Abstract
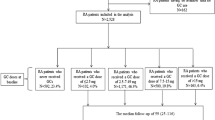
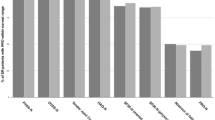
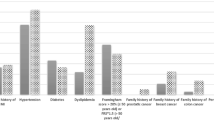
The objective of the study is to assess the disease course and associated healthcare costs in a cohort of established rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients in Turkey. The study cohort consisted of 75 RA patients from our outpatient clinic who took part in a previous multicenter study assessing RA-related healthcare costs 6 years ago. In March 2018, we attempted to re-evaluate these patients with the same questionnaire of the previous study enabling us to get information on medication use, comorbidities, and RA-related healthcare costs. We used RAPID-3 for assessing disease activity, HAQ-DI for functional status and EQ-5D for quality of life. Sixty-two (83%) patients were re-evaluated, seven (9.3%) had died and three (4%) were receiving palliative care following major cardiovascular events. Forty-seven (76%) patients had used at least one biologic agent during 79.1 ± 3.3 months after the previous study. At the last evaluation, 34 patients (55%) were on biologics, 22 (35%) were on csDMARDs and 6 (9.6%) were off RA treatment. The mean RAPID3 score (4.3 ± 1.6 SD) was similar to that of the previous study. HAQ-DI (0.69 ± 0.57 SD) and EQ-5D (0.68 ± 0.21 SD) scores showed significant improvement over time. Median direct costs (€2998) were higher than indirect costs (€304). Medication costs were high (€2958). Disease activity remained stable, while functional status and QoL had improved over time. Serious infections and cardiovascular disability are a concern. Medication costs are still the main determinant of RA-related healthcare costs.
Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
In case of any requests, the corresponding author will provide the data.
References
Smolen JS, Aletaha D, Barton A, Burmester GR, Emery P, Firestein GS, Kavanaugh A, McInnes IB, Solomon DH, Strand V, Yamamoto K (2018) Rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Dis Prim 2018(4):18001. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2018.1
Jagpal A, Navarro-Millan I (2018) Cardiovascular co-morbidity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a narrative review of risk factors, cardiovascular risk assessment and treatment. BMC Rheumatol 2:10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41927-018-0014-y
Smolen JS, Landewe R, Bijlsma J, Burmester G, Chatzidionysiou K, Dougados M, Nam J, Ramiro S (2017) EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2016 update. Ann Rheum Dis 76:960–977. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210715
Shadick NA, Gerlanc NM, Frits ML, Stolshek BS, Brady BL, Iannaccone C, Collier D, Cui J, Mutebi A, Weinblatt ME (2019) The longitudinal effect of biologic use on patient outcomes (disease activity, function, and disease severity) within a rheumatoid arthritis registry. Clin Rheumatol 38:3081–3092. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-019-04649-4
Boonen A, Severens JL (2011) The burden of illness of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 30(Suppl 1):3–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-010-1634-9
Pugner KM, Scott DI, Holmes JW, Hieke K (2000) The costs of rheumatoid arthritis: an international long-term view. Semin Arthritis Rheum 29:305–320
Furneri G, Mantovani LG, Belisari A, Mosca M, Cristiani M, Bellelli S, Cortesi PA, Turchetti G (2012) Systematic literature review on economic implications and pharmacoeconomic issues of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 30(Suppl 73):72–84
Malhan S, Akbulut LA, Bodur H, Tulunay CF (2010) Annual costs of rheumatoid arthritis in Turkey. Rheumatol Int 30:637–641. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-009-1040-2
Malhan S, Pay S, Ataman S, Dalkilic E, Dinc A, Erken E, Ertenli I, Ertugrul E, Gogus F, Hamuryudan V, Inanc M, Karaarslan Y, Karadag O, Karakoc Y, Keskin G, Kisacik B, Kiraz S, Oksel F, Oksuz E, Pirildar T, Sari I, Soy M, Senturk T, Taylan A (2012) The cost of care of rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis patients in tertiary care rheumatology units in Turkey. Clin Exp Rheumatol 30:202–207
Baser O, Baser E, Altinbas A, Burkan A (2013) Severity index for rheumatoid arthritis and its association with health care costs and biologic therapy use in Turkey. Health Econ Rev 3:5. https://doi.org/10.1186/2191-1991-3-5
Baser O, Burkan A, Baser E, Koselerli R, Ertugay E, Altinbas A (2013) Direct medical costs associated with rheumatoid arthritis in Turkey: analysis from National Claims Database. Rheumatol Int 33:2577–2584. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-013-2782-4
Hamuryudan V, Direskeneli H, Ertenli I, Inanc M, Karaaslan Y, Oksel F, Ozbek S, Pay S, Terzioglu E, Balkan Tezer D, Hacibedel B, Akkoc N (2016) Direct and indirect healthcare costs of rheumatoid arthritis patients in Turkey. Clin Exp Rheumatol 34:1033–1037
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS, Healey LA, Kaplan SR, Liang MH, Luthra HS et al (1988) The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 31:315–324. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.1780310302
Hallert E, Husberg M, Bernfort L (2012) The incidence of permanent work disability in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in Sweden 1990–2010: before and after introduction of biologic agents. Rheumatology (Oxford) 51:338–346. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/ker332
Harty L, O'Toole G, FitzGerald O (2015) Profound reduction in hospital admissions and musculoskeletal surgical procedures for rheumatoid arthritis with concurrent changes in clinical practice (1995–2010). Rheumatology (Oxford) 54:666–671. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keu340
Hacioglu A, Hatemi G, Esatoglu SN, Hamuryudan V (2018) Tapering tumour necrosis factor inhibitors in rheumatoid arthritis: a retrospective study. Clin Exp Rheumatol 37(Suppl 122):8
Tanaka Y (2016) Stopping tumour necrosis factor-targeted biological DMARDs in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 55:ii15–ii22
Lacaille D, Avina-Zubieta JA, Sayre EC, Abrahamowicz M (2017) Improvement in 5-year mortality in incident rheumatoid arthritis compared with the general population-closing the mortality gap. Ann Rheum Dis 76:1057–1063. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209562
Md Yusof MY, Vital EM, McElvenny DM, Hensor EMA, Das S, Dass S, Rawstron AC, Buch MH, Emery P, Savic S (2019) Predicting severe infection and effects of hypogammaglobulinaemia during therapy with rituximab in rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases. Arthritis Rheumatol 71:1812–1823. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.40937
Reddy KR, Beavers KL, Hammond SP, Lim JK, Falck-Ytter YT (2015) American Gastroenterological Association Institute guideline on the prevention and treatment of hepatitis B virus reactivation during immunosuppressive drug therapy. Gastroenterology 148:215–219. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2014.10.039
Mackey RH, Kuller LH, Moreland LW (2018) Update on cardiovascular disease risk in patients with rheumatic diseases. Rheum Dis Clin N Am 44:475–487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rdc.2018.03.006
Liao KP (2017) Cardiovascular disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Trends Cardiovasc Med 27:136–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcm.2016.07.006
Avina-Zubieta JA, Thomas J, Sadatsafavi M, Lehman AJ, Lacaille D (2012) Risk of incident cardiovascular events in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Ann Rheum Dis 71:1524–1529. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-200726
Wallman JK, Eriksson JK, Nilsson JA, Olofsson T, Kristensen LE, Neovius M, Geborek P (2016) Costs in relation to disability, disease activity, and health-related Quality of Life in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Observational Data from Southern Sweden. J Rheumatol 43:1292–1299. https://doi.org/10.3899/jrheum.150617
Huscher D, Mittendorf T, von Hinuber U, Kotter I, Hoese G, Pfafflin A, Bischoff S, Zink A (2015) Evolution of cost structures in rheumatoid arthritis over the past decade. Ann Rheum Dis 74:738–745. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204311
Fautrel B, Cukierman G, Joubert JM, Laurendeau C, Gourmelen J, Fagnani F (2016) Healthcare service utilisation costs attributable to rheumatoid arthritis in France: analysis of a representative national claims database. Jt Bone Spine 83:53–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbspin.2015.02.023
Acknowledgements
Support for the statistical analysis was taken from Omega Contract Research Organization (CRO). We did not receive editing support.
Funding
This study was supported by an unrestricted Grant from Pfizer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors made substantial contributions to the conception or design of the work; or the acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data for the work; and drafted the work or revised it critically for important intellectual content; and approved the final version to be published; and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved and all co-authors take full responsibility for the integrity of the study and the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
This study was supported by an unrestricted grant from Pfizer. The authors, G. Ayan and S.N. Esatoglu declare no other competing interests. G. Hatemi has received research/grant support, consulting fees and speaker fees from Celgene, speaker fees from Abbvie, UCB pharma and Novartis.V. Hamuryudan has received honoraria and speaker fees from Amgen, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche UCB and Abbvie.
Ethics approval
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. The ethics committee of Cerrahpasa Medical Faculty of Istanbul University-Cerrahpasa approved the study (89540/07.03.2018).
Consent to participate
Patients having a short-term (< 6 months) appointment gave their written consent at the time of their evaluation in the clinic (n = 52). We posted the consent to ten patients with appointments beyond 6 months after obtaining their verbal consent with a phone call. These patients signed and posted the consent forms back. Ten patients were either deceased or were receiving palliative care. Information on their outcome was obtained from central healthcare system database and from their family members after explaining the aim of the study. Verbal consent was obtained from family members to report their outcome information.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Related congress abstract publication
Disease course and costs of a cohort of rheumatoid arthritis patients over a period of 6 years. Ann Rheum Dis, volume 78, supplement 2, year 2019, page A1577. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-eular.984.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ayan, G., Esatoglu, S.N., Hatemi, G. et al. Disease course and healthcare costs of a cohort of rheumatoid arthritis patients from Turkey. Rheumatol Int 40, 1037–1044 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-020-04574-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-020-04574-9