wilson JM et al (2003) Alkaline environmental pH has no effect on ammonia excretion in the mudskipper Periophthalmodon schlosseri but inhibits ammonia excretion in the related species Boleophthalmus boddaerti. Physiol Biochem Zool 76:204–214. doi:https://doi.org/10.1086/374281
Clayton DA (1993) Mudskippers. Oceanogr Mar Biol Annu Rev 31:507–577
Clayton DA, Snowden R (2000) Surface activity in the mudskipper, Periophthalmus waltoni in relation to prey activity and environmental factors. Trop Zool 13:239–249
Clayton DA, Vaughan TC (1988) Ethogram of Boleophthalmus boddarti (Pallas), a mudskipper found on the mudflats of Kuwait. J Univ Kuwait Sci 15:115–138
Coleman JM, Gagliano SM, Smith WG (1970) Sedimentation in a Malaysian high tide tropical delta. In: Morgan JP (ed) Deltaic sedimentation, modern and ancient. Special Publ. No 15, S.E.P.M., pp 185–197
Colombini I, Berti R, Ercolini A et al (1995) Environmental factors influencing the zonation and activity patterns of a population of Periophthalmus sobrinus Eggert in a Kenyan mangrove. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 190:135–149. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-0981(95)00020-R
Darumas U, Tantichodok P (2002) A new species of mudskipper (Gobiidae: Oxudercinae) from southern Thailand. Phuket Mar Biol Cent Res Bull 64:101–107
Dyer KR, Christie MC, Wright EW (2000) The classification of intertidal mudflats. Cont Shelf Res 20:1039–1060. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S0278-4343(00)00011-X
Frith DW, Tantanasiriwong R, Bathia O (1976) Zonation and abundance of macrofauna on a mangrove shore, Phuket Island. Phuket Mar Biol Cent Res Bull 10:1–37
Gibson RN (1982) Recent studies on the biology of intertidal fishes. Oceanogr Mar Biol Annu Rev 20:363–414
Gibson RN (1999) Methods for studying intertidal fishes. In: Horn MH, Martin KLM, Chotkowski MA (eds) Intertidal fishes: life in two worlds. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 7–25
Gotelli NJ, Ellison AM (2004) A primer of ecological statistics. Sinauer Associates Inc, Sunderland
Gotelli NJ, Entsminger GL (2001) EcoSim: null models software for ecology. Version 7.0. Acquired Intelligence Inc. & Kesey-Bear. Available via DIALOG. http://homepages.together.net/~gentsmin/ecosim.htm. Accessed 20 Nov 2009
Harris VA (1960) On the locomotion of the mud-skipper Periophthalmus koelreuteri (Pallas): (Gobiidae). Proc Zool Soc Lond 134:107–135
Hong W, Chen S, Zhang Q, Wang Q (2007) Reproductive ecology of the mudskipper Boleophthalmus pectinirostris. Acta Oceanol Sin 26:72–81
Hydrographic Directorate (1996) Tide tables. RMN, Ministry of Defence, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Ip YK, Low WP, Lim ALL, Chew SF (1990) Changes in lactate content in the gills of the mudskipper Periophthalmus chrysospilos and Boleophthalmus boddaerti in response to environmental hypoxia. J Fish Biol 36:481–487. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8649.1990.tb03550.x
Ip YK, Lim CB, Chew SF et al (2001) Partial amino acid catabolism leading to the formation of alanine in Periophthalmodon schlosseri (mudskipper): a strategy that facilitates the use of amino acids as an energy resource during locomotory activity on land. J Exp Biol 204:1615–1624
Ishimatsu A, Hishida Y, Takita T et al (1998) Mudskipper store air in their burrows. Nature 391:237–238. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/34560
Jaafar Z, Larson HK (2008) A new species of mudskipper, Periophthalmus takita (Teleostei: Gobiidae: Oxudercinae), from Australia, with a key to the genus. Zool Sci 25:946–952. doi:https://doi.org/10.2108/zsj.25.946
Jaafar Z, Lim KKP, Chou LM (2006) Taxonomical and morphological notes on two species of mudskippers, Periophthalmus walailakae and Periophthalmodon schlosseri (Teleostei: Gobiidae) from Singapore. Zool Sci 23:1043–1047. doi:https://doi.org/10.2108/zsj.23.1043
Jayne BC, Voris HK, Heang KB (1988) Diet, feeding behaviour, growth and numbers of a population of Cerebrus rynchops (Serpentes: Homalopsinae) in Malaysia. Fieldiana Zool 50:1–15
Jobson JD (1992) Applied multivariate data analysis. Volume II: Categorical and multivariate methods. Springer, New York, pp 462–465
Johnson RA, Wichern DW (1992) Applied multivariate statistical analysis. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, pp 584–602
Khaironizam MZ, Norma-Rashid Y (2002) A new record of mudskipper Periophthalmus spilotus (Gobiidae: Oxudercinae) from Selangor coast, Peninsular Malaysia. Nat Hist Bull Siam Soc 50:245–250
Khaironizam MZ, Norma-Rashid Y (2003) First record of the mudskipper, Periophthalmodon septemradiatus (Hamilton) (Teleostei: Gobiidae) from Peninsular Malaysia. Raffles Bull Zool 51:97–100
Khaironizam MZ, Norma-Rashid Y (2005) Distribution of mudskippers (Gobiidae: Oxudercinae) on the Selangor coast. In: Sasekumar A, Chong VC (eds) Ecology of the Klang Strait. Faculty of Science, University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur, pp 101–114
Kok WK, Lim CB, Lam TJ, Ip YK (1998) The mudskipper Periophthalmodon schlosseri respires more efficiently on land than in water and vice versa for Boleophthalmus boddaerti. J Exp Zool 280:86–90. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-010X(19980101)280:1<86::AID-JEZ10>3.0.CO;2-U
Koumans FP (1953) Gobioidea. In: Weber M, de Beaufort LF (eds) Fishes of the Indo–Australian archipelago, 10. EJ Brill, Leiden, pp 1–423
Larson HK, Takita T (2004) Two new species of Periophthalmus (Teleostei: Gobiidae: Oxudercinae) from northern Australia, and a re-diagnosis of Periophthalmus novaeguineaensis. The Beagle. Rec Mus Art Galleries N Territ 20:175–185
Lee HJ, Martinez CA, Hertzberg KJ et al (2005) Burrow air phase maintenance and respiration by the mudskipper Scartelaos histophorus (Gobiidae: Oxudercinae). J Exp Biol 208:169–177. doi:https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.01361
Low WP, Ip YK, Lane DJW (1990) A comparative study of the gill and skin morphometries of three mudskippers: Periophthalmus chrysospilos, Boleophthalmus boddaerti and Periophthalmodon schlosseri: correlations and interpretations. Zool Sci 7:29–38
Macintosh DJ (1977) Some responses of tropical mangrove fiddler crabs (Uca spp.) to high environmental temperatures: physiology and behaviour of marine organisms. In: McLusky DS, Berry AJ (eds) Proceedings of the 12th European symposium on marine biology. Pergamon Press, Stirling, pp 49–56
Macnae W (1968) A general account of the fauna and flora of mangrove swamps and forests in the Indo-West-Pacific region. Adv Mar Biol 6:73–270. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2881(08)60438-1
Milward NE (1974) Studies on the taxonomy, ecology and physiology of Queensland mudskippers. PhD dissertation. University of Queensland, Brisbane
Murdy EO (1986) Mudskippers of Malaysia: the lords of the mudflat. Freshw Mar Aquar 9:20–23
Murdy EO (1989) A taxonomic revision and cladistic analysis of the oxudercine gobies (Gobiidae: Oxudercinae). Rec Aust Mus Suppl No. 11:1–93
Murdy EO, Takita T (1999) Periophthalmus spilotus, a new species of mudskipper from Sumatra (Gobiidae: Oxudercinae). Ichthyol Res 46:367–370. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02673979
Nateewathana A, Tantichodok P (1984) Species composition, density and biomass of macrofauna of a mangrove. In: Soepadmo E et al (eds) Proceedings of the Asean symposium on the mangrove and management: research and management. University of Malaya and UNESCO, Kuala Lumpur, pp 258–285
Norma-Rashid Y, Khaironizam MZ (2005) Some biological aspects of mudskippers (Gobiidae: Oxudercinae) from Langkawi Island. Malays J Sci 24:139–144
Noske RA (1995) The ecology of mangrove forest birds in Peninsular Malaysia. Ibis 137:250–263. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1474-919X.1995.tb03247.x
Nursall JR (1981) Behaviour and habitat affecting the distribution of five species of sympatric mudskippers in Queensland. Bull Mar Sci 31:730–735
Polgar G (2008) Species–area relationship and potential role as a biomonitor of mangrove communities of Malayan mudskippers. Wetland Ecol Manage 17:157–164. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11273008-9090-x
Polgar G, Khaironizam Md Z (2008) First record of Periophthalmus walailakae (Gobiidae: Oxudercinae) from Peninsular Malaysia. Cybium 32:349–351
Polunin I (1972) Who says fish can’t climb trees? Natl Geogr Mag 141:84–92
Rainboth WJ (1996) Fishes of the Cambodian Mekong: FAO Species identification field guide for fishery purposes. FAO, Rome
Robertson AI, Alongi DM (1992) Tropical mangrove ecosystems: coastal estuarine studies 41. American Geophysical Union, Washington DC
Sarpedonti V, Sasekumar A (1996) The abundance of diatom species on a low-shore mangrove forest, Sementa, Malaysia. Wallaceana 77:21–26
Sasekumar A (1974) Distribution of macrofauna on a Malayan mangrove shore. J Anim Ecol 43:51–69. doi:https://doi.org/10.2307/3157
Sasekumar A (1980) The present state of mangrove ecosystems in southeast Asia and the impact of pollution. FAO/UNEP project: impact of pollution on the mangrove ecosystem and its productivity in Southeast Asia; (SCS/80/WP/94b). Publication of the South China Sea Fisheries Development and Coordinating Programme, 4–8 February 1980, Manila
Sasekumar A (1994) Meiofauna of a mangrove shore on the west coast of peninsular Malaysia. Raffles Bull Zool 42:901–915
Sasekumar A, Chong EL (1986) The macrobenthos at feeding sites of shorebirds in Pulau Tengah. Wallaceana 45:6–7
Sasekumar A, Chong VC, Lim KH, Singh HR (1994) The fish community of Matang mangrove waters, Malaysia. In: Sudara S, Wilkinson CR, Chou LM (eds) Proceedings of the third ASEAN: Australia symposium on living coastal resources. Research papers, vol 2. Chulalonghorn University, Bangkok, pp 457–464
Sayer MDJ (2005) Adaptations of amphibious fish for surviving life out of water. Fish Fish 6:186–211. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-2979.2005.00193.x
Stone L, Roberts A (1990) The checkerboard score and species distributions. Oecologia 85:74–79. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00317345
Swennen C, Ruttanadakul N, Haver M et al (1995) The five sympatric mudskippers (Teleostei: Gobioidea) of Pattani area, Southern Thailand. Nat Hist Bull Siam Soc 42:109–129
Takita T, Agusnimar, Ali AB (1999) Distribution and habitat requirements of oxudercine gobies (Gobiidae: Oxudercinae) along the Straits of Malacca. Ichthyol Res 46:131–138. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02675431
Tomlinson PB (1986) The botany of mangroves. Cambridge University Press, London
Townsend KA, Tibbetts IR (1995) Re-appearance of the blue mudhopper, Scartelaos histophorus in the Greater Brisbane area. Mem Qld Mus 38:671–676
Townsend KA, Tibbetts IR (2005) Behaviour and sexual dimorphism of the blue mudskipper, Scartelaos histophorus (Pisces: Gobiidae). Proc R Soc Qld 112:53–62
Wilson KA (1989) Ecology of mangrove crabs. predation, physical factors and refuges. Bull Mar Sci 44:263–273
Yang KYJ (1996) The feeding ecology of the mudskipper Boleophthalmus pectinirostris (Pisces: Periophthalmidae) at the Mai Po marshes nature reserve, Hong Kong. MP dissertation, Faculty of Science, Hong Kong University, Hong Kong
Yang KY, Lee SY, Williams GA (2003) Selective feeding by the mudskipper (Boleophthalmus pectinirostris) on the microalgal assemblage of a tropical mudflat. Mar Biol (Berl) 143:245–256. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-003-1067-y
Zhang J, Taniguchi T, Takita T, Ali AB (2000) On the epidermal structure of Boleophthalmus and Scartelaos mudskippers with reference to their adaptation to terrestrial life. Ichthyol Res 47:359–366. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02674263
Zhang J, Taniguchi T, Takita T, Ali AB (2003) A study on the epidermal structure of Periophthalmodon and Periophthalmus mudskippers with reference to their terrestrial adaptation. Ichthyol Res 50:310–317. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s10228-003-0173-7
Acknowledgments
Thanks to Dr. A. Sasekumar (University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur), who greatly helped with the field collection and granted access to the zoological collection of the museum of the University of Malaya. Thanks also to Mr. M. Rasainthiran (Park Manager of the Kuala Selangor Marine Nature Park in 1996), Dr. H. K. Larson (Museum and Art Gallery, Darwin, Australia) and Dr. T. Takita (University of Nagasaki, Japan) for their help and support. Many thanks also to the staff of all the museums and institutions that loaned fish specimens or sent photos. The survey made in 2006 was the result of a scientific collaboration between GP and Prof. J. Pignatti (University of Rome “La Sapienza”, Italy), Dr. A. Sasekumar and Prof. V. C. Chong (University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur), Mr. H. Singh and Mrs. L. Tokiman (Kukup and Tanjung Piai Taman Negara, Johor National Parks Corporation). Part of this survey was funded by a doctoral grant by the University of Rome “La Sapienza”. Thanks to Prof. M. Rosenzweig (University of Arizona, USA); Prof. J. Clack (University of Cambridge, UK); Prof. S. Milli and Dr. F. Colloca (University of Rome “La Sapienza”), and to the three anonymous reviewers for a revision of the manuscript. GP also wishes to thank the Yoon family in Petaling Jaya for facilities during the stay in 1996.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by J. P. Grassle.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Polgar, G., Crosa, G. Multivariate characterisation of the habitats of seven species of Malayan mudskippers (Gobiidae: Oxudercinae). Mar Biol 156, 1475–1486 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-009-1187-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-009-1187-0