Abstract
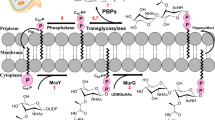
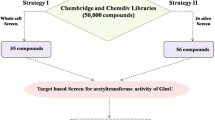
Bacterial cell has always been an attractive target for anti-infective drug discovery. MurA (UDP-N-acetylglucosamine enolpyruvyl transferase) enzyme of Escherichia coli (E.coli) is crucial for peptidoglycan biosynthetic pathway, as it is involved in the early stages of bacterial cell wall biosynthesis. In the present study we aim to identify novel chemical structures targeting the MurA enzyme. For screening purpose, we used in silico approach (pharmacophore based strategy) for 52,026 library compounds (Chembridge, Chemdiv and in house synthetics) which resulted in identification of 50 compounds. These compounds were screened in vitro against MurA enzyme and release of inorganic phosphate (Pi) was estimated. Two compounds (IN00152 and IN00156) were found to inhibit MurA enzyme > 70% in primary screening and IC50 of 14.03 to 32.30 μM respectively. These two hits were further evaluated for their mode of inhibition studies and whole-cell activity where we observed 2-4 folds increase in activity in presence of Permeabilizer EDTA (Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid). Combination studies were also performed with known antibiotics in presence of EDTA. Hits are reported for the first time against this target and our report also support the use of OM permeabilizer in combination with antibacterial compounds to address the permeability and efficacy issue. These lead hits can be further optimized for drug discovery.
Key points
• Emerging Gram negative resistant strains is a matter of concern.
• Need for new screening strategies to cope with drying up antibiotics pipeline.
• Outer membrane permeabilizers could be useful to improve potency of molecules to reach its target.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Data will be made available on reasonable request.
References
Avery LM, Sutherland CA, Nicolau DP (2019) Prevalence of in vitro synergistic antibiotic interaction between fosfomycin and non susceptible antimicrobials in carbapenem resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Med Microbiol 68(6):893–897. https://doi.org/10.1099/jmm.0.000984
Bachelier A, Mayer R, Klein CD (2006) Sesquiterpene lactones are potent and irreversible inhibitors of the antibacterial target enzyme MurA. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16:5605–5609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2006.08.021
Bassetti M, Ginocchio F, Mikulska M (2011) New treatment options against gram-negative organisms. Critical Care 15(2):215. https://doi.org/10.1186/cc9997
Baum EZ, Montenegro DA, Licata L, Turchi I, Webb GC, Foleno BD, Bush K (2001) Identification and characterization of new inhibitors of the Escherichia coli MurA enzyme. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 45:3182–3188. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.45.11.3182-3188.2001
Bourjilat F, Bouchrif B, Dersi N, Claude JDPG, Amarouch H, Timinouni M (2011) Emergence of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli in community-acquired urinary infections in Casablanca, Morocco. J Infect Dev Ctries 5(12):850–855. https://doi.org/10.3855/jidc.1490
Brown ED, Marquardt JL, Lee JP, Walsh CT, Anderson KS (1994) Detection and characterization of a phospholactoyl-enzyme adduct in the reaction catalyzed by UDP-N-acetylglucosamine enolpyruvoyl transferase, MurZ. Biochemistry 33(35):10638–10645. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00201a010
Brown ED, Vivas EI, Walsh CT, Kolter R (1995) MurA (MurZ), the enzyme that catalyzes the first committed step in peptidoglycan biosynthesis, is essential in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 177:4194–4197. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.177.14.4194-4197.1995
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2013) Antibiotic resistance threats in the United States. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Atlanta, GA: CDC: 2013
Christensen BG, Leanza WJ, Beattie TR, Patchett AA, Arison BH, Ormond RE, Kuehl JFA, Albers-Schonberg G, Jardetzky O (1969) Phosphonomycin: structure and synthesis. Science 166(3901):123–125. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.166.3901.123
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (2009) Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bacteria that grow aerobically: approved standard, vol 2, 9th Ed., M07-A8. CLSI, Wayne, PA
Copeland RA (2004) Enzymes: a practical introduction to structure, mechanism, and data analysis, 2nd edn. Wiley, NY
Dai HJ, Parker CN, Bao JJ (2002) Characterization and inhibition study of MurA enzyme by capillary electrophoresis. J Chromatogr B 766(1):123–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4347(01)00461-3
Dixon SL, Smondyrev AM, Rao SN (2006) PHASE: A novel approach to pharmacophore modeling and 3D database searching. Chem Biol Drug Des 67(5):370–372. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1747-0285.2006.00384.x
Dorsey WC, Tchounwou PB, Sutton D (2004) Mitogenic and cytotoxic effects of pentachlorophenol to AML 12 mouse hepatocytes. Int J Environ Res Publ Health 1:100–105. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph2004020100
Dunsmore CJ, Miller K, Blake KL, Patching SG, Henderson PJF, Garnett JA, Stubbings WJ, Phillips SEV, Palestrant DJ, Los Angeles JD, Leeds JA, Chopra I, Fishwick CWG (2008) 2-Aminotetralones: novel inhibitors of MurA and MurZ. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18:1730–1734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2008.01.089
El Zoeiby A, Sanschagrin F, Levesque RC (2003) Structure and function of the Mur enzymes: development of novel inhibitors. Mol Microbiol 47:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03289.x
Eniyan K, Kumar A, Rayasam GV, Perdih A, Bajpai U (2016) Development of a one-pot assay for screening and identification of Mur pathway inhibitors in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Sci Rep 6:35134. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep35134
Eschenburg S, Schonbrunn E (2000) Comparative X-Ray Analysis of the Un-Liganded Fosfomycin-Target MurA. Proteins Struct Funct Genet 40:290–298. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0134(20000801)
Eschenburg S, Priestman M, Schonbrunn E (2004) Evidence that the fosfomycin target Cys115 in UDP-N acetylglucosamine enolpyruvyl transferase (MurA) is essential for product release. J Biol Chem 280:3757–3763. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M411325200
Eschenburg S, Priestman MA, Abdul-Latif FA, Delachaume C, Fassy F, Schoenbrunn E (2005) A novel inhibitor that suspends the induced fit mechanism of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine enolpyruvyl transferase (MurA). J Bio Chem 280:14070–14075. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M414412200
Farrag HA, Abdallah N, Shehata MMK, Awad EM (2019) Natural outer membrane permeabilizers boost antibiotic action against irradiated resistant bacteria. J Biomed Sci 26:69. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12929-019-0561-6
Gautam A, Rishi P, Tewari R (2011) UDP-N-acetylglucosamine enolpyruvyl transferase as a potential target for antibacterial chemotherapy: recent developments. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol potential 92:211–225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3512-z
Haque H, Russell AD (1974) Effect of Chelating Agents on the Susceptibility of Some Strains of Gram-Negative Bacteria to Some Antibacterial Agents. Antimicrob Ag Chemother 6(2):200–206. https://doi.org/10.1128/aac.6.2.200
Hendlin D, Stapley EO, Jackson M, Wallick H, Miller AK, Wolf FJ, Miller TW, Chaiet L, Kahan FM, Foltz EL, Woodruff HB, Mata JM, Hernandez S, Mochales S (1969) Phosphonomycin, a new antibiotic produced by strains of streptomyces. Science 166:122–123. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.166.3901.122
Kahan FM, Kahan JS, Cassidy PJ, Kropp H (1974) The mechanism of action of fosfomycin (phosphonomycin). Ann NY Acad Sci 235:364–386. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb43277.x
Kim DH, Lees WJ, Kempsell KE, Lane WS, Duncan K, Walsh CT (1996) Characterization of a Cys115 to Asp substitution in the Escherichia coli cell wall biosynthetic enzyme UDP-GlcNAc Enolpyruvyl transferase (MurA) that Confers resistance to inactivation by the antibiotic fosfomycin. Biochemistry 35:4923–4928. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi952937w
King JB, West MB, Cook PF, Hanigan MH (2009) A novel, species-specific class of uncompetitive inhibitors of γ-Glutamyltranspeptidase. J Biol Chem 284(14):9059–9065. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M809608200
Konovalova S, Avdeenko A, Lubenets V, Novikov V (2020) Synthesis and bioactivity of benzohydrazide derivatives. Biointerface Res Appl Chem 10(4):5797–5802. https://doi.org/10.33263/BRIAC104.797802
Koul SK, Taneja SC, Sethi VK, Sharma A, Sarin AN, Chopra CL, Dhar KL (1990) Synthesis of antitubercular compounds based on the isoniazid model. Indian Drugs 27(4):227–238
Leive L (1965) Release of lipopolysaccharide by EDTA treatment of E. coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 21(4):290–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-291x(65)90191-9
LigPrep, Version 2.5, Schrodinger, LLC, New York, NY, 2012
Manikandan V, Balaji S, Senbagam R, Vijayakumar R, Rajarajan M, Vanangamudi G, Arulkumaran R, Sundararajan R, Thirunarayanan G (2017) Synthesis and antimicrobial activities of some (E)-N'-1-(substituted benzylidene) benzohydrazides. Int J Adv Chem 5(1):17–24. https://doi.org/10.14419/ijac.v5i1.7155
Marquardt JL, Siegele DA, Kolter R, Walsh CT (1992) Cloning and sequencing of Escherichia coli Mur Z and purification of its product, a UDP-N-acetylglucosamineenolpyruvyl transferase. J Bacteriol 174:5748–5752. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.174.17.5748-5758.1992
Marquardt JL, Brown ED, Walsh CT, Anderson KS (1993) Isolation and structural elucidation of a tetrahedral intermediate in the UDP-N-acetylglucosamine enolpyruvoyl transferase enzymatic pathway. J Am Chem Soc 115(22):10398–10399. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja00075a081
Marquardt JL, Brown ED, Lane WS, Haley TM, Ichikawa Y, Wong CH, Walsh CT (1994) Kinetics, stoichiometry and identification of the reactive thiolate in the inactivation of UDP-GlcNAc enolpyruvoyl transferase by the antibiotic fosfomycin. Biochemistry 33:10646–10651. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00201a011
McGovern SL, Caselli E, Grigorieff N, Shoichet BK (2002) A common mechanism underlying promiscuous inhibitors from virtual and high-throughput screening. J Med Chem 45:1712–1722. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm010533y
Mendgen T, Scholz T, Klein CD (2010) Structure–activity relationships of tulipalines, tuliposides, and related compounds as inhibitors of MurA. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20(19):5757–5762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.07.139
Miller K, Dunsmore CJ, Leeds JA, Patching SG, Sachdeva M, Blake KL, Stubbings WJ, Simmons KJ, Henderson PJF, Los Angeles JD, Fishwick CWG, Chopra I (2010) Benzothioxalone derivatives as novel inhibitors of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine enolpyruvyl transferases (MurA and MurZ ). J Antimicrob Chemother 65:2566–2573. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkq349
Osorio TM, Monache FD, Chiaradia ID, Mascarello A, Stumpf TR, Zanetti CR, Silveria DB, Monte Barardi CR, Albino Smania EF, Viancelli A, Totaro Garcia IA, Yunes RA, Jose NR, Smania A (2012) Antibacterial activity of chalcones, hydrazones and oxadiazoles against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 22:225–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2011.11.059
Pereira MP, Blanchard JE, Murphy C, Roderick SL, Brown ED (2009) High throughput screening identifies novel inhibitors of the acetyltransferase activity of E. coli GlmU. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 53:2306–2311. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.01572-08
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Sarkar P, Yarlagadda V, Ghosh C, Haldar J (2017) A review on cell wall synthesis inhibitors with an emphasis on glycopeptide antibiotics. Med Chem Comm 8(3):516–533. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6md00585c
Sastry GM, Adzhigirey M, Day T, Annabhimoju R, Sherman W (2013) Protein and ligand preparation: parameters, protocols, and influence on virtual screening enrichments. J comput Aided Mol Des 27(3):221–234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10822-013-9644-8
Scholz T, Heyl CL, Bernardi D, Zimmermann S, Kattner L, Klein CD (2013) Chemical, biochemical and microbiological properties of a brominated nitrovinylfuran with broad-spectrum antibacterial activity. Bioorg Med Chem 21(3):795–804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2012.11.018
Schonbrunn E, Sack S, Eschenburg S, Perrakis A, Krekel F, Amrhein N, Mandelkow E (1996) Crystal structure of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine enolpyruvyl transferase, the target of the antibiotic fosfomycin. Structure 4:1065–1075. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0969-2126(96)00113-X
Schonbrunn E, Svergun DI, Amrhein N, Koch MHJ (1998) Studies on the conformational changes in the bacterial cell wall biosynthetic enzyme UDP-N-acetyl glucosamine enolpyruvyl transferase (MurA). Eur J Biochem 253:406–412. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1432-1327.1998.2530406.x
Schwaber MJ, Carmeli Y (2007) Mortality and delay in effective therapy associated with extended-spectrum b-lactamase production in Enterobacteriaceae bacteraemia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Antimicrob Chemother 60(5):913–920. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkm318
Seong-Gu H, Lee WK, Jin BS, Lee KI, Lee HH, Yu JYG (2013) Identification of Novel Irreversible Inhibitors of UDP-N-Acetylglucosamine Enolpyruvyl Transferase (MurA) from Haemophilus influenzae. Microbiol Biotechnol 23(3):329–334. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1210.10053
Sherman W, Beard HS, Farid R (2006) Use of an induced fit receptor structure in virtual screening. Chembiol Drug Des 67(1):83–84. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1747-0285.2005.00327.x
Skarzynski T, Mistry A, Wonacott A, Hutchinson SE, Kelly VA, Duncan K (1996) Structure of UDP-N acetylglucosamine enolpyruvyl transferase, an enzyme essential for the synthesis of bacterial Peptidoglycan, complexed with substrate UDP-N-acetylglucosamine and the drug fosfomycin. Structure 4:1465–1474. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0969-2126(96)00153-0
Steinbach A, Scheidig AJ, Klein CD (2008) The unusual binding mode of Cnicin to the antibacterial target enzyme MurA revealed by X-ray Crystallography. J Med Chem 51:5143–5147. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm800609p
Umerska A, Strandh M, Cassisa V, Matougui N, Eveillard M, Saulnier P (2018) Synergistic effect of combinations containing EDTA and the antimicrobial peptide AA230, an Arenicin-3 Derivative, on Gram-negative bacteria. Biomolecules 8(4):122. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom8040122
Vaara M (1992) Agents that Increase the permeability of the outer membrane. Microbiol Rev 56(3):395–411
Van Heijenoort J (2001) Recent advances in the formation of the bacterial peptidoglycan monomer unit. Nature Prod Rep 18:503–519. https://doi.org/10.1039/A804532A
Watts KS, Dalal P, Murphy RB, Sherman W, Friesner RA, Shelley JC (2010) Conf Gen: A conformational search method for efficient generation of bioactive conformers. J Chem Inf Model 50(4):534–546. https://doi.org/10.1021/ci100015j
Wooley RE, Jones MS (1983) Action of EDTA-Tris and antimicrobial agent combinations on selected pathogenic bacteria. Vet Microbiol 8(3):271–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-1135(83)90079-2
World Health Organization (2014) Antimicrobial resistance: global report on surveillance. Geneva, World Health Organisation. Geneva,Switzerland: WHO:2014
Zhang JH, Chung TD, Oldenburg KR (1999) A simple statistical parameter for use in evaluation and validation of high throughput screening assays. J Biomol Screen 4:67–73. https://doi.org/10.1177/108705719900400206
Zhu JY, Yang Y, Han H, Betzi S, Olesen SH, Marsilio F, Schonbrunn E (2012) Functional Consequence of Covalent Reaction of Phosphoenolpyruvate with UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 1-Carboxyvinyltransferase (MurA). J Biol Chem 287(16):12657–12667. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.342725
Acknowledgments
Authors are thankful to the repository of CSIR-IIIM for providing library compounds. The manuscript bears Institutional Publication No. CSIR-IIIM/IPR/00232
Funding
This work was supported by Department of Health Research (DHR), New Delhi India (Grant no.GAP-2128)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DR performed the major experiments and wrote the manuscript.
HT performed the in silico screening of library.
SS and D contributed in cloning and assay optimization studies.
PKC synthesized the compounds.
AN guided the in silico and pharmacophore studies.
PLS designed the synthetic compounds.
KE and UB standardized the MurA assays.
RAV guided in the compound synthesis and overall manuscript.
FGK principal investigator of the project and contributed in the molecular biology studies.
SS provided into in the biological part and helped in the final draft preparation.
IAK conceptualized the whole manuscript and edited the draft and submitted the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not required.
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(PDF 429 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raina, D., Tiwari, H., Sharma, S. et al. Screening of compound library identifies novel inhibitors against the MurA enzyme of Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105, 3611–3623 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11272-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11272-4