Abstract
Recently, evidence was provided for common familial occurrence of systemic mast cell activation disease (MCAD), i.e., mast cell disorders characterized by aberrant release of mast cell mediators and/or accumulation of pathological mast cells in potentially any tissue. Since there is accumulating evidence that epigenetic processes may have transgenerational consequences, the aim of the present study was to investigate by two different experimental approaches whether epigenetic effects may contribute to the familial occurrence of MCAD. (1) High throughput profiling of the methylation status of the genomic DNA in leukocytes from MCAD patients in comparison to healthy subjects revealed for the first time an association of MCAD with alterations in DNA methylation comprising genes encoding proteins crucially involved in DNA/RNA repair and processing, apoptosis, cell activity, and exocytosis/cell communication. A set of 195 differentially methylated CpG sites could be regarded as candidates for a MCAD signature at the methylation level of the DNA. (2) In a cohort of MCAD patients, a correlation between age at symptom onset and year of birth (reflecting different generations) was observed suggesting the presence of the phenomenon of anticipation. In conclusion, the present findings suggest that epigenetic processes could substantially contribute to the transgenerational transmission of MCAD.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akin C, Valent P, Metcalfe DD (2010) Mast cell activation syndrome: proposed diagnostic criteria. J Allergy Clin Immunol 126:1099–1104
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT et al (2000) Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat Genet 25:25–29
Baylin SB (2005) DNA methylation and gene silencing in cancer. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 2(1):S4–S11
Bodemer C, Hermine O, Palmérini F, Yang Y, Grandpeix-Guyodo C, Leventhal PS, Hadj-Rabia S, Nasca L, Georgin-Lavialle S, Cohen-Akenine A et al (2010) Pediatric mastocytosis is a clonal disease associated with D(816)V and other activating c-KIT mutations. J Invest Dermatol 130:804–815
Crews D, Gillette R, Scarpino SV, Manikkam M, Savenkova MI, Skinner MK (2012) Epigenetic transgenerational inheritance of altered stress responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:9143–9148
Davis CD, Uthus EO (2004) DNA methylation, cancer susceptibility, and nutrient interactions. Exp Biol Med 229:988–995
Dolinoy DC, Weidman JR, Waterland RA, Jirtle RL (2006) Maternal genistein alters coat color and protects Avy mouse offspring from obesity by modifying the fetal epigenome. Environ Health Perspect 114:567–572
Dolinoy DC, Das R, Weidman JR, Jirtle RL (2007) Metastable epialleles, imprinting, and the fetal origins of adult diseases. Pediatr Res 61:30R–37R
Du P, Kibbe WA, Lin SM (2008) lumi: a pipeline for processing Illumina microarray. Bioinformatics 24:1547–1548
Du P, Zhang X, Huang CC, Jafari N, Kibbe WA, Hou L, Lin SM (2010) Comparison of Beta-value and M-value methods for quantifying methylation levels by microarray analysis. BMC Bioinformatics 11:587
Eden A, Gaudet F, Waghmare A, Jaenisch R (2003) Chromosomal instability and tumors promoted by DNA hypomethylation. Science 300:455
Fraga MF, Ballestar E, Paz MF, Ropero S, Setien F, Ballestar ML, Heine-Suñer D, Cigudosa JC, Urioste M, Benitez J et al (2005) Epigenetic differences arise during the lifetime of monozygotic twins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:10604–10609
Frieling T, Meis K, Kolck UW et al (2011) Evidence for mast cell activation in patients with therapy-resistant irritable bowel syndrome. Z Gastroenterol 49:191–194
Goeman JJ, van de Geer SA, de Kort F, van Houwelingen HC (2004) A global test for groups of genes: testing association with a clinical outcome. Bioinformatics 20:93–99
Haenisch B, Nöthen MM, Molderings GJ (2012) Systemic mast cell activation disease: the role of molecular genetic alterations in pathogenesis, heritability and diagnostics. Immunology 137:197–205
Hamilton MJ, Hornick JL, Akin C, Castells MC, Greenberger NJ (2011) Mast cell activation syndrome: a newly recognized disorder with systemic clinical manifestations. J Allergy Clin Immunol 128:147–152
Harris MA, Clark J, Ireland A, Lomax J, Ashburner M, Foulger R, Eilbeck K, Lewis S, Marshall B, Mungall C et al (2004) The Gene Ontology (GO) database and informatics resource. Nucleic Acids Res 32:D258–D261
Häsler R, Feng Z, Bäckdahl L, Spehlmann ME, Franke A, Teschendorff A, Rakyan VK, Down TA, Wilson GA, Feber A et al (2012) A functional methylome map of ulcerative colitis. Genome Res 22:2130–2137
Hermine O, Lortholary O, Leventhal PS, Catteau A, Soppelsa F, Baude C, Cohen-Akenine A, Palmérini F, Hanssens K, Yang Y et al (2008) Case-control cohort study of patients’ perceptions of disability in mastocytosis. PLoS ONE 3:e2266
Jaenisch R, Bird A (2003) Epigenetic regulation of gene expression: how the genome integrates intrinsic and environmental signals. Nat Genet 33:245–254
Laird PW (2010) Principles and challenges of genome-wide DNA methylation analysis. Nat Rev Genet 11:191–203
Lanternier F, Cohen-Akenine A, Palmerini F, Feger F, Yang Y, Zermati Y, Barète S, Sans B, Baude C, Ghez D et al (2008) Phenotypic and genotypic characteristics of mastocytosis according to the age of onset. PLoS One 3:e1906
Marabita F, Almgren M, Lindholm ME, Ruhrmann S, Fagerström-Billai F, Jagodic M, Sundberg CJ, Ekström TJ, Teschendorff AE, Tegnér J et al (2013) An evaluation of analysis pipelines for DNA methylation profiling using the Illumina HumanMethylation450 BeadChip platform. Epigenetics 8:333–346
Martino DJ, Tulic MK, Gordon L, Hodder M, Richman TR, Metcalfe J, Prescott SL, Saffery R (2011) Evidence for age-related and individual-specific changes in DNA methylation profile of mononuclear cells during early immune development in humans. Epigenetics 6:1085–1094
Molderings GJ, Kolck UW, Scheurlen C, Brüss M, Homann J, Von Kügelgen I (2007) Multiple novel alterations in Kit tyrosine kinase in patients with gastrointestinally pronounced systemic mast cell activation disorder. Scand J Gastroenterol 42:1045–1053
Molderings GJ, Meis K, Kolck UW, Homann J, Frieling T (2010) Comparative analysis of mutation of tyrosine kinase kit in mast cells from patients with systemic mast cell activation syndrome and healthy subjects. Immunogenetics 62:721–727
Molderings GJ, Brettner S, Homann J, Afrin LB (2011) Mast cell activation disease: a concise practical guide for diagnostic workup and therapeutic options. J Hematol Oncol 4:10
Molderings GJ, Haenisch B, Bogdanow M, Fimmers R, Nöthen MM (2013) Familial occurrence of systemic mast cell activation disease. PLoS One 8:e76241
Nadeau JH (2009) Transgenerational genetic effects on phenotypic variation and disease risk. Hum Mol Gen 18:R202–R210
Petronis A (2010) Epigenetics as a unifying principle in the aetiology of complex traits and diseases. Nature 465:721–727
Rakyan VK, Beyan H, Down TA, Hawa MI, Maslau S, Aden D, Daunay A, Busato F, Mein CA, Manfras B et al (2011) Identification of type 1 diabetes-associated DNA methylation variable positions that precede disease diagnosis. PLoS Genet 7:e1002300
Rassoulzadegan M, Grandjean V, Gounon P, Vincent S, Gillot I, Cuzin F (2006) RNA-mediated non-mendelian inheritance of an epigenetic change in the mouse. Nature 441:469–474
Sartor MA, Leikauf GD, Medvedovic M (2009) LRpath: a logistic regression approach for identifying enriched biological groups in gene expression data. Bioinformatics 25:211–217
Skinner MK (2011) Environmental epigenetic transgenerational inheritance and somatic epigenetic mitotic stability. Epigenetics 6:838–842
Smyth GK (2005) Limma: linear models for microarray data. In: Gentleman R, Carey V, Dudoit S, Irizarry R, Huber W (eds) Bioinformatics and computational biology solutions using R and bioconductor. Springer, New York, pp 397–420
Szyf M, McGowan P, Meaney MJ (2008) The social environment and the epigenome. Environ Mol Mutagen 49:46–60
Teschendorff AE, Marabita F, Lechner M, Bartlett T, Tegner J, Gomez-Cabrero D, Beck S (2013) A beta-mixture quantile normalization method for correcting probe design bias in Illumina Infinium 450k DNA methylation data. Bioinformatics 29:189–196
Valent P, Akin C, Escribano L, Födinger M, Hartmann K, Brockow K, Castells M, Sperr WR, Kluin-Nelemans HC, Hamdy N et al (2007) Standards and standardization in mastocytosis: consensus statements on diagnostics, treatment recommendations and response criteria. Eur J Clin Invest 37:435–453
Valent P, Akin C, Arock M, Brockow K, Butterfield JH, Carter MC, Castells M, Escribano L, Hartmann K, Lieberman P et al (2012) Definitions, criteria and global classification of mast cell disorders with special reference to mast cell activation syndromes: a consensus proposal. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 157:215–225
van Overveld PG, Lemmers RJ, Sandkuijl LA, Enthoven L, Winokur ST, Bakels F, Padberg GW, van Ommen GJ, Frants RR, van der Maarel SM (2003) Hypomethylation of D4Z4 in 4q-linked and non-4q-linked facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy. Nat Genet 35:315–317
Verzijl A, Heide R, Oranje AP, van Schaik RHN (2007) c-Kit Asp-816-Val mutation analysis in patients with mastocytosis. Clin Lab Invest 214:15–20
Warnes GR, Liu P (2006) Sample size estimation for microarray experiments. Technical report. Department of Biostatistics and Computational Biology, University of Rochester
Waterland RA, Jirtle RL (2003) Transposable elements: targets for early nutritional effects on epigenetic gene regulation. Mol Cell Biol 23:5293–5300
Woo HD, Kim J (2012) Global DNA hypomethylation in peripheral blood leukocytes as a biomarker for cancer risk: a meta-analysis. PLoS One 7:e34615
Acknowledgments
The technical assistance of Mrs. Nadine Fricker and Mrs. Sandra Barth is gratefully acknowledged. The study was supported by grants of the B. Braun-Stiftung, Germany and the Förderclub Mastzellforschung e.V., Germany.
Ethical standards
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the University of Bonn (Germany) and has therefore been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. All probands gave informed consent prior to the investigation according to the guidelines of the local Ethics Committee.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Online Resource Fig. S1
Required sample size to detect a twofold change of methylation at Bonferroni corrected p value of 0.05 and statistical power of 80 % (PDF 53 kb)
Online Resource Fig. S2
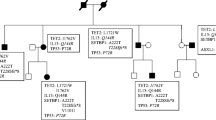
Pedigree of a family with a high familial loading of mast cell activation disease showing anticipation (PDF 53 kb)
Online Resource Fig. S3
Sample clustering (Ward’s method) before and after normalization (PDF 53 kb)
Online Resource Table S1
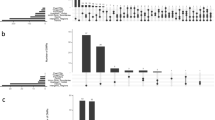
CpG sites with significantly (adjusted p value <0.05) different methylation between patient and control samples (XLS 110 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haenisch, B., Fröhlich, H., Herms, S. et al. Evidence for contribution of epigenetic mechanisms in the pathogenesis of systemic mast cell activation disease. Immunogenetics 66, 287–297 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-014-0768-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-014-0768-3