Abstract
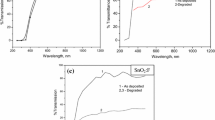
Transparent conductive ZnO:Al and ZnO:Ga ultrathin films have been developed on glass substrate at room temperature by non-reactive RF magnetron sputtering using sintered ceramic disc of ZnO:Al target (ZnO 98%, Al 2%), and ZnO:Ga target (ZnO 97%, Ga 3%). The thin films (90–250 nm) of ZnO:Al and ZnO:Ga show low resistivity of 8.6 × 10−5 and 4.5 × 10− 4 Ω cm, respectively. The ZnO:Al thin film exhibits highest transparency of 92%, haze factor of 54% in the visible region and electrical mobility of 12 cm2/V s. Similar kinds of results (highest electrical mobility is 10 cm2/V s, haze factor varies from 28 to 44%) are observed for ZnO:Ga thin films. The moderate improvement on thickness-dependent electrical mobility for very thin ZnO:Ga and ZnO:Al films are due to improved crystallinity, increased crystallite sizes but negative effect comes from grain boundary scattering and higher surface roughness. X-ray diffraction spectra reveal polycrystalline nature of ZnO:Ga and ZnO:Al thin films with grain size 22 and 19 nm, respectively. Variation of thickness and composition-dependent structural, morphological and optical haze properties of Al- and Ga-doped ZnO thin films have been compared with that of conventional ITO and SnO2:F thin films.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Das, K. Adhikary, S. Ray, Comparison of electrical, optical and structural properties of RF-sputtering ZnO thin film deposited under different gas ambient. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 47(3), 1501–1506 (2008)
A.S. Riad, S.A. Mahmoud, A.A. Ibrahim, Structural and DC electrical investigations of ZnO thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis technique. Phys. B Phys. Condens. Matter. 296(4), 319–325 (2001)
S. Tüzemen, G. Xiong, B. Mischuck, K.B. Ucer, R.T. Williams, Production and properties of p–n junctions in reactively sputtered ZnO. Physica B 308–310, 1197–1200 (2001) (1198)
U. Ozgur, Y.I. Alivov, C. Liu, A. Teke, A.M. Reshchikov, S. Doan, V. Avrutin, J.S. Cho, H. Morkoc, A comprehensive review of ZnO materials and devices. J. Appl. Phys. 98(4), 041301 (2005)
R. Das, K. Adhikary, S. Ray, The role of oxygen and hydrogen partial pressures on structural and optical properties of ITO films deposited by reactive RF-magnetron sputtering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 253(14), 6068–6073 (2007)
Z.L. Wang, Zinc oxide nanostructures: growth, properties and applications. J. Phys. Condens. Mater. 16(25), R829–R858 (2004)
J. Müller, B. Rech, J. Springer, M. Vanecek, TCO and light trapping in silicon thin film solar cells. Sol. Energy 77, 917–930 (2004)
W.J. Jeong, S.K. Kim, G.C. Park, Preparation and characteristic of ZnO thin film with high and low resistivity for an application of solar cell. Thin Solid Films 506–507, 180–183 (2006)
M.C. Jeong, B.Y. Oh, O.H. Nam, T. Kim, J.M. Myoung, Three-dimensional ZnO hybrid nanostructures for oxygen sensing application. Nanotechnology 17(2), 526–530 (2006)
R. Das, H.S. Das, Merits and demerits of transparent conducting magnetron sputtered ZnO:Al, ITO and SnO2:F thin films for solar cell applications. J. Inst. Eng. (India) Ser. D 98(1), 85–90 (2017)
Y.R. Ryu, J.A. Lubguban, T.S. Lee, H.W. White, Y.S. Park, C.J. Youn, Next generation of oxide photonic devices: ZnO-based ultraviolet light emitting diodes. J. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88(25), 241108 (2006)
P.F. Carcia, R.S. McLean, M.H. Reilly, G. Nunes Jr., Transparent ZnO thin-film transistor fabricated by RF magnetron sputtering. Appl. Phys. Lett. 82(7), 1117 (2003)
Z.L. Wang, J. Song, Piezoelectric-nanogenerators based on zinc oxide nanowire arrays. Science 312 (5771), 242–246 (2006)
R.N. Chauhan, C. Singh, R. Singh, A.J. Kumar, Thickness-dependent structural, optical, and electrical characteristics of ZnO:Al thin films and application in OLEDs. IEEE Trans. Electron Dev. 61 (11), 3775–3782 (2014)
Y. Aoun, B. Benhaoua, B. Gasmi, S. Benramache, Structural, optical and electrical properties of zinc oxide thin films deposited by a spray pyrolysis technique. J. Semicond. 36(1), 013002 (2015)
M. Novotný, J. Cizek, R.Kužel,J. Bulíř, J. Lančok, J. Connolly, E. McCarthy, S. Krishnamurthy, J.-P. Mosnier, W. Anwand, G. Brauer, Structural characterization of ZnO thin films grown on various substrates by pulsed laser deposition. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 45(22), 225101 (2012)
D.C. Agarwal, R.S. Chauhan, Synthesis and characterization of ZnO thin film grown by electron beam evaporation. J. Appl. Phys. 99, 123105 (2006)
D. Nakamura, K. OkazakiI., A. Palani, M. Higashihata, T. Okada, Influence of Sb on a controlled-growth of aligned ZnO nanowires in nanoparticle-assisted pulsed-laser deposition. Appl. Phys. A. 103(4), 959–963 (2011)
R. Das, H.S. Das, Effect of hydrogen on the properties of RF-magnetron sputtering ZnO:Al films as an alternative to commercially available TCO films. J. Inst. Eng. (India) Ser. D 98(2), 203–210 (2017)
W. Gao, Z. Li, ZnO thin films produced by magnetron sputtering. Ceram. Int. 30(7), 1155–1159 (2004) Issue.
R. Das, S. Ray, Zinc oxide—a transparent, conducting IR-reflector prepared by RF-magnetron sputtering. J Phys. D Appl. Phys. 32(2), 152–155 (2003)
H.W. Wu, C.H. Chu, Y.F. Chen, Y.W. Chen, W.H. Tsai, S.H. Huang, G.S. Chen, Study of AZO thin films under different Ar flow and sputtering power by RF magnetron sputtering-011. Proceedings of the International Multi Conference of Engineers and Computer Scientists 2013, Vol II, IMECS 2013 (2013)
E.G. Fua, D.M. Zhuanga, G. Zhanga, Z. Minga, W.F. Yangc, J.J. Liua, Properties of transparent conductive ZnO:Al thin films prepared by magnetron sputtering. Microelectron. J. 35(4), 383–387 (2004)
H. Agura, A. Suzuki, T. Mastushita, T. Aoki, M. Okuda, Low resistivity transparent conducting Al-doped ZnO films prepared by pulsed laser deposition. Thin Solid Films 445(2), 263–267 (2003)
B.Z. Dong, G.J. Fang, J.F. Wang, W.J. Guan, X.Z. Zhao, Effect of thickness on structural, electrical, and optical properties of ZnO: Al films deposited by pulsed laser deposition. J.Appl. Phy. 101(3), 033713 (2007)
S.O. El hamali, W.M. Cranton, N. Kalfagiannis, X. Hou, R. Ranson, D.C. Koutsogeorgis, Enhanced electrical and optical properties of room temperature deposited aluminium doped zinc oxide (AZO) thin films by excimer laser annealing. Opt. Lasers Eng. 80, 45–51 (2016)
N. Akin, S.S. Cetin, M. Cakmak, T. Memmedli, S. Ozcelik, Effect of film thickness on properties of aluminum doped zinc oxide thin films deposition on polymer substrate. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 24, 5091–5096 (2013)
A. Suzuki, T. Matsushita, N. Wada, Y. Sakamoto, M. Okuda, Transparent conducting Al-doped ZnO thin films prepared by pulsed laser deposition. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 35(Part 2, No. 1A), L56–L59 (1996)
H.S. Das, A. Dey, P.P. Ray, R. Das, Room temperature deposited transparent conducting in ZnO:Ga thin films by non-reactive RF-magnetron sputtering. Mater. Today Proc. 4(14), 12610–12614 (2017)
X. Yu, J. Ma, F. Ji, Y. Wang, C. Cheng, H. Ma, Thickness dependence of properties of ZnO:Ga ilms deposited by rf magnetron sputtering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 245, 310–315 (2005)
D.H. Kim, H.R. Kim, S.H. Lee, E. Byon, G.H. Lee, Electrical and structural properties of multi component transparent conducting oxide films prepared by co sputtering of AZO and ITO. J. Non Cryst. Solids 356(35–36), 1779–1783 (2010)
R. Groenen, J. Loffler, J.L. Linden, R.E.I. Schropp, M.C.M. van de Sanden, Property control of expanding thermal plasma deposited textured zinc oxide with focus on thin film solar cell applications. Thin Solid Films 492 (1–2), 298–306 (2005)
H. Kim, J.S. Horwitz, G. Kushto, A. Piqué, Z.H. Kafafi, C.M. Gilmore, D.B. Chrisey, Effect of film thickness on the properties of indium tin oxide thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 88, 6021 (2000)
J.K. Kim, S.J. Yun, J.M. Lee, J.W. Lim, Effect of RF-power density on the resistivity of Ga-doped ZnO film deposited by RF-magnetron sputter deposition technique. Curr. Appl. Phys. 10(3), S451–S454 (2010)
Q. Li, X. Li, J. Zhang, Microstructure, optical and electrical properties of gallium-doped ZnO films prepared by sol gel method. J. Alloys Compd. 572, 175–179 (2013)
F. Wu, L. Fang, Y.J. Pan, K. Zhou, H.B. Ruan, G.B. Liu, C.Y. Kong, Effect of annealing treatment on structural, electrical, and optical properties of Ga doped ZnO thin films deposited by RF magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films 520, 703–707 (2011)
S. Blackwell, R. Smith, S.D. Kenny, J.M. Walls, C.F. Sanz, Navarro-modelling the growth of ZnO thin films by PVD methods and the effects of post-annealing. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 25(13), 135002 (2013)
G. Haacke, Transparent electrode properties of cadmium stannate. Appl. Phys. Lett. 28(10), 622 (1976)
H. Mahdhi, Z. Ben Ayadi, S. Alaya, J.L. Gauffier, K. Djessas, The effects of dopant concentration and deposition temperature on the structural, optical and electrical properties of Ga-doped ZnO thin films. Superlattices Microstruct. 72, 60–71 (2014)
G.A. Hirata, J. McKittrick, T. Cheeks, J.M. Siqueiros, J.A. Diaz, O. Contreras, O.A. Lopez, Synthesis and optoelectronic characterization of gallium doped zinc oxide transparent electrodes. Thin Solid Films 288(1–2), 29–31 (1996)
J. Rodríguez-Báez, A. Maldonado, G. Torres-Delgado, R. Castanedo-Pérez, M.L. de la Olvera, Influence of the molar concentration and substrate temperature on fluorine-doped zinc oxide thin films chemically sprayed. Mater. Lett. 60(3), 1594–1598 (2006)
F. Wang, H. Chang, C. Tseng, C. Huang, H. Liu, Influence of hydrogen plasma treatment on Al-doped ZnO thin films for amorphous silicon thin film solar cells. Curr. Appl. Phys. 11(1), S12–S16 (2011)
M. Suchea, S. Christoulakis, N. Katsarakis, T. Kitsopoulos, G. Kiriakidis, Comparative study of zinc oxide and aluminum doped zinc oxide transparent thin films grown by direct current magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films 515, 6562–6566 (2007)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge Department of Science and Technology, Govt. of India [DST/TM/ SERI/2K10/67(G)] for financial support for pursuing the R&D activity. S. Biring acknowledges financial supports from Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan (MOST 105-2218-E-131-003, 106-2221-E-131-027).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Das, R., Das, H.S., Nandi, P.K. et al. Comparative studies on the properties of magnetron sputtered transparent conductive oxide thin films for the application in solar cell. Appl. Phys. A 124, 631 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-2043-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-2043-1