Abstract
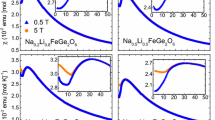
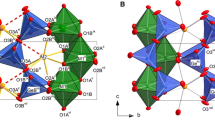
The pyroxene-type compound LiCrGe2O6, the Li- and Ge-analogue to the silicate mineral kosmochlor, has been synthesized at 1373 K and investigated by neutron diffraction between 0.5 and 1473 K in order to investigate the variation in magnetic and crystal structure with temperature. A structural phase transition from a low-temperature P21/c to a high-temperature C2/c structure was found around 1140 K. The two different structures exhibit different thermal expansion behavior with temperature with a reversal of the largest thermal expansion from the c-axis to the b-axis in the P21/c and C2/c phase, respectively. The structural phase transition is accompanied by a large volume increase of 1.9 % and sharp discontinuities in bond lengths, especially for the Li–O and—to a lesser extent—for the Cr–O bonds. At low temperature, some additional nonlinear changes in lattice parameters occur, which are associated with a magnetoelastic couplings of the lattice. Magnetic ordering is observed below 6 K in the neutron diffraction data. Data could be indexed with k = (0 0 0), giving rise to magnetic space group P21′/c. This model of the magnetic structure has a pure antiferromagnetic arrangement of spins, both within and between the M1 chains. The spins are oriented within the a–c plane with an almost nil component along [0 1 0]. A shift of the Cr atom out of the center in the equatorial plane of the octahedron is observed below 6 K and is associated with the magnetic phase transition.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angel R (2011) Win_Strain 4.11. http://www.rossangel.com/home.htm
Bertaut EF (1968) Representation analysis of magnetic structures. Acta Crystallogr A A24:217–231
Blundell SJ, Steer CA, Pratt FL, Marshall IM, Hayes W, Ward RCC (2003) Detection of magnetic order in the S = 1 chain compound LiVGe2O6 using implanted spin-polarized muons. Phys Rev 67:224411
Cámara F, Iezzi G, Oberti R (2003a) HT-XRD study of synthetic ferrian magnesian spodumene: the effect of site dimension on the P21/c ↔ C2/c phase transition. Phys Chem Miner 30:20–30
Cámara F, Carpenter MA, Domeneghetti MC, Tazzoli V (2003b) Coupling between non-convergent ordering and transition temperature in the C2/c ↔ P21/c phase transition in pigeonite. Am Mineral 88:1115–1128
Cámara F, Nestola F, Angel RJ, Ohashi H (2009) Spontaneous strain variations through the low-temperature displacive phase transition of LiGaSi2O6 clinoyproxene. Eur J Mineral 21:599–614
Goodenough JB (1963) Magnetism and the chemical bond. Wiley, New York
Hoelzel M, Senyhyn A, Gilles R, Boysen H, Fuess H (2007) The structure powder diffractometer SPODI. Neutron News 18(4):23–26
Janson O, Nénert G, Isobe M, Skourski Y, Ueda Y, Rosner H, Tsirlin AA (2014) Magnetic pyroxenes LiCrGe2O6 and LiCrSi2O6: dimensionality crossover in a non-frustrated S = 3/2 Heisenberg model. arXiv:1402.5054v1
Jodlauk S, Becker P, Mydosh JA, Khomskii DI, Lorenz T, Streltsov SV, Hezel DC, Bohaty L (2007) Pyroxenes: a new class of multiferroics. J Phys Condens Matters 19(43):432201
Knight KS (1996) A neutron powder diffraction determination of the thermal expansion tensor of crocoite (PbCrO4) between 60 K and 290 K. Mineral Mag 60:963–972
Litvin DB (2008) Tables of crystallographic properties of magnetic space groups. Acta Crystallogr A 64:419–424
Matsushita Y, Izumi F, Isobe M, Ueda Y (2010) Crystal structures of Cr-based magnetic pyroxenes. Solid State Sci 12(5):676–679
Nenert G, Ritter C, Isobe M, Isnard O, Vasiliev AN, Ueda Y (2009a) Magnetic and crystal structures of the one-dimensional ferromagnetic chain pyroxene NaCrGe2O6. Phys Rev B 80:024402
Nenert G, Isobe M, Ritter C, Isnard O, Vasiliev AN, Ueda Y (2009b) Magnetic and crystal structures of the magnetoelectric pyroxene LiCrSi2O6. Phys Rev B 79:064416
Nenert G, Kim I, Isobe M, Ritter C, Vasiliev AN, Kim KH, Ueda Y (2010a) Magnetic and magnetoelectric study of pyroxene NaCrSi2O6. Phys Rev B81:184408
Nenert G, Isobe M, Kim I, Ritter C, Colin CV, Vasiliev AN, Kim KH, Ueda Y (2010b) Interplay between low dimensionality and magnetic frustration in the magnetoelectric pyroxenes LiCrX2O6 (X = Ge, Si). Phys Rev B 82:024429
Nestola F, Boffa Ballaran T, Ohashi H (2008) The high-pressure C2/c–P21/c phase transition along the LiAlSi2O6–LiGaSi2O6 solid solution. Phys Chem Miner 35:477–484
Nestola F, Redhammer GJ, Pamato MG, Secco L, Dal Negro A (2009) High-pressure phase transformation in LiFeGe2O6 pyroxene. Am Mineral 94:616–621
Ohashi Y, Burnham CW (1973) Clinopyroxene lattice deformations: the roles of chemical substitutions and temperature. Am Mineral 58:843–849
Prencipe M, Tribaudino M, Pavese M, Hoser A, Reehuis M (2000) A single-crystal neutron-diffraction investigation of diopside at 10 K. Can Mineral 38:183–189
Redhammer GJ, Roth G (2004a) Structural changes upon the temperature dependent C2/c → P21/c phase transition in LiMe3+Si2O6 clinopyroxenes, Me = Cr, Ga, Fe, V and Sc. Zeitschrift für Kristallographie 219(10):585–605
Redhammer GJ, Roth G (2004b) Structural variation and crystal chemistry of LiMe3+Si2O6 clinopyroxenes, Me3+ = Al, Ga, Cr, V, Fe, Sc and In. Z Kristallogr 219:278–294
Redhammer GJ, Roth G, Paulus W, André G, Lottermoser W, Amthauer G, Treutmann W, Koppelhuber-Bitschnau B (2001) Crystal and magnetic structure of Li-aegirine LiFe3+Si2O6: a temperature dependent study. Phys Chem Miner 28:337–346
Redhammer GJ, Roth G, Ohashi H (2003) Single crystal structure refinement of NaTiSi2O6 clinopyroxene at low temperatures (100 K < T < 298 K). Acta Crystallogr A B59:730–746
Redhammer GJ, Roth G, Treutmann W, Paulus W, André G, Pietzonka C, Amthauer G (2008) Magnetic ordering and spin structure in Ca-bearing clinopyroxenes CaM2+(Si, Ge)2O6, M = Fe, Ni Co, Mn. J Solid State Chem 181:3163–3176
Redhammer GJ, Roth G, Amthauer G (2009a) Chromium-based clinopyroxene-type germanates NaCrGe2O6 and LiCrGe2O6 at 298 K. Acta Crystallogr A C64:i97–i102
Redhammer GJ, Roth G, Treutmann W, Hoelzel M, Paulus W, André G, Pietzonka C, Amthauer G (2009b) The magnetic structure of clinopyroxene-type LiFeGe2O6 and revised data on multiferroic LiFeSi2O6. J Solid State Chem 182:2374–2384
Redhammer GJ, Senyshin A, Tippelt G, Pietzonka C, Roth G, Amthauer G (2010a) Magnetic and nuclear structure and thermal expansion of orthorhombic and monoclinic polymorphs of CoGeO3 pyroxene. Phys Chem Miner 37(5):311–332
Redhammer GJ, Cámara F, Alvaro M, Nestola F, Tippelt G, Prinz S, Simons J, Roth G, Amthauer G (2010b) Thermal expansion and high temperature P21/c–C2/c phase transition in clinopyroxene-type LiFeGe2O6 and comparison to NaFe(Si, Ge)2O6. Phys Chem Miner 37:685–704
Redhammer GJ, Senyshyn A, Meven M, Roth G, Prinz S, Pachler A, Tippelt G, Piezonka C, Treutmann W, Hoelzel M, Pedersen B, Amthauer G (2011a) Nuclear and incommensurate magnetic structure of NaFeGe2O6 between 5 K and 298 K and some comparison to NaFeSi2O6. Phys Chem Miner 38:139–157
Redhammer GJ, Senyshyn A, Tippelt G, Roth G (2011b) Magnetic spin structure of pyroxene-type MnGeO3. J Phys Condens Matter 23:254202
Redhammer GJ, Senyshyn A, Tippelt G, Pietzonka C, Treutmann W, Roth G, Amthauer G (2012) Magnetic and low temperature structural behavior of clinopyroxene-type FeGeO3: a neutron diffraction, magnetic susceptibility and 57Fe Mössbauer study. Am Mineral 97(3):694–706
Redhammer GJ, Roth G, Senyshyn A, Tippelt G, Pietzonka C (2013) Crystal and magnetic spin structure of Germanium–Hedenbergite, CaFeGe2O6, and a comparison with other magnetic/magnetoelectric/multiferroic pyroxenes. Z Kristallogr 228(3):140–150
Rodríguez-Carvajal J (2001) Recent developments of the program. In: Commission on powder diffraction (IUCr). Newsletter 26:12–19. http://journals.iucr.org/iucr-top/comm/cpd/Newsletters/
Schlenker JL, Gibbs GV, Boisen MB Jr (1975) Thermal expansion coefficients for monoclinic crystals: a phenomenological approach. Am Mineral 60:828–833
Schonfield PF, Knight KS, van der Houwen JAM, Valsami-Jones E (2004) The role of hydrogen bonding in the thermal expansion and dehydration of brushite, di-calcium phosphate dihydrate. Phys Chem Miner 31:606–624
Shannon RD, Prewitt CT (1969) Effective ionic radii in oxides and fluorides. Acta Crystallogr A B25:925–946
Streltsov SV, Khomskii DI (2008) Electronic structure and magnetic properties of pyroxenes (Li, Na)TM(Si, Ge)2O6: low-dimensional magnets with 90° bonds. Phys Rev B 77:064405
Tribaudino M, Mantovani L (2014) Thermal expansion in C2/c pyroxenes: a review and new high-temperature structural data for a pyroxene of composition (Na0.53Ca0.47)(Al0.53Fe0.47)Si2O6 (Jd53Hd47). Mineral Mag 78(2):311–324
Tribaudino M, Nestola F, Cámara F, Domeneghetti MC (2002) The high-temperature P21/c↔C2/c phase transition in Fe-free pyroxene (Ca0.15Mg1.85Si2O6): structural and thermodynamic behavior. Am Mineral 87:648–657
Tribaudino M, Nestola F, Meneghini C, Bromiley GD (2003) The high-temperature P2/c1–C2/c phase transition in Fe-free Ca-rich P21/c clinopyroxenes. Phys Chem Miner 30:27–535
Tribaudino M, Bromiley G, Ohashi H, Nestola F (2009) Synthesis, TEM characterization and thermal behavior of LiNiSi2O6 pyroxene. Phys Chem Miner 36:527–536
Willis BTM, Pyror AW (1975) Thermal vibrations in crystallography, vol 1. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Acknowledgments
Neutron diffraction experiments have been supported by the European Commission under the 7th Framework Programme through the “Research Infrastructures” action of the “Capacities” Programme, Contract No: CP_CSA_Infra-2008-1.1.1 Number 226507-NIMI3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Redhammer, G.J., Senyshyn, A., Tippelt, G. et al. Structural and magnetic phase transitions in the synthetic clinopyroxene LiCrGe2O6: a neutron diffraction study between 0.5 and 1473 K. Phys Chem Minerals 42, 491–507 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00269-015-0738-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00269-015-0738-9