Abstract
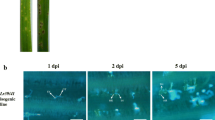
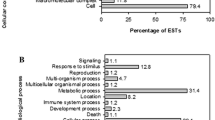
Hybrid lethality is an important problem for cross-breeding; however, its molecular mechanism is not clear. The purpose of the present study was to identify the genes expressed during hybrid lethality in the hybrid cells (Nicotiana suaveolens × N. tabacum). In order to identify these genes, we employed suppression subtractive hybridization (SSH) between RNA isolated from cells expressing lethality (lethal hybrid line; LH line) and cells overcoming lethality fortuitously (a surviving hybrid line; SH line). Four populations of cDNA were created from the time points corresponding to before and during induction, and at and after the point of no return (PNR) during the process of programmed cell death (PCD) that occurs during hybrid lethality. By SSH and following dot-blot macroarray analysis, 99 genes out of 138 isolated clones were identified as hybrid lethality-related (HLR) genes. Quantitative real-time PCR analysis data indicated that ten clones were expressed specifically in LH line cells. The HLR genes in these clones show homology to genes involved in disease resistance, ethylene-induced reactions, phosphorylation, ubiquitination, jasmonic acid-related reactions, calcium signaling and self-incompatibility. These data suggested that at least some parts of the mechanism of hybrid lethality are shared with those of the putative functions of the HLR gene-related pathways.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HLR:
-
Hybrid lethality related
- LH:
-
Lethal hybrid
- PCD:
-
Programmed cell death
- PNR:
-
Point of no-return
- SH:
-
Surviving hybrid
- SSH:
-
Suppression subtractive hybridization
References
Afford A, Randhawa S (2000) Apoptosis. Mol Pathol 53:55–63
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Aravind L, Dixit VM, Koonin EV (1999) The domains of death: evolution of the apoptosis machinery. Trends Biochem Sci 24:47–53
Dambrauskas G, Aves SJ, Bryant JA, Francis D, Rogers H (2003) Genes encoding two essential DNA replication activation proteins, Cdc6 and Mcm3, exhibit very different patterns of expression in the tobacco BY-2 cell cycle. J Exp Bot 54:699–706
Durrant WE, Rowland O, Piedras P, Hammond-Kosack KE, Jones JD (2000) cDNA-AFLP reveals a striking overlap in race-specific resistance and wound response gene expression profiles. Plant Cell 12:963–977
Fujimoto S Y, Ohta M Usui A, Shinshi H, Ohme-Takagi M (2000) Arabidopsis ethylene- responsive element binding factors act as transcriptional activators or repressors of GCC box-mediated gene expression. Plant Cell 12:393–404
Inai S, Ishikawa K, Nonomura O, Ikehashi H (1993) Genetic analysis of stunted growth by nuclear-cytoplasmic interaction in interspecific hybrids of Capsicum by using RAPD markers. Theor Appl Genet 87:416
Kim GT, Tsukaya H (2002) Regulation of the biosynthesis of plant hormones by cytochrome P450s. J Plant Res 115:168–177
Kobori S, Masuda Y, Marubashi W (2005) Heat treatment temporarily suppresses expression of programmed cell death in hybrid tobacco cells (Nicotiana suaveolens x N. tabacum) expressing hybrid lethality. Plant Biotechnol 22:345–348
Lam E (2004) Controlled cell death, plant survival and development. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5:305–315
Maki M, Yamaguchi K, Kitaura Y, Satoh H, Hitomi K (1998) Calcium-induced exposure of a hydrophobic surface of mouse ALG-2, which is a member of the penta-EF-hand protein family. J Biochem 124:1170–1177
Manabe T, Marubashi W, Onozawa Y (1989) Temperature-dependent conditional lethality in interspecific hybrids between Nicotiana suaveolens Lehm. × N. tabacum L. In: Proceedings of the 6th international congress, SABRAO, pp 459–462
Marubashi W, Yamada T, Niwa M (1999) Apoptosis detected in hybrids between Nicotiana glutinosa and N. repanda expressing lethality. Planta 210:168–171
Marubashi W, Onosato K (2002) Q chromosome controls the lethality of interspecific hybrids between Nicotiana tabacum and N. suaveolens. Breed Sci 52:137–142
Masuda Y, Yamada T, Marubashi W (2003) Time course analysis of apoptotic cell death during expression of hybrid lethality in hybrid tobacco cells (Nicotiana suaveolens x N. tabacum). Plant Cell Physiol 44:420–427
McLean, MD, Hoover G, Makhmoudova A, Clark SM, Welacky T, Simmonds DH, Shelp BJ (2005) Overexpression of Hs1pro-1 in transgenic soybean confirms resistance to the soybean cyst nematode. EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ databases (submitted)
Mills JC (2001) Mechanisms underlying the hallmark features of the execution-phase of apoptosis. In: Mattoson MP, Estus S, Rangnekar VM (eds) Advances in cell aging and gerontology, programmed cell death. Cellular and molecular mechanisms, vol 1. Elsevier, Baltimore, pp 1–38
Mino M, Maekawa K, Ogawa K, Yamagishi H, Inoue M (2002) Cell death processes during expression of hybrid lethality in interspecific F1 hybrid between Nicotiana gossei Domin and Nicotiana tabacum. Plant Physiol 130:1776–1787
Oka H, Doida Y (1962) Phylogenetic differentiation of cultivated rice. XX. Analysis of the genetic basis of hybrid breakdown in rice. Jpn J Gent 37:24–35
Pennell RI, Lamb C (1997) Programmed cell death in plants. Plant Cell 9:1157–1168
Phillips LL, Reid RK (1975) Interspecific incompatibility in Gossypium. II. Light and electron microscope studies of cell necrosis and tumorigenesis in hybrids of G. klotzschianum. Am J Bot 62:790–796
Provine WB (1991) Alfred Henry Sturtevant and crosses between Drosophila melanogaster and Drosophila simulans. Genetics 129:1–5
Sano T, Kuraya Y, Nagata T (1999) Phosphate as a limiting factor for the cell division of tobacco BY-2 cells. Plant Cell Physiol 40:1–8
Stebbins GL (1966) Reproductive isolation and the origin of species. In: Processes of organic evolution. Prentice-Hall, New Jersey, pp 85–112
Tezuka T, Marubashi W (2004) Apoptotic cell death observed during the expression of hybrid lethality in interspecific hybrids between Nicotiana tabacum and N. suaveolens. Breed Sci 54:59–66
Tezuka T, Marubashi W (2006) Hybrid lethality in interspecific hybrids between Nicotiana tabacum and N. suaveolens: evidence that the Q chromosome causes hybrid lethality based on Q-chromosome-specific DNA markers. Theor Appl Genet 112:1172–1178
Thurau T, Kifle S, Jung C, Cai D (2003) The promoter of the nematode resistance gene Hs1pro-1 activates a nematode-responsive and feeding site-specific gene expression in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) and Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol 52:643–660
Tournier B, Sanchez-Bellesta MT, Jones B, Pesquet E, Regad F, Latche A, Pech JC, Bouzayen M (2003) New members of the tomato ERF family show specific expression pattern and diverse DNA-binding capacity to the GCC box element. FEBS Lett 550:149–154
van Engelen FA, Hartog MV, Thomas TL, Taylor B, Sturm A, van Kammen A, de Vries SC (1993) The carrot secreted glycoprotein gene EP1 is expressed in the epidermis and has sequence homology to Brassica S-locus glycoproteins. Plant J 4:855–862
Yamada T, Marubashi W (2003) Overproduced ethylene causes programmed cell death leading to temperature-sensitive lethality in hybrid seedlings from the cross Nicotiana suaveolens × N. tabacum. Planta 217:690–698
Yamada T, Marubashi W, Niwa M (2000) Apoptotic cell death induces temperature-sensitive lethality in hybrid seedlings and calli derived from the cross of Nicotiana suaveolens × N. tabacum. Planta 211:614–622
Yamada T, Marubashi W, Niwa M (2001) Facile induction of apoptosis into plant cells associated with temperature-sensitive lethality shown on interspecific hybrid from the cross Nicotiana suaveolens × N. tabacum. Plant Cell Physiol 42:204–213
Zeven AC (1981) Eighth supplementary list of wheat varieties classified according to their genotype for hybrid necrosis. Euphytica 30:521–539
Acknowledgments
This work was partly supported by the Sasakawa Scientific Research Grant from The Japan Science Society, and a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) No. 15580003 from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by C.F. Quiros.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Masuda, Y., Yamada, T., Kuboyama, T. et al. Identification and characterization of genes involved in hybrid lethality in hybrid tobacco cells (Nicotiana suaveolens × N. tabacum) using suppression subtractive hybridization. Plant Cell Rep 26, 1595–1604 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-007-0352-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-007-0352-5