Abstract
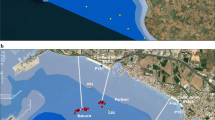
The waters offshore the Shandong Peninsula separate the North Yellow Sea from the South Yellow Sea, and receive a large amount of terrestrial material from Chinese and Korean rivers, making it an ideal area for studying land-sea interactions. However, little attention has been given to measuring sediment transportation in most previous studies. Based on an analysis in composition of major and trace elements and particle size characteristics from 62 surface sediment samples from the northeastern region off Shandong Peninsula, the type, element composition, and controlling factors of the surface sediments were investigated. In addition, the transportation of sediments from source to sink was described from measured thermohaline data. The results show two types of surface sediments: sandy silt and silt. The sediments were mainly terrestrial; and marine carbonate had little effect on sediment composition. Shown on a binary diagram of Rb/Sc to Co/Sc, the Huanghe (Yellow) and Changjiang (Yangtze) rivers are the main sources of surface sediments in the study area. The component mixing model showed that the relative contribution of sediment from the Huanghe River was up to 92%, followed by the Changjiang River (8%). The Yellow Sea Warm Current and the North Shandong Peninsula Coastal Current met at ∼37.7°N in the study area, and were the main forces carrying sediment from the two main river sources. However, there was a deficit of transported material into the study area in summer. The secondary distribution of sediment from the two river sources was controlled by tidal currents and waves.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Bao X W, Li N, Yao Z G, Wu D X. 2009. Seasonal variation characteristics of temperature and salinity of the North Yellow Sea. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 39(4): 553–562. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Beardsley R C, Limeburner R, Yu H, Cannon G A. 1985. Discharge of the Changjiang (Yangtze River) into the East China Sea. Continental Shelf Research, 4(1–2): 57–76.
Bi N H, Yang Z S, Wang H J, Fan D J, Sun X X, Lei K. 2011. Seasonal variation of suspended-sediment transport through the southern Bohai Strait. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 93(3): 239–247.
Bian C W. 2012. Chinese coastal sediment transport in the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea and East China Sea. PhD thesis. Ocean University of China, Qingdao. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Chen J S, Wang F Y, Li X D, Song J J. 2000. Geographical variations of trace elements in sediments of the major rivers in eastern China. Environmental Geology, 39(12): 1 334–1 340.
Cheng P. 2000. Sediment characteristics and transport processes of fine-grained material over the Northern Yellow Sea. PhD thesis. The Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Cho Y G. 1994. Distribution and Origin of Metallic Elements in Marine Sediments Around Korean Peninsula. PhD thesis. Seoul National University, Seoul. p.25–45.
Cho Y G, Lee C B, Choi M S. 1999. Geochemistry of surface sediments off the southern and western coasts of Korea. Marine Geology, 159(1–4): 111–129.
Dou Y G, Li J, Yang S Y. 2012. Element compositions and provenance implication of surface sediments in offshore areas of the eastern Shandong Peninsula in China. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 34(1): 109–119. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Fang H C, Huang P, Zhou Y, Zhang J, Li A C, Yan J S. 2015. Distribution and controlling factors of the major elements in surface sediments of the North Yellow Sea. Marine Sciences, 39(4): 108–116. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Folk R L, Ward A W C. 1957. Brazos River bar [Texas]; A study in the significance of grain size parameters. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 27(1): 3–26.
Gao S, Park Y A, Zhao Y Y, Qin Y S, Lee C B. 1996. Transport and resuspension of fine-grained sediments over the Southeastern Yellow Sea. In: Proceedings of the KoreaChina International Seminar on Holocene and Late Pleistocene Environments in the Yellow Sea Basin. Seoul National University Press, Seoul. p.83–98.
Gao S. 2003. Tracer methods in marine sediment dynamics. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 21(1): 61–65. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Guan B X. 1963. A preliminary study of the temperature variations and the characteristics of the circulation of the cold water mass of the Yellow Sea. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 5(4): 255–284. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Hay W W. 1998. Detrital sediment fluxes from continents to oceans. Chemical Geology, 145(3–4): 287–323.
Kim G, Yang H S, Church T M. 1999. Geochemistry of alkaline earth elements (Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba) in the surface sediments of the Yellow Sea. Chemical Geology, 153(1–4): 1–10.
Kremling K, Streu P. 1993. Saharan dust influenced trace element fluxes in deep North Atlantic subtropical waters. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 40(6): 1 155–1 168.
Lan X H, Chen X H, Mi B B, Li R H, Qin Y C, Wang Z B. 2015a. Distribution pattern and source of major and trace elements in the central North Yellow Sea since late Pleistocene. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 35(4): 1–10. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Lan X H, Mi B B, Chen X H, Li R H, Wang Z B, Lu K. 2015b. Tracing of rare earth elements in late quaternary sediments from central North Yellow Sea. Journal of the Chinese Society of Rare Earths, 33(2): 241–252. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li G G, Hu B Q, Li J, Bu R Y, Yang M, Dou Y G. 2012. Geochemistry of major elements in the surface sediments of the offshore area of Shandong Peninsula and its geological implication. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 32(3): 45–54. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li G X, Yue S H, Zhao D B, Sun Y T. 2004. Rapid deposition and dynamic processes in the modern Yellow River Mouth. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 24(3): 29–36. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li J R, Liu S F, Feng X L, Sun X Q, Shi X F. 2017. Major and trace element geochemistry of the mid-Bay of Bengal surface sediments: implications for provenance. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 36(3): 82–90.
Li J S, Gao J H, Li J, Wang Z Y, Yan J, Bai F L, Cheng Y. 2010. Distribution and controlling factors of major elements in sediments of the Yalu River estuary. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 30(1): 25–31. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li Y, Li A C, Huang P, Xu F J, Zheng X F. 2014. Clay minerals in surface sediment of the north Yellow Sea and their implication to provenance and transportation. Continental Shelf Research, 90: 33–40.
Lim D, Jung H S, Choi J Y. 2014. REE partitioning in riverine sediments around the Yellow Sea and its importance in shelf sediment provenance. Marine Geology, 357: 12–24.
Liu J, Saito Y, Kong X H, Wang H, Zhao L. 2009. Geochemical characteristics of sediment as indicators of post-glacial environmental changes off the Shandong Peninsula in the Yellow Sea. Continental Shelf Research, 29(7): 846–855.
Liu J P, Milliman J D, Gao S, Cheng P. 2004. Holocene development of the Yellow River’s subaqueous delta, North Yellow Sea. Marine Geology, 209(1–4): 45–67.
Lu J, Qiao F L, Wang X H, Wang Y G, Teng Y, Xia C S. 2011. A numerical study of transport dynamics and seasonal variability of the Yellow River sediment in the Bohai and Yellow seas. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 95(1): 39–51.
Lü X X, Song J M, Li X G, Yuan H M, Zhan T R, Li N, Gao X L. 2005. Geochemical characteristics and early diagenesis of nitrogen in the northern Yellow Sea Sediments. Acta Geologica Sinica, 79(1): 114–123. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Martin J M, Zhang J, Shi M C, Zhou Q. 1993. Actual flux of the Huanghe (Yellow River) sediment to the Western Pacific Ocean. Netherlands Journal of Sea Research, 31(3): 243–254.
McManus J, Berelson W M, Klinkhammer G P, Johnson K S, Coale K H, Anderson R F, Kumar N, Burdige D J, Hammond D E, Brumsack H J, McCorkle D C, Rushdi A. 1999. Geochemistry of barium in marine sediments: implications for its use as a paleoproxy. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 62(21–22): 3 453–3 473.
Milliman J D, Meade R H. 1983. World-wide delivery of river sediment to the oceans. The Journal of Geology, 91(1): 1–21.
Miao J B, Liu X Q, Xue Y. 1990. A preliminary study on the formation mechanism of the North Yellow Sea cold water mass I. Model solution. Chinese Science (PartB Chemical Life Science Geosciences), (12): 1 311–1 321. (in Chinese)
Miao J B, Liu X Q, Xue Y. 1991. A preliminary study of the formation mechanism of the north Yellow Sea cold water mass -II. Discussion of the model solution. Chinese Science (Series B Chemical Life Sciences Geosciences), (1): 74–81. (in Chinese)
Pattan J N, Parthiban G, PrakashBabu C, Khadge N H, Paropkari A L, Kodagali V N. 2008. A note on geochemistry of surface sediments from Krishna-Godavari Basin, East Coast of India. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 71(1): 107–114.
Qi J, Li F Y, Song J M, Gao S, Wang G Z, Cheng P. 2004. Sedimentation rate and flux of the North Yellow Sea. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 24(2): 9–14. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Qiao S Q, Shi X F, Wang G Q, Zhou L, Hu B Q, Hu L M, Yang G, Liu Y G, Yao Z Q, Liu S F. 2017. Sediment accumulation and budget in the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Marine Geology, 390: 270–281.
Qin Y S, Li F. 1986. The influence of the sediment from the Yellow River into the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea. Studia Marina Sinica, 27: 125–135. (in Chinese)
Qin Y S, Zhao Y Y, Chen L R, Chen S L. 1989. Yellow Sea Geology. Science Press, Beijing. p.1–289. (in Chinese)
Riedlinger S K, Jacobs G A. 2000. Study of the dynamics of wind-driven transports into the Yellow Sea during winter. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 105(C12): 2 8695–2 8708.
Schubel J R, Shen H T, Park M J. 1984. A comparison of some characteristic sedimentation processes of estuaries entering the Yellow Sea. In: Park Y A, Pilkey O H, Kim S W eds. Marine Geology and Physical Processes of the Yellow Sea. Korea Institute of Energy Resources, Seoul. p.286–308.
Shi Y, Gao J H, Sheng H, Du J, Jia J J, Wang Y P, Li J, Bai F L, Chen Y N. 2019. Cross-front sediment transport induced by quick oscillation of the Yellow Sea Warm Current: evidence from the sedimentary record. Geophysical Research Letters, 46(1): 226–234.
State Oceanic Administration. 1991. Chinese Harbours and Embayments (Part 3)—Northernand Eastern Shandong Peninsula. China Ocean Press, Beijing. p.1–488. (in Chinese)
State Oceanic Administration. 1998. Chinese Harbours and Embayments (Volume 14): Important Estuaries. China Ocean Press, Beijing. p.386–432. (in Chinese)
Su J L. 2001. A review of circulation dynamics of the coastal oceans near China. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 23(4): 1–16. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Teague W J, Jacobs G A. 2000. Current observations on the development of the Yellow Sea Warm Current. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 105(C2): 3 401–3 411.
Tripathy G R, Singh S K, Ramaswamy V. 2014. Major and trace element geochemistry of Bay of Bengal sediments: implications to provenances and their controlling factors. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 397: 20–30.
Wang A M, Ralston D K, Bi N S, Cheng Z, Wu X, Wang H J. 2019. Seasonal variation in sediment transport and deposition on a muddy clinoform in the Yellow Sea. Continental Shelf Research, 179: 37–51.
Watson J G, Robinson N F, Chow J C, Henry R C, Kim B M, Pace T G, Meyer E L, Nguyen Q. 1990. The USEPA/DRI chemical mass balance receptor model, CMB 7.0. Environmental Software, 5(1): 38–49.
Xu L L, Wu D X, Lin X P, Ma C. 2009. The study of the Yellow Sea warm current and its seasonal variability. Journal of Hydrodynamics, Ser. B, 21(2): 159–165.
Yang S Y, Jung H, Li C X, Lim D I. 2004b. Major element geochemistry of sediments from Chinese and Korean Rivers. Geochimica, 33(1): 99–105. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang S Y, Jung H S, Lim D I, Li C X. 2003a. A review on the provenance discrimination of sediments in the Yellow Sea. Earth-Science Reviews, 63(1–2): 93–120.
Yang S Y, Li C X. 1999a. Characteristic element compositions of the Yangtze and the Yellow River sediments and their geological background. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 19(2): 19–26.
Yang S Y, Li C X. 1999b. Element composition and tracing in modern surface sediments of the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers. Progress in Natural Science, 9(10): 9 30–9 37. (in Chinese)
Yang S Y, Li C X, Jung H S, Lee H J. 2002. Discrimination of geochemical compositions between the Changjiang and the Huanghe sediments and its application for the identification of sediment source in the Jiangsu coastal plain, China. Marine Geology, 186(3–4): 229–241.
Yang S Y, Li C X, Jung H, Lim D I, Choi M S. 2003b. Geochemistry of trace elements in Chinese and Korean River sediments. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 23(2): 19–24. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang S Y, Lim D I, Jung H S, Oh B C. 2004a. Geochemical composition and provenance discrimination of coastal sediments around Cheju Island in the southeastern Yellow Sea. Marine Geology, 206(1–4): 41–53.
Yang S Y, Youn J S. 2007. Geochemical compositions and provenance discrimination of the central south Yellow Sea sediments. Marine Geology, 243(1–4): 229–241.
Yang Z S, Dai H M, Wang K R. 2005. Daily variations of water discharge and sediment discharge into the sea from Yellow River from 1950 to 2000 and relevant influential factors that generate these changes. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 35(2): 237–244. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang Z S, Liu J P. 2007. A unique Yellow River-derived distal subaqueous delta in the Yellow Sea. Marine Geology, 240(1–4): 169–176.
Yu F, Zhang Z X, Diao X Y, Guo J S. 2010. Observational evidence of the Yellow Sea warm current. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 28(3): 677–683.
Zhang K N. 2018. The influence of the North Yellow Sea cold water mass on the properties of suspended particulate matter and sedimentary environment. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (The Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences), Qingdao. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang S W, Wang Q Y, Lü Y, Cui H, Yuan Y L. 2008. Observation of the seasonal evolution of the Yellow Sea Cold Water Mass in 1996–1998. Continental Shelf Research, 28(3): 442–457.
Zhao Y Y, Qin Z Y, Li F Y, Chen Y W. 1990. On the source and genesis of the mud in the central area of the South Yellow Sea. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 8(1): 66–73.
Zhong W, Zhu L H, Dong P, Hu R J, Wu J Z, Zhu Y T, Duan H Q. 2020. Mechanisms of sediment trapping in coastal embayments off the Shandong Peninsula in summer—A case study in Weihai Bay. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 236: 106623.
Zhu X M, Bao X W, Song D H, Qiao L L, Huang B G, Shi X G. 2012. Numerical study on the tides and tidal currents in Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Oceanologia etLimnologia Sinica, 43(6): 1 103–1 113. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank MA Li, QI Luyang, XIE Hang, and LIU Tao from the Ocean University of China for assistance with laboratory analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41776059)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Y., Feng, X., Zhu, L. et al. Origin and geochemistry of surface sediments in the mud deposit area offshore the Shandong Peninsula, China. J. Ocean. Limnol. 39, 483–499 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-020-9300-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-020-9300-9