Abstract
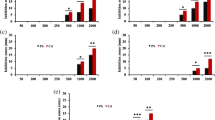
Accumulation of toxic metal ions in food and water is nowadays a growing health-related problem. One detoxification method involves the use of microorganisms naturally inhabiting the gastrointestinal tract (GIT). The purpose of this study was to prove that lactic acid bacteria derived from the GIT are able to effectively remove Cd2+ from water solution. Seven strains of lactobacilli, out of 11 examined, showed tolerance to high concentrations of cadmium ions. The metal-removal efficiencies of these seven lactobacilli ranged from 6 to 138.4 μg/h mg. Among these bacteria, Lactobacillus gallinarum and Lactobacillus crispatus belonged to the highest (85%) Cd-removal efficiency class. An analysis of the zeta potential (ζ) indicated that the bacterial cell surface had a negative charge at the pH ranging from 3 to 10. The presence of carboxyl, amide, and phosphate groups was favorable for Cd2+ binding to the cell surface, which found confirmation in FTIR-ATR spectra. Elemental SEM/EDS analysis and TEM imaging not only confirmed the adsorption of Cd2+ on the cell envelope but also gave us a reason to suppose that Lb. crispatus accumulates metal ions inside the cell. Our findings open perspectives for further research on the new biological function of GIT lactobacilli as natural biosorbents.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhakta JN, Ohnishi K, Munekage Y, Iwasaki K, Wei MQ (2012) Characterization of lactic acid bacteria-based probiotics as potential heavy metal sorbents. J Appl Microbiol 112:1193–1206
Boonaert CJ, Rouxhet PG (2000) Surface of lactic acid bacteria: relationships between chemical composition and physicochemical properties. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:2548–2554
Cieśla J, Bieganowski A, Janczarek M, Urbanik-Sypniewska T (2011) Determination of the electrokinetic potential of Rhizobium legumnosarum bv. trifolii Rt24.2 using laser Doppler velocimetry—a methodological study. J Microbiol Methods 85:199–205
Costello EK, Gordon JI, Secor SM, Knight R (2010) Postprandial remodeling of the gut microbiota in Burmese pythons. ISME J 11:1375–1385
Deepika G, Green RJ, Frazier RA, Charalampopoulos D (2009) Effect of growth time on the surface and adhesion properties of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG. J Appl Microbiol 107:1230–1240
Delgado AV, Gonzales-Caballero F, Hunter RJ, Koopal LK, Lyklema J (2007) Measurement and interpretation of electrokinetic phenomena. J Colloid Interface Sci 309:194–224
Egan SK, Bolger PM, Carrington CD (2007) Update of US FDA’s total diet study food list and diets. J Expos Sci Environ Epidemiol 17:573–582
François F, Lombard C, Guigner JM, Soreau P, Brian-Jaisson F, Martino G, Vandervennet M, Garcia D, Molinier AL, Pignol D, Peduzzi J, Zirah S, Rebuffata S (2012) Isolation and characterization of environmental bacteria capable of extracellular biosorption of mercury. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(4):1097–1106
Gong X, Yu H, Chen J, Han B (2012) Cell surface properties Lactobacillus salivarius under osmotic stress. Eur Food Res Technol 234:671–678
Halttunen T, Salminen S, Meriluoto J, Tahvonen R, Lertola K (2008) Reversible surface binding of cadmium and lead by lactic acid and bifidobacteria. Int J Food Microbiol 125:170–175
Haltunnen T, Salminen S, Tahvonen R (2007) Rapid removal of lead and cadmium from water by specific lactic acid bacteria. Int J Food Microbiol 114:30–35
Hoving ME, Sowers M, Humphrey HEB (1993) Environmental exposure and lifestyle predictors of lead, cadmium, PCB, and DDT levels in Great Lake fish eaters. Arch Environ Health 48:98–104
Huang W, Liu Z (2013) Biosorption of Cd(II)/Pb(II) from aqueous solution by biosurfactant-producing bacteria: isotherm kinetic characteristic and mechanism studies. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 105:113–119
Ibrahim F, Halttunen T, Tahvonen R, Salminen S (2006) Probiotic bacteria as potential detoxification tools: assessing their heavy metal binding isotherms. Can J Microbiol 52:877–885
Karasov WH, Martinez del Rio C (2007) Physiological ecology: how animals process energy, nutrients, and toxins. How Animals Deal with Poisons and Pollutants. Princeton University Press, Princeton, pp 479–518
Kaur S, Kamli MR, Ali A (2011) Role of arsenic and its resistance in nature. Can J Microbiol 57:769–774
Kim YO, Patel DH, Lee DS, Song Y, Bae HJ (2011) High cadmium binding ability of a novel Colocasia esculenta metallothionein increases cadmium tolerance in Escherichia coli and tobacco. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 75:1912–1920
Kinoshita H, Sohma Y, Ohtake F, Ishida M, Kawai Y, Kitazawa H, Saito T, Kimura K (2013) Biosorption of heavy metals by lactic acid bacteria and identification of mercury binding protein. Res Microbiol 164:701–709
Kohl KD (2012) Diversity and function of the avian gut microbiota. J Comp Physiol B 182:591–602
Leitch S, Bradley MJ, Rowe JL, Chivers PT, Maroney MJ (2007) Nickel-specific response in the transcriptional regulator, Escherichia coli NikR. J Am Chem Soc 129:5085–5095
Leser TD, Mølbak L (2009) Better living through microbial action: the benefits of the mammalian gastrointestinal microbiota on the host. Environ Microbiol 11:2194–2206
Llobet JM, Falcό G, Casas C, Teixidό A, Domingo JL (2003) Concentrations of arsenic, cadmium, mercury, and lead in common foods and estimated daily intake by children, adolescents, adults, and seniors of Catalonia, Spain. J Agric Food Chem 51:838–842
Lόpez E, Arce C, Oset-Gasque MJ, Caňadas S, González MP (2006) Cadmium induces reactive oxygen species generation and lipid peroxidation in cortical neurons in culture. Free Radic Biol Med 40:940–951
Millsap KW, Raid G, van der Mei HC, Bussher HJ (1996) Adhesion of Lactobacillus species in urine and phosphate buffer to silicone rubber and glass under flow. Biomaterials 18:87–91
Monachese M, Burton JP, Reid G (2012) Bioremediation and tolerance of humans to heavy metals through microbial processes: a potential role for probiotics? Appl Environ Microbiol 78(18):6397–6404
Olsson I, Bensryd I, Lundh T, Ottosson H, Skerfving S, Oskarsson A (2002) Cadmium in blood and urine: impact of age, sex, dietary intake, iron status, and former smoking: association of renal effects. Environ Health Perspect 110:1185–1190
Pazirandeh M, Wells BM, Ryan RL (1998) Development of bacterium-based heavy metal biosorbents: enhanced uptake of cadmium and mercury by Escherichia coli expressing a metal binding motif. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:4068–4072
Polak-Berecka M, Waśko A, Szwajgier D, Choma A (2013) Bifidogenic and antioxidant activity of exopolysaccharides produced by Lactobacillus rhamnosus E/N on different carbon sources. Polish J Microbiol 62(2):181–189
Polak-Berecka M, Szwajgier D, Waśko A (2014a) Biosorption of Al+3 and Cd+2 by an exopolysaccharide from Lactobacillus rhamnosus. J Food Sci 79(11):T2404–T2408
Polak-Berecka M, Waśko A, Paduch R, Skrzypek T, Sroka-Bartnicka A (2014b) The effect of cell surface components on adhesion ability of Lactobacillus rhamnosus. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 106:751–762
Ravikumar S, Yoo IK, Lee SY, Hong SH (2011) Construction of copper removing bacteria through the integration of two-component system and cell surface display. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 165:1674–1681
Reid G, Bialkowska-Hobrzanska H, van der Mei HC, Busscher HJ (1999) Correlation between genetic, physico-chemical surface characteristics and adhesion of four strains of Lactobacillus. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 13:75–81
Rossi M, Martínez-Martínez D, Amaretti A, Ulrici A, Raimondi S, Moya A (2016) Mining metagenomic whole genome sequences revealed subdominant but constant Lactobacillus population in the human gut microbiota. Environ Microbiol Rep 8(3):399–406
Saha JK, Panwar NR, Singh NR (2010) Determination of lead and cadmium concentration limits in agricultural soil land municipal soil waste compost through an approach of zero tolerance to food contamination. Environ Monit Assess 168:397–406
Schut S, Zauner S, Hampel G, König H, Claus H (2011) Biosorption of copper by wine-relevant lactobacilli. Int J Food Microbiol 145:126–131
Sinha V, Mishra R, Kumar A, Kannan A, Upreti RK (2011) Amplification of arsH gene in Lactobacillus acidophilus resistant to arsenite. Biotechnol 10:101–107
Srivastava S, Verma PC, Singh A, Mishra M, Singh N, Sharma N, Singh N (2012) Isolation and characterization of Staphylococcus sp. strain NBRIEAG-8 from arsenic contaminated site of West Bengal. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 95(5):1275–1291
Teemu H, Seppo S, Jussi M, Raija T, Kalle L (2008) Reversible surface binding of cadmium and lead by lactic acid and bifidobacteria. Int J Food Microbiol 125:170–175
Walter J (2008) Ecological role of lactobacilli in the gastrointestinal tract: implications for fundamental and biomedical research. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(16):4985–4996
Weser U, Rupp H, Donay F, Linnemann F, Voelter W, Voetsch W, Jung G (1973) Characterization of Cd, Zn-thionein (metallothionein) isolated from rat and chicken liver. Eur J Biochem 39:127–140
Wilson WW, Wade MM, Holman SC, Champlin FR (2001) Status of methods for assessing bacterial cell surface charge properties based on zeta potential measurements. J Microbiol Methods 43:153–164
Young JC, Zhou T, Yu H, Zhu H, Gong J (2007) Degradation of trichothecene mycotoxins by chicken intestinal microbes. Food Chem Toxicol 45:136–143
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Polak-Berecka, M., Boguta, P., Cieśla, J. et al. Studies on the removal of Cd ions by gastrointestinal lactobacilli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101, 3415–3425 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-8048-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-8048-9