Abstract
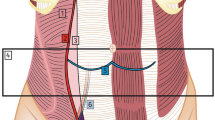
Deep gluteal syndrome (DGS) is an underdiagnosed entity characterized by pain and/or dysesthesias in the buttock area, hip or posterior thigh and/or radicular pain due to a non-discogenic sciatic nerve entrapment in the subgluteal space. Multiple pathologies have been incorporated in this all-included “piriformis syndrome,” a term that has nothing to do with the presence of fibrous bands, obturator internus/gemellus syndrome, quadratus femoris/ischiofemoral pathology, hamstring conditions, gluteal disorders and orthopedic causes. The concept of fibrous bands playing a role in causing symptoms related to sciatic nerve mobility and entrapment represents a radical change in the current diagnosis of and therapeutic approach to DGS. The development of periarticular hip endoscopy has led to an understanding of the pathophysiological mechanisms underlying piriformis syndrome, which has supported its further classification. A broad spectrum of known pathologies may be located nonspecifically in the subgluteal space and can therefore also trigger DGS. These can be classified as traumatic, iatrogenic, inflammatory/infectious, vascular, gynecologic and tumors/pseudo-tumors. Because of the ever-increasing use of advanced magnetic resonance neurography (MRN) techniques and the excellent outcomes of the new endoscopic treatment, radiologists must be aware of the anatomy and pathologic conditions of this space. MR imaging is the diagnostic procedure of choice for assessing DGS and may substantially influence the management of these patients. The infiltration test not only has a high diagnostic but also a therapeutic value. This article describes the subgluteal space anatomy, reviews known and new etiologies of DGS, and assesses the role of the radiologist in the diagnosis, treatment and postoperative evaluation of sciatic nerve entrapments, with emphasis on MR imaging and endoscopic correlation.



























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tibor LM, Sekiya JK. Differential diagnosis of pain around the hip joint. Arthroscopy. 2008;24(12):1407–21.
Martin HD, Shears SA, Johnson JC, Smathers AM, Palmer IJ. The endoscopic treatment of sciatic nerve entrapment/deep gluteal syndrome. Arthroscopy. 2011;27(2):172–81.
Martin HD, Palmer IJ, Hatem MA. Deep gluteal syndrome. In: Nho S, Leunig M, Kelly B, Bedi A, Larson C, editors. Hip arthroscopy and hip joint preservation surgery. New York: Springer; 2014. p. 1–17.
Guanche CA. Hip arthroscopy techniques: deep gluteal space access. In: Nho S, Leunig M, Kelly B, Bedi A, Larson C, editors. Hip arthroscopy and hip joint preservation surgery. New York: Springer; 2014. p. 1–12.
Kulcu DG, Naderi S. Differential diagnosis of intraspinal and extraspinal non-discogenic sciatica. J Clin Neurosci. 2008;15(11):1246–52.
Bierry G, Simeone FJ, Borg-Stein JP, Clavert P, Palmer WE. Sacrotuberous ligament: relationship to normal, torn, and retracted hamstring tendons on MR images. Radiology. 2014;271(1):162–71.
Coppieters MW, Alshami AM, Babri AS, Souvlis T, Kippers V, Hodges PW. Strain and excursion of the sciatic, tibial, and plantar nerves during a modified straight leg raising test. J Orthop Res. 2006;24(9):1883–9.
Martin HD, Kivlan BR, Palmer IJ, Martin RL. Diagnostic accuracy of clinical tests for sciatic nerve entrapment in the gluteal region. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014;22(4):882–8.
Ergun T, Lakadamyali H. CT and MRI in the evaluation of extraspinal sciatica. Br J Radiol. 2010;83(993):791–803.
Güvençer M, Akyer P, Iyem C, Tetik S, Naderi S. Anatomic considerations and the relationship between the piriformis muscle and the sciatic nerve. Surg Radiol Anat. 2008;30(6):467–74.
Papadopoulos EC, Khan SN. Piriformis syndrome and low back pain: a new classification and review of the literature. Orthop Clin North Am. 2004;35(1):65–71.
Foster MR. Piriformis syndrome. Orthopedics. 2002;25(8):821–5.
Lewis AM, Layzer R, Engstrom JW, Barbaro NM, Chin CT. Magnetic resonance neurography in extraspinal sciatica. Arch Neurol. 2006;63(10):1469–72.
Boyajian-O’Neill LA, McClain RL, Coleman MK, Thomas PP. Diagnosis and management of piriformis syndrome: an osteopathic approach. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2008;108:657–64.
Russell JM, Kransdorf MJ, Bancroft LW, Peterson JJ, Berquist TH, Bridges MD. Magnetic resonance imaging of the sacral plexus and piriformis muscles. Skeletal Radiol. 2008;37(8):709–13.
Benzon HT, Katz JA, Benzon HA, Iqbal MS. Piriformis syndrome: anatomic considerations, a new injection technique, and a review of the literature. Anesthesiology. 2003;98(6):1442–8.
Fanucci E, Masala S, Sodani G, Varrucciu V, Romagnoli A, Squillaci E, et al. CT-guided injection of botulinic toxin for percutaneous therapy of piriformis muscle syndrome with preliminary MRI results about denervative process. Eur Radiol. 2001;11(12):2543–8.
Dezawa A, Kusano S, Miki H. Arthroscopic release of the piriformis muscle under local anesthesia for piriformis syndrome. Arthroscopy. 2003;19(5):554–7.
Masala S, Crusco S, Meschini A, Taglieri A, Calabria E, Simonetti G. Piriformis syndrome: long-term follow-up in patients treated with percutaneous injection of anesthetic and corticosteroid under CT guidance. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2012;35(2):375–82.
Beaton LE, Anson BJ. The relation of the sciatic nerve and its subdivisions to the piriformis muscle. Anat Rec. 1937;70:1–5.
Smoll NR. Variations of the piriformis and sciatic nerve with clinical consequence: a review. Clin Anat. 2010;23(1):8–17.
Natsis K, Totlis T, Konstantinidis GA, Paraskevas G, Piagkou M, Koebke J. Anatomical variations between the sciatic nerve and the piriformis muscle: a contribution to surgical anatomy in piriformis syndrome. Surg Radiol Anat. 2014;36(3):273–80.
Güvençer M, Iyem C, Akyer P, Tetik S, Naderi S. Variations in the high division of the sciatic nerve and relationship between the sciatic nerve and the piriformis. Turk Neurosurg. 2009;19(2):139–44.
Windisch G, Braun EM, Anderhuber F. Piriformis muscle: clinical anatomy and consideration of the piriformis syndrome. Surg Radiol Anat. 2007;29(1):37–45.
Arora J, Mehta V, Kumar H, Suri RK, Rath G, Das S. A rare bimuscular conglomeration gluteopiriformis case report. Morphologie. 2010;94(305):40–3.
Filler AG, Gilmer-Hill H. Piriformis syndrome, obturator internus syndrome, pudendal nerve entrapment, and other pelvic entrapments. In: Winn HR, editor. Youmans neurological surgery. 6th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders; 2009. p. 2447–55.
Murata Y, Ogata S, Ikeda Y, Yamagata M. An unusual cause of sciatic pain as a result of the dynamic motion of the obturator internus muscle. Spine J. 2009;9(6):e16–8.
Meknas K, Kartus J, Letto JI, Christensen A, Johansen O. Surgical release of the internal obturator tendon for the treatment of retro-trochanteric pain syndrome: a prospective randomized study, with long-term follow-up. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2009;17(10):1249–56.
Kassarjian A, Tomas X, Cerezal L, Canga A, Llopis E. MRI of the quadratus femoris muscle: anatomic considerations and pathologic lesions. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;197(1):170–4.
Taneja AK, Bredella MA, Torriani M. Ischiofemoral impingement. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2013;21(1):65–73.
Torriani M, Souto SC, Thomas BJ, Ouellette H, Bredella MA. Ischiofemoral impingement syndrome: an entity with hip pain and abnormalities of the quadratus femoris muscle. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009;193(1):186–90.
Bucknor MD, Steinbach LS, Saloner D, Chin CT. Magnetic resonance neurography evaluation of chronic extraspinal sciatica after remote proximal hamstring injury: a preliminary retrospective analysis. J Neurosurg. 2014;121(2):408–14.
Chen CK, Yeh L, Chang WN, Pan HB, Yang CF. MRI diagnosis of contracture of the gluteus maximus muscle. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006;187(2):W169–174.
Delaney H1, Bencardino J, Rosenberg ZS. Magnetic resonance neurography of the pelvis and lumbosacral plexus. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2014;24(1):127–50.
Fabeck L, Tolley M, Rooze M, Burny F. Theoretical study of the decrease in the femoral neck anteversion during growth. Cells Tissues Organs. 2002;171:269–75.
Pace JB, Nagle D. Piriformis syndrome. West J Med. 1976;124:435–9.
Aaron M, Robert Layzer L, Engstrom JW, Barbaro NM, Chin CT. Magnetic resonance neurography in extraspinal sciatica. Arch Neurol. 2006;63:1469–72.
Chhabra A1, Chalian M, Soldatos T, Andreisek G, Faridian-Aragh N, Williams E. 3-T high-resolution MR neurography of sciatic neuropathy. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2012;198(4):W357–64.
Cejas C1, Aguilar M, Falcón L, Caneo N, Acuña MC. High resolution (3T) magnetic resonance neurography of the sciatic nerve. Radiología. 2013;55(3):195–202.
Filler AG, Haynes J, Jordan SE, et al. Sciatica of nondisc origin and piriformis syndrome: diagnosis by magnetic resonance neurography and interventional magnetic resonance imaging with outcome study of resulting treatment. J Neurosurg Spine. 2005;2:99–115.
Moore KR, Tsuruda JS, Dailey AT. The value of MR neurography for evaluating extraspinal neuropathic leg pain: a pictorial essay. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001;22:786–94.
Petchprapa CN, Rosenberg ZS, Sconfienza LM, Cavalcanti CF, Vieira RL, Zember JS. MR imaging of entrapment neuropathies of the lower extremity part 1. the pelvis and hip. Radiographics. 2010;30(4):983–1000.
Chalabra A, Andreisk G, Soldatos T, Wang KC. MR neurography: past, present, and future. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;197(3):583–91.
Chhabra A1, Zhao L, Carrino JA, Trueblood E, Koceski S, Shteriev F, Lenkinski L, Sinclair CD, Andreisek G. MR Neurography: Advances. Radiol Res Pract. 2013;2013:809568.
Guggenberger R, Markovic D, Eppenberger P, Chhabra A, Shiller A. Assessment of median nerve with MR neurography by using diffusion-tensor imaging: normative and pathologic diffusion values. Radiology. 2012;265(1):194–203.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Dr. Suzanne Anderson for her contribution to the revision of the translation of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare they do not have any conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Video 1
Normal excursion of the sciatic nerve. The video shows the sciatic nerve proximal excursion of 28.0 mm medially, toward the hip joint during hip flexion, adduction and internal rotation and leg raise with knee extension. (MP4 5618 kb)
Video 2
Fibrovascular band. The video shows the endoscopic resection of a fibrovascular band containing a macroscopically identifiable artery. Care must be taken during this procedure because of the high risk of bleeding. (MP4 14409 kb)
Video 3
Compressive or bridge-type band. The video shows a type 1B fibrous band, which limits the movement of the sciatic nerve compressing it from posterior to anterior. This fibrous band extends from the posterior border of the greater trochanter to the gluteus maximus and extends up to the greater sciatic notch. (MP4 9936 kb)
Endoscopic view of type-B Beaton and Anson piriformis muscle in the same patient shown in video 7. (MPG 21020 kb)
Video 5
Sciatic nerve entrapment secondary to fibrosis after open surgery of piriformis syndrome. The video shows bands anchored to the sciatic nerve in multiple directions with undefined distribution (type-3 bands) that prevent its proper mobility. (MP4 7527 kb)
Video 6
Sciatic nerve/obturator internus complex variation. The video shows an obturator internus penetrating the sciatic nerve and the subsequent endoscopic resection by radiofrequency of its tendon. (MP4 5978 kb)
Infiltration test. Axial MDCT video after performing the infiltration test shows the final distribution of the solution around the sciatic nerve throughout its length along the subgluteal space. (MOV 7779 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hernando, M.F., Cerezal, L., Pérez-Carro, L. et al. Deep gluteal syndrome: anatomy, imaging, and management of sciatic nerve entrapments in the subgluteal space. Skeletal Radiol 44, 919–934 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-015-2124-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-015-2124-6