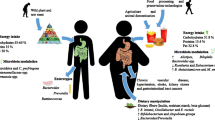
Abstract
The prevalence of obesity is rapidly becoming endemic in industrialized countries and continues to increase in developing countries worldwide. Obesity predisposes people to an increased risk of developing metabolic syndrome. Recent studies have described an association between obesity and certain gut microbiota, suggesting that gut microbiota might play a critical role in the development of obesity. Although probiotics have many beneficial health effects in humans and animals, attention has only recently been drawn to manipulating the gut microbiota, such as lactic acid bacteria (LAB), to influence the development of obesity. In this review, we first describe the causes of obesity, including the genetic and environmental factors. We then describe the relationship between the gut microbiota and obesity, and the mechanisms by which the gut microbiota influence energy metabolism and inflammation in obesity. Lastly, we focus on the potential role of LAB in mediating the effects of the gut microbiota in the development of obesity.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal J, Swami G, Kumar M (2013) Probiotics and their effects on metabolic diseases: an update. J Clin Diagn Res 7:173–177
Ahima RS, Flier JS (2000) Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. Trends Endocrinol Metab 11:327–332
Alberti KG, Zimmet P, Shaw J (2005) The metabolic syndrome—a new worldwide definition. Lancet 366:1059–1062
Anagnostis P, Athyros VG, Tziomalos K, Karagiannis A, Mikhailidis DP (2009) Clinical review: the pathogenetic role of cortisol in the metabolic syndrome: a hypothesis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94:2692–2701
Arora T, Anastasovska J, Gibson G, Tuohy K, Sharma RK, Bell J, Frost G (2012) Effect of Lactobacillus acidophilus NCDC 13 supplementation on the progression of obesity in diet-induced obese mice. Br J Nutr 108:1382–1389
Backhed F, Ding H, Wang T, Hooper LV, Koh GY, Nagy A, Semenkovich CF, Gordon JI (2004) The gut microbiota as an environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:15718–15723
Backhed F, Manchester JK, Semenkovich CF, Gordon JI (2007) Mechanisms underlying the resistance to diet-induced obesity in germ-free mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:979–984
Bray GA (2004) Medical consequences of obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:2583–2589
Burkman RT (2002) Venous thromboembolism and oral contraceptives: current status and clinical implications. Treat Endocrinol 1:143–147
Cai D, Yuan M, Frantz DF, Melendez PA, Hansen L, Lee J, Shoelson SE (2005) Local and systemic insulin resistance resulting from hepatic activation of IKK-beta and NF-kappaB. Nat Med 11:183–190
Cani PD, Neyrinck AM, Fava F, Knauf C, Burcelin RG, Tuohy KM, Gibson GR, Delzenne NM (2007) Selective increases of bifidobacteria in gut microflora improve high-fat-diet-induced diabetes in mice through a mechanism associated with endotoxaemia. Diabetologia 50:2374–2383
Cani PD, Bibiloni R, Knauf C, Waget A, Neyrinck AM, Delzenne NM, Burcelin R (2008) Changes in gut microbiota control metabolic endotoxemia-induced inflammation in high-fat diet-induced obesity and diabetes in mice. Diabetes 57:1470–1481
Cani PD, Possemiers S, Van de Wiele T, Guiot Y, Everard A, Rottier O, Geurts L, Naslain D, Neyrinck A, Lambert DM, Muccioli GG, Delzenne NM (2009) Changes in gut microbiota control inflammation in obese mice through a mechanism involving GLP-2-driven improvement of gut permeability. Gut 58:1091–1103
Choi I, Kim Y, Park Y, Seog H, Choi H (2007) Anti-obesity activities of fermented soygerm isoflavones by Bifidobacterium breve. Biofactors 29:105–112
Claesson MJ, Cusack S, O'Sullivan O, Greene-Diniz R, de Weerd H, Flannery E, Marchesi JR, Falush D, Dinan T, Fitzgerald G, Stanton C, van Sinderen D, O'Connor M, Harnedy N, O'Connor K, Henry C, O'Mahony D, Fitzgerald AP, Shanahan F, Twomey C, Hill C, Ross RP, O'Toole PW (2011) Composition, variability, and temporal stability of the intestinal microbiota of the elderly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108(Suppl 1):4586–4591
Clarke SF, Murphy EF, O'Sullivan O, Ross RP, O'Toole PW, Shanahan F, Cotter PD (2013) Targeting the microbiota to address diet-induced obesity: a time dependent challenge. PLoS One 8:e65790
Commerford SR, Pagliassotti MJ, Melby CL, Wei Y, Gayles EC, Hill JO (2000) Fat oxidation, lipolysis, and free fatty acid cycling in obesity-prone and obesity-resistant rats. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 279:E875–E885
Cotter PD, Hill C, Ross RP (2005) Bacteriocins: developing innate immunity for food. Nat Rev Microbiol 3:777–788
de Hartog JJ, Lanki T, Timonen KL, Hoek G, Janssen NA, Ibald-Mulli A, Peters A, Heinrich J, Tarkiainen TH, van Grieken R, van Wijnen JH, Brunekreef B, Pekkanen J (2009) Associations between PM2.5 and heart rate variability are modified by particle composition and beta-blocker use in patients with coronary heart disease. Environ Health Perspect 117:105–111
de Vrese M, Schrezenmeir J (2008) Probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 111:1–66
Decaria JE, Sharp C, Petrella RJ (2012) Scoping review report: obesity in older adults. Int J Obes (Lond) 36:1141–1150
Delzenne NM, Neyrinck AM, Backhed F, Cani PD (2011) Targeting gut microbiota in obesity: effects of prebiotics and probiotics. Nat Rev Endocrinol 7:639–646
Drago L, Gismondo MR, Lombardi A, de Haen C, Gozzini L (1997) Inhibition of in vitro growth of enteropathogens by new Lactobacillus isolates of human intestinal origin. FEMS Microbiol Lett 153:455–463
Enriori PJ, Evans AE, Sinnayah P, Cowley MA (2006) Leptin resistance and obesity. Obesity (Silver Spring) 14(Suppl 5):254S–258S
Esposito E, Iacono A, Bianco G, Autore G, Cuzzocrea S, Vajro P, Canani RB, Calignano A, Raso GM, Meli R (2009) Probiotics reduce the inflammatory response induced by a high-fat diet in the liver of young rats. J Nutr 139:905–911
Gerritsen J, Smidt H, Rijkers GT, de Vos WM (2011) Intestinal microbiota in human health and disease: the impact of probiotics. Genes Nutr 6:209–240
Hill JO (2006) Understanding and addressing the epidemic of obesity: an energy balance perspective. Endocr Rev 27:750–761
Hooper LV, Wong MH, Thelin A, Hansson L, Falk PG, Gordon JI (2001) Molecular analysis of commensal host-microbial relationships in the intestine. Science 291:881–884
Howland RH (2008) Pharmacotherapy for psychotropic drug-related weight gain. J Psychosoc Nurs Ment Health Serv 46:15–18
Kadooka Y, Sato M, Imaizumi K, Ogawa A, Ikuyama K, Akai Y, Okano M, Kagoshima M, Tsuchida T (2010) Regulation of abdominal adiposity by probiotics (Lactobacillus gasseri SBT2055) in adults with obese tendencies in a randomized controlled trial. Eur J Clin Nutr 64:636–643
Kahn SE, Hull RL, Utzschneider KM (2006) Mechanisms linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nature 444:840–846
Kang JH, Yun SI, Park MH, Park JH, Jeong SY, Park HO (2013) Anti-obesity effect of Lactobacillus gasseri BNR17 in high-sucrose diet-induced obese mice. PLoS One 8:e54617
Kaoutari AE, Armougom F, Gordon JI, Raoult D, Henrissat B (2013) The abundance and variety of carbohydrate-active enzymes in the human gut microbiota. Nat Rev Microbiol 11:497–504
Kim NH, Moon PD, Kim SJ, Choi IY, An HJ, Myung NY, Jeong HJ, Um JY, Hong SH, Kim HM (2008) Lipid profile lowering effect of Soypro fermented with lactic acid bacteria isolated from Kimchi in high-fat diet-induced obese rats. Biofactors 33:49–60
Kolata GB (2007) Rethinking thin: the new science of weight loss—and the myths and realities of dieting. Farrar Straus and Giroux, New York
Kondo S, Xiao JZ, Satoh T, Odamaki T, Takahashi S, Sugahara H, Yaeshima T, Iwatsuki K, Kamei A, Abe K (2010) Antiobesity effects of Bifidobacterium breve strain B-3 supplementation in a mouse model with high-fat diet-induced obesity. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 74:1656–1661
Laugerette F, Vors C, Peretti N, Michalski MC (2011) Complex links between dietary lipids, endogenous endotoxins and metabolic inflammation. Biochimie 93:39–45
Lee BH, Lo YH, Pan TM (2013) Anti-obesity activity of Lactobacillus fermented soy milk products. J Funct Foods 5:905–913
Ley RE (2010) Obesity and the human microbiome. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 26:5–11
Ley RE, Backhed F, Turnbaugh P, Lozupone CA, Knight RD, Gordon JI (2005) Obesity alters gut microbial ecology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:11070–11075
Ley RE, Turnbaugh PJ, Klein S, Gordon JI (2006) Microbial ecology: human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature 444:1022–1023
Loos RJ, Bouchard C (2008) FTO: the first gene contributing to common forms of human obesity. Obes Rev 9:246–250
Masi LN, Martins AR, Rosa Neto JC, do Amaral CL, Crisma AR, Vinolo MA, de Lima Junior EA, Hirabara SM, Curi R (2012) Sunflower oil supplementation has proinflammatory effects and does not reverse insulin resistance in obesity induced by high-fat diet in C57BL/6 mice. J Biomed Biotechnol. doi:10.1155/2012/945131
Matarese G, Mantzoros C, La Cava A (2007) Leptin and adipocytokines: bridging the gap between immunity and atherosclerosis. Curr Pharm Des 13:3676–3680
Meydani SN, Ha WK (2000) Immunologic effects of yogurt. Am J Clin Nutr 71:861–872
Miller LJ (2009) Management of atypical antipsychotic drug-induced weight gain: focus on metformin. Pharmacotherapy 29:725–735
Morrison RF, Farmer SR (1999) Insights into the transcriptional control of adipocyte differentiation. J Cell Biochem Suppl 32–33:59–67
Murphy EF, Cotter PD, Hogan A, O'Sullivan O, Joyce A, Fouhy F, Clarke SF, Marques TM, O'Toole PW, Stanton C, Quigley EM, Daly C, Ross PR, O'Doherty RM, Shanahan F (2013) Divergent metabolic outcomes arising from targeted manipulation of the gut microbiota in diet-induced obesity. Gut 62:220–226
Newman L, Haryono R, Keast R (2013) Functionality of fatty acid chemoreception: a potential factor in the development of obesity? Nutrients 5:1287–1300
Ohland CL, Macnaughton WK (2010) Probiotic bacteria and intestinal epithelial barrier function. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 298:G807–G819
Ouwehand AC, Isolauri E, Kirjavainen PV, Tolkko S, Salminen SJ (2000) The mucus binding of Bifidobacterium lactis Bb12 is enhanced in the presence of Lactobacillus GG and Lact. delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus. Lett Appl Microbiol 30:10–13
Owen J, Reisin E (2012) Non-communicable disease: a welcome and long needed addition to the WHO's 2012 World Health Statistics. Curr Hypertens Rep 14:475–477
Park DY, Ahn YT, Park SH, Huh CS, Yoo SR, Yu R, Sung MK, McGregor RA, Choi MS (2013) Supplementation of Lactobacillus curvatus HY7601 and Lactobacillus plantarum KY1032 in diet-induced obese mice is associated with gut microbial changes and reduction in obesity. PLoS One 8:e59470
Parnell JA, Reimer RA (2012) Prebiotic fiber modulation of the gut microbiota improves risk factors for obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Gut Microbes 3:29–34
Pascual M, Hugas M, Badiola JI, Monfort JM, Garriga M (1999) Lactobacillus salivarius CTC2197 prevents Salmonella enteritidis colonization in chickens. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:4981–4986
Poirier P, Giles TD, Bray GA, Hong Y, Stern JS, Pi-Sunyer FX, Eckel RH (2006) Obesity and cardiovascular disease: pathophysiology, evaluation, and effect of weight loss. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 26:968–976
Sakai T, Taki T, Nakamoto A, Shuto E, Tsutsumi R, Toshimitsu T, Makino S, Ikegami S (2013) Lactobacillus plantarum OLL2712 regulates glucose metabolism in C57BL/6 mice fed a high-fat diet. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo) 59:144–147
Samuel BS, Shaito A, Motoike T, Rey FE, Backhed F, Manchester JK, Hammer RE, Williams SC, Crowley J, Yanagisawa M, Gordon JI (2008) Effects of the gut microbiota on host adiposity are modulated by the short-chain fatty-acid binding G protein-coupled receptor, Gpr41. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:16767–16772
Scarpellini E, Campanale M, Leone D, Purchiaroni F, Vitale G, Lauritano EC, Gasbarrini A (2010) Gut microbiota and obesity. Intern Emerg Med 5(Suppl 1):S53–S56
Shoelson SE, Herrero L, Naaz A (2007) Obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Gastroenterology 132:2169–2180
Takemura N, Okubo T, Sonoyama K (2010) Lactobacillus plantarum strain no. 14 reduces adipocyte size in mice fed high-fat diet. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 235:849–856
Tappy L, Le KA (2010) Metabolic effects of fructose and the worldwide increase in obesity. Physiol Rev 90:23–46
Tilg H (2010) Obesity, metabolic syndrome, and microbiota: multiple interactions. J Clin Gastroenterol 44(Suppl 1):S16–S18
Tsai YT, Cheng PC, Fan CK, Pan TM (2008) Time-dependent persistence of enhanced immune response by a potential probiotic strain Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei NTU 101. Int J Food Microbiol 128:219–225
Tsai YT, Cheng PC, Pan TM (2010) Immunomodulating activity of Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei NTU 101 in enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7-infected mice. J Agric Food Chem 58:11265–11272
Turnbaugh PJ, Hamady M, Yatsunenko T, Cantarel BL, Duncan A, Ley RE, Sogin ML, Jones WJ, Roe BA, Affourtit JP, Egholm M, Henrissat B, Heath AC, Knight R, Gordon JI (2009) A core gut microbiome in obese and lean twins. Nature 457:480–484
Uemura H, Katsuura-Kamano S, Yamaguchi M, Nakamoto M, Hiyoshi M, Arisawa K (2013) Abundant daily non-sedentary activity is associated with reduced prevalence of metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance. J Endocrinol Invest. doi:10.3275/9066
Vijay-Kumar M, Aitken JD, Carvalho FA, Cullender TC, Mwangi S, Srinivasan S, Sitaraman SV, Knight R, Ley RE, Gewirtz AT (2010) Metabolic syndrome and altered gut microbiota in mice lacking Toll-like receptor 5. Science 328:228–231
Voshol PJ, Rensen PC, van Dijk KW, Romijn JA, Havekes LM (2009) Effect of plasma triglyceride metabolism on lipid storage in adipose tissue: studies using genetically engineered mouse models. Biochim Biophys Acta 1791:479–485
Weisberg SP, McCann D, Desai M, Rosenbaum M, Leibel RL, Ferrante AW Jr (2003) Obesity is associated with macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J Clin Invest 112:1796–1808
Xu J, Gordon JI (2003) Honor thy symbionts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:10452–10459
Xu J, Mahowald MA, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, Hamady M, Martens EC, Henrissat B, Coutinho PM, Minx P, Latreille P, Cordum H, Van Brunt A, Kim K, Fulton RS, Fulton LA, Clifton SW, Wilson RK, Knight RD, Gordon JI (2007) Evolution of symbiotic bacteria in the distal human intestine. PLoS Biol 5:e156
Yadav H, Lee JH, Lloyd J, Walter P, Rane SG (2013) Beneficial metabolic effects of a probiotic via butyrate induced GLP-1 secretion. J Biol Chem. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.452516
Yin YN, Yu QF, Fu N, Liu XW, Lu FG (2010) Effects of four Bifidobacteria on obesity in high-fat diet induced rats. World J Gastroenterol 16:3394–3401
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yueh-Ting Tsai and Po-Ching Cheng contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsai, YT., Cheng, PC. & Pan, TM. Anti-obesity effects of gut microbiota are associated with lactic acid bacteria. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98, 1–10 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5346-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5346-3