Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate and compare pathological characteristics of renal cysts Bosniak IIF, III and IV in light of recent histological classification.
Patients and methods
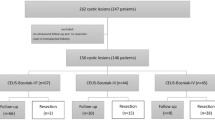
The French research network for kidney cancer UroCCR conducted a multicentre study on patients treated surgically for a renal cyst between 2007 and 2016. Independent radiological and centralized pathological reviews were performed for every patient. Pathological characteristics were compared to the Bosniak classification.
Results
Of a total 216 patients included, 175 (81.0%) tumours (90.9% of Bosniak IV, 69.8% of Bosniak III) were malignant or had a low malignant potential, with 60% of clear cell renal cell carcinoma (CCRCC), 24% of papillary RCC (PRCC) and 6.9% of multilocular cystic renal tumour of low malignant potential (MCRTLMP). Malignancies were mostly of low pT stage (86.4% of pT1–2), and low ISUP grade (68.0% of 1–2). Bosniak III cysts had a lower rate of CCRCC (46.7 vs. 67.3%), higher rate of PRCC (30 vs. 20.9%) and MCRTLMP (18.3 vs. 0.9%) compared to Bosniak IV (p < 0.001). Low-malignant potential lesions were less likely Bosniak IV and pT3–4 stage was more frequent in Bosniak IV vs. III (15.7 vs. 3.5%; p = 0.04). There were two recurrences (1.1%) and no cancer-related death occurred during follow-up.
Conclusion
These results confirmed that cystic renal malignancies have excellent prognosis. Bosniak III cysts had a low malignant potential, which suggests surveillance could be an option for these lesions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ljungberg B, Campbell SC, Choi HY et al (2011) The epidemiology of renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol 60:615–621
Ascenti G, Mazziotti S, Zimbaro G et al (2007) Complex cystic renal masses: characterization with contrast-enhanced US. Radiology 243:158–165
Warren KS, McFarlane J (2005) The Bosniak classification of renal cystic masses. BJU Int 95:939–942
Bosniak MA (1986) The current radiological approach to renal cysts. Radiology 158:1–10
Israel GM, Bosniak MA (2005) An update of the Bosniak renal cyst classification system. Urology 66:484–488
Ljungberg B, Bensalah K, Bex A et al (2015) EAU guidelines on renal cell carcinoma: 2014 update. Eur Urol. 67(5):913–924
Schoots IG, Zaccai K, Hunink MG et al (2017) Bosniak classification for complex renal cysts reevaluated: a systematic review. J Urol 198:12–21
Bielsa O, Lloreta J, Gelabert-Mas A (1998) Cystic renal cell carcinoma: pathological features, survival and implications for treatment. Br J Urol 82:16–20
Bensalah K, Albiges L, Bernhard J-C et al (2016) CCAFU french national guidelines 2016–2018 on renal cancer. Prog Urol. 27(Suppl 1):S27–S51
Moch H, Cubilla AL, Humphrey PA et al (2016) The 2016 WHO classification of tumours of the urinary system and male genital organs-part a: renal, penile, and testicular tumours. Eur Urol 70:93–105
Li T, Chen J, Jiang Y et al (2016) Multilocular cystic renal cell neoplasm of low malignant potential: a series of 76 cases. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 14:e553–e557
Aydin H, Chen L, Cheng L et al (2010) Clear cell tubulopapillary renal cell carcinoma: a study of 36 distinctive low-grade epithelial tumors of the kidney. Am J Surg Pathol 34:1608–1621
Tran T, Jones CL, Williamson SR et al (2016) Tubulocystic renal cell carcinoma is an entity that is immunohistochemically and genetically distinct from papillary renal cell carcinoma. Histopathology 68:850–857
Diolombi ML, Cheng L, Argani P et al (2015) Do clear cell papillary renal cell carcinomas have malignant potential? Am J Surg Pathol 39:1621–1634
Sevcenco S, Spick C, Helbich TH et al (2016) Malignancy rates and diagnostic performance of the Bosniak classification for the diagnosis of cystic renal lesions in computed tomography - a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Radiol 27(6):2239–2247
Hélénon O, Delavaud C, Dbjay J et al (2017) A practical approach to indeterminate and cystic renal masses. Semin Ultrasound CT MR 38:10–27
Bosniak MA (1997) The use of the Bosniak classification system for renal cysts and cystic tumors. J Urol 157:1852–1853
Kutikov A, Uzzo RG (2009) The R.E.N.A.L. nephrometry score: a comprehensive standardized system for quantitating renal tumor size, location and depth. J Urol 182:844–853
Patard J-J, Leray E, Rioux-Leclercq N et al (2005) Prognostic value of histologic subtypes in renal cell carcinoma: a multicenter experience. J Clin Oncol 23:2763–2771
Reese AC, Johnson PT, Gorin MA et al (2014) Pathological characteristics and radiographic correlates of complex renal cysts. Urol Oncol Semin Orig Investig. 32:1010–1016
Beck SDW, Patel MI, Snyder ME et al (2004) Effect of papillary and chromophobe cell type on disease-free survival after nephrectomy for renal cell carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 11:71–77
Teloken PE, Thompson RH, Tickoo SK et al (2009) Prognostic impact of histological subtype on surgically treated localized renal cell carcinoma. J Urol 182:2132–2136
Leibovich BC, Lohse CM, Crispen PL et al (2010) Histological subtype is an independent predictor of outcome for patients with renal cell carcinoma. J Urol 183:1309–1315
Chandrasekar T, Ahmad AE, Fadaak K, et al. (2017) Natural history of complex renal cysts: clinical evidence supporting active surveillance. J Urol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2017.09.078
Smith AD, Allen BC, Sanyal R et al (2015) Outcomes and complications related to the management of Bosniak cystic renal lesions. AJR Am J Roentgenol 204:550–556
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FXN: Project development, data collection, data analysis, manuscript writing. JCB: Project development, data collection, data analysis, manuscript writing. PB: Project development, data collection, manuscript writing. ZEK: Data collection. FA: Data collection. HL: Data collection. SB: Data collection. GF: Data collection. NG: Data collection. FC: Data collection. CN: Data collection. SB: Data collection. GF-H: Data collection. YA: Data collection. VL: Data collection. VV: Data collection. LD: Data collection. MY: Project development, data collection. JMC: Project development, data collection. AM: Project development, ,manuscript editing. NR-L: Project development, data analysis, manuscript editing. KB: Project development, data analysis, manuscript editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval/statement of human rights
All procedures performed in this study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional review board and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. A signed informed consent form has been obtained for every patient before inclusion.
Additional information
From The French research network for kidney cancer (UroCCR) and The Oncology Committee of the French Urology Association (CCAFU).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nouhaud, FX., Bernhard, JC., Bigot, P. et al. Contemporary assessment of the correlation between Bosniak classification and histological characteristics of surgically removed atypical renal cysts (UroCCR-12 study). World J Urol 36, 1643–1649 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-018-2307-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-018-2307-6