Abstract
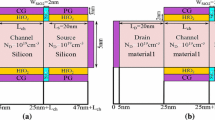
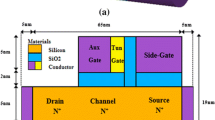
In this paper, a gate-all-around junctionless tunnel field effect transistor (JLTFET) based on heterostructure of compound and group III–V semiconductors is introduced and simulated. In order to blend the high tunneling efficiency of narrow band gap material JLTFETs and the high electron mobility of III–V JLTFETs, a type I heterostructure junctionless TFET adopting Ge–Al x Ga1−x As–Ge system has been optimized by numerical simulation in terms of aluminum (Al) composition. To improve device performance, we considered a nanowire structure, and it was illustrated that high-performance logic technology can be achieved by the proposed device. The optimal Al composition founded to be around 20 % (x = 0.2). The numerical simulation results demonstrate that the proposed device has low leakage current I OFF of ~1.9 × 10−17, I ON of 4 µA/µm, I ON/I OFF current ratio of 1.7 × 1011 and subthreshold swing SS of 12.6 mV/decade at the 40 nm gate length and temperature of 300 K.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Anwar, I. Hossain, A comparative numerical simulation of a nanoscaled body on insulator FinFET, in Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Microelectronics (MIEL) (2010), pp. 16–19
R. Coquand et al. Strain-induced performance enhancement of tri-gate and omega-gate nanowire fets scaled down to 10 nm width, in IEEE Symposium on VLSI Technology Digest of Technical Papers (2012), pp. 13–14
J.Y. Song et al., Design optimization of gate-all-around (GAA) MOSFETs. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 5(3), 186–191 (2006)
J.-P. Colinge, C.-W. Lee, A. Afzalian, N.D. Akhavan, R. Yan, I. Ferain, P. Razavi, B. O’Neill, A. Blake, M. White, A.-M. Kelleher, B. McCarthy, R. Murphy, Nanowire transistors without junctions. Nat. Nanotechnol. 5(3), 225–229 (2010)
C.-W. Lee, I. Ferain, A. Afzalian, R. Yan, N.D. Akhavan, P. Razavi, J.P. Colinge, Performance estimation of junctionless multigate transistors. Solid State Electron. 54(2), 97–103 (2010)
W.Y. Choi, B.-G. Park, J.D. Lee, T.-J. King Liu, Tunneling field-effect transistors (TFETs) with subthreshold swing (SS) less than 60 mV/dec. IEEE Electron Dev. Lett. 28, 743–745 (2007)
Qin Zhang, Wei Zhao, Alan Seabaugh, Low-subthreshold-swing tunnel transistors. IEEE Electron Dev. Lett. 27, 297–300 (2006)
O.M. Nayfeh, C.N. Chleirigh, J. Hennessy, L. Gomez, J.L. Hoyt, D.A. Antoniadis, Design of tunneling field-effect transistors using strained-silicon/strained-germanium type-II staggered heterojunctions. IEEE Electron Dev. Lett. 29, 1074–1077 (2008)
Y. Khatami, K. Banerjee, Steep subthreshold slope n- and p-type tunnel-FET devices for low-power and energy-efficient digital circuits. IEEE Electron Dev. Lett. 56, 2752–2761 (2009)
U. E. Avci, I. A. Young, Heterojunction TFET scaling and resonant-TFET for steep subthreshold slope at sub-9 nm gate-length, in Proceedings of the IEEE International Electron Device Meeting (IEDM), Washington, DC, USA (2013), pp. 4.3.1–4.3.4
M. Luisier, G. Klimeck, Performance comparisons of tunneling field-effect transistors made of InSb, Carbon, and GaSb–InAs broken gap heterostructures, in Proceedings of the IEEE International Electron Device Meeting (IEDM), Baltimore, MD, USA (2009), pp. 1–4
A.C. Seabaugh, Q. Zhang, Low-voltage tunnel transistors for beyond CMOS logic. Proc. IEEE 98(12), 2095–2110 (2010)
L. Knoll et al., Inverters with strained Si nanowire complementary tunnel field-effect transistors. IEEE Electron Dev. Lett. 34(6), 813–815 (2013)
K. Ganapathi, Y. Yoon, S. Salahuddin, Analysis of InAs vertical and lateral band-to-band tunneling transistors: leveraging vertical tunneling for improved performance. Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 033504 (2010)
A.M. Ionescu, H. Riel, Tunnel field-effect transistors as energyefficient electronic switches. Nature 479(7373), 329–337 (2011)
B. Ghosh, M.W. Akram, Junctionless tunnel field effect transistor. IEEE Electron Dev. Lett. 35(5), 584–586 (2013)
P.K. Asthana, B. Ghosh, S.B. Rahi et al., Improved performance of junctionless tunnel filed effect transistor with Si and SiGe hetro-structure for ultra low power application. RSC Adv. (2015). doi:10.1039/C5RA03301B
P.K. Asthana, High performance 20 nm GaSb/InAs junctionless fiels effect transistor for low power supply. J. Semicond. 36(2), 1–6 (2015)
B. Ghosh, P. Bal, P. Mondal, A junctionless tunnel field effect transistor with low subthreshold slope. J. Comput. Electron. (2013). doi:10.1007/s10825-013-0450-2
Y. Taur, T.H. Ning, Fundamentals of Modern VLSI Devices (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1998)
R. Eisberg, R. Resnick, Quantum Physics of Atoms, Molecules, Solids, Nuclei and Particles, 2nd edn. (Wiley Student Edition, New York, 2012)
W. Long, H. Ou, J.M. Kuo et al., Dual-material gate (DMG) field effect transistor. IEEE Trans. Electron. Dev. 46(5), 865 (1999)
K.Y. Na, Y.S. Kim, Silicon complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors with dual work function gate. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 45(12), 9033 (2006)
C.H. Wang, H. Chu, Y.S. Lai, et al., Dual work-function metal gates. US Patent, No. 73 81619B2, Jun. 3, 2008
U. Konig et al., N- and p-type Si–SiGe hetero FETs, in IEEE International Symposium on High Performance Electron Devices for Microwave and Optoelectronic Applications, vol. 8 (2000), pp. 1–7
B.M. Borg, K.A. Dick, B. Ganjipou et al., InAs/GaSb heterostructure nanowires for tunnel field-effect transistors. Nano Lett. 10(10), 4080 (2010)
K. Boucart, A.M. Ionescu, Double-gate tunnel FET with high-κ gate dielectric. IEEE Trans. Electron Dev. 54(7), 1725–1733 (2007)
Silvaco, Version 5.15.32.R. (2009). http://www.silvaco.com
K. Boucart, A.M. Ionescu, Double-gate tunnel FET with High-κ gate dielectric. IEEE Trans. Electron Dev. 54(7), 1725–1733 (2007)
A. Villalon et al., First demonstration of strained SiGe nanowires TFETs with ION beyond 700 μA/μm, in Proceedings Symposium on VLSI Technology (VLSIT), Honolulu, HI, USA (2014), pp. 66–67
W. Hansch, T. Vogelsang, R. Kirchner, M. Orlowski, Carrier transport near the Si/SiO2 interface of a MOSFET. Solid State Electron. 32(10), 839–849 (1989)
A. Schenk, A model for the field and temperature dependence of SRH lifetimes in silicon. Solid State Electron. 35(11), 1585–1596 (1992)
C. Wang, S.Y. Chou, Self-aligned fabrication of 10 nm wide asymmetric trenches for Si/SiGe heterojunction tunneling field effect transistors using nanoimprint lithography, shadow evaporation, and etching. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 27(6), 2790–2794 (2009)
O.M. Nayfeh, C.N. Chleirigh, J. Hennessy, L. Gomez, J.L. Hoyt, D.A. Antoniadis, Design of tunneling field-effect transistors using strained-silicon/strained-germanium type-II staggered heterojunctions. IEEE Electron Dev. Lett. 29(9), 1074–1077 (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Molaei Imen Abadi, R., Sedigh Ziabari, S.A. Representation of type I heterostructure junctionless tunnel field effect transistor for high-performance logic application. Appl. Phys. A 122, 616 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-016-0151-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-016-0151-3