Abstract
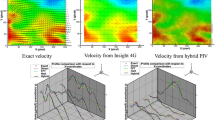
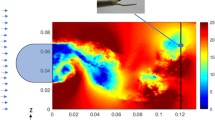
In this study, we propose a method to enhance the particle image velocimetry (PIV) velocity resolution using global optical flow along with image warping. A global optical flow formula proposed by Brox et al. (High accuracy optical flow estimation based on a theory for warping. In: Proceedings of the 8th European conference on computer vision, vol 4, pp 25–36, 2004) is adopted to compensate the intensity changes of PIV image pairs, which depend on the set-up and synchronization of a laser and a camera. The proposed method is quantitatively evaluated and validated using synthetic particle image pairs generated for Rankine vortices and reference DNS-based velocity data. The proposed method outperforms the conventional PIV method in capturing small scale vortex and turbulent structures due to its enhanced spatial resolution. In addition, the proposed method shows good performance in large displacement fields and varying image intensity whereas optical flow is applicable to small displacement and susceptible to image intensity variation in general. Finally, the proposed method is applied to real PIV particle images of a multiple rectangular jet flow. The results show that the proposed method successfully works out high-resolution fluid mechanical structure and quantities while preserving the conventional PIV results.
Graphic abstract















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrian RJ (1991) Particle-imaging techniques for experimental fluid mechanics. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 23(1):261–304
Alvarez L, Castano CA, Garcia M, Krissian K, Mazorra L, Salgado A, Sanchez J (2009) A new energy-based method for 3D motion estimation of incompressible PIV flows. Comput Vis Image Underst 113:802–810
Baker S, Scharstein D, Lewis JP, Roth S, Black MJ, Szeliski R (2011) A Database and evaluation methodology for optical flow. Int J Comput Vis 92:1–31
Becker F, Wieneke B, Petra S, Schröder A, Schnörr C (2012) Variational adaptive correlation method for flow estimation. IEEE Trans Image Process 21(6):3053–3065
Brox T, Bruhn A, Papenberg N, Weickert J (2004) High accuracy optical flow estimation based on a theory for warping. In: Proceedings of the 8th European conference on computer vision, vol 4, pp 25–36
Cai S, Mémin É, Dérian P, Xu C (2018) Motion estimation under location uncertainty for turbulent fluid flows. Exp Fluids 59(1):8
Cariler J (2005) Second set of fluid mechanics image sequences, European Project Fluid Image Analysis and Description (FLUID). http://www.fluid.irisa.fr
Cassisa C, Simoens S, Prinet V, Shao L (2011) Subgrid scale formulation of optical flow for the study of turbulent flow. Exp Fluids 51(6):1739–1754
Chen X, Zille P, Shao L, Corpetti T (2015) Optical flow for incompressible turbulence motion estimation. Exp Fluids 56:8
Corpetti T, Mémin E, Perez P (2002) Dense estimation of fluid flow. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 24(3):365–380
Corpetti T, Heitz D, Arroyo G, Mémin E, Santa-Cruz A (2006) Fluid experimental flow estimation based on an optical-flow scheme. Exp Fluids 40(1):80–97
Dérian P, Héas P, Herzet C, Mémin É (2012) Wavelet-based fluid motion estimation. scale space and variational methods in computer vision. Springer, Berlin, pp 737–748
Dérian P, Héas P, Herzet C, Mémin É (2013) Wavelets and optical flow motion estimation. Numer Math Theory Methods Appl 6(1):116–137
Di Florio D, Di Felice F, Romano GP (2002) Windowing, re-shaping and re-orientation interrogation windows in particle image velocimetry for the investigation of shear flows. Meas Sci Technol 13:953
Hart DP (2000) PIV error correction. Exp Fluids 29(1):13–22
Heitz D, Héas P, Mémin E, Carlier J (2008) Dynamic consistent correlation-variational approach for robust optical flow estimation. Exp Fluids 45(4):595–608
Heitz D, Mémin E, Schnörr C (2010) Variational fluid flow measurements from image sequences: synopsis and perspectives. Exp Fluids 48:369–393
Horn BK, Schunck BG (1981) Determining optical flow. Artif Intell 17(1–3):185–203
Huang HT, Fiedler HE, Wang JJ (1993) Limitation and improvement of PIV. Part2: particle image distortion, ad novel technique. Exp Fluids 15:263–273
Jambunathan K, Ju XY, Dobbins BN, Ashforth-Frost S (1995) An improved cross correlation technique for particle image velocimetry. Meas Sci Technol 6:507–514
Kadri-Harouna S, Dérian P, Héas P, Mémin E (2013) Divergence-free wavelets and high order regularization. Int J Comput Vis 103(1):80–99
Koenderink JJ (1975) Invariant properties of the motion parallax field due to the movement of rigid bodies relative to an observer. Opt Acta 22(9):773–791
Liu T (2017) OpenOpticalFlow: an open source program for extraction of velocity fields from flow visualization images. J Open Res Softw 5(1):29
Liu T, Shen L (2008) Fluid flow and optical flow. J Fluid Mech 614:253–291
Liu T, Merat A, Makhmalbaf MHM, Fajardo C, Merati P (2015) Comparison between optical flow and cross-correlation methods for extraction of velocity fields from particle images. Exp Fluids 56:166
Lucas B, Kanade T (1981) An iterative image registration technique with an application to stereo vision. Proceedings international joint conference on artificial intelligence. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, San Francisco, pp 674–679
Raffel M, Willert CE, Scarano F, Kähler CJ, Wereley ST, Kompenhans J (2018) Particle image velocimetry: a practical guide, 3rd edn. Springer, Berlin
Reeder MF, Crafton JW, Estevadeordal J, DeLapp J, McNiel C, Peltier D, Reynolds T (2010) Clean seeding for flow visualization and velocimetry measurements. Exp Fluids 48(5):889–900
Ruhnau P, Kohlberger T, Schnörr C, Nobach H (2005) Variational optical flow estimation for particle image velocimetry. Exp Fluids 38(1):21–32
Scarano F (2002) Iterative image deformation methods in PIV. Meas Sci Technol 13(1):R1
Scarano F (2003) Theory of non-isotropic spatial resolution in PIV. Exp Fluids 35:268–277
Scarano F, Riethnuller ML (1999) Iterative multigrid approach in PIV image processing with discrete window offset. Exp Fluids 26(6):513–523
Scarano F, Riethmuller ML (2000) Advances in iterative multigrid PIV image processing. Exp Fluids 29(7):S051–S060
Theunissen R, Scarano F, Riethmuller ML (2007) An adaptive sampling and windowing interrogation method in PIV. Meas Sci Technol 18:275–287
Theunissen R, Scarano F, Riethmuller ML (2010) Spatially adaptive PIV interrogation based on data ensemble. Exp Fluids 48:875–887
Thielicke W, Stamhuis EJ (2014) PIVlab—towards user-friendly, affordable and accurate digital particle image velocimetry in MATLAB. J Open Res Softw 2(1):e30
Uras S, Girosi F, Verri A, Torre V (1988) A computational approach to motion perception. Biol Cybern 60:79–87
Wedel A, Pock T, Zach C, Cremers D, Bischof H (2009) An improved algorithm for TV-L1 optical flow. Statistical and geometrical approaches to visual motion analysis. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 23–45
Wereley ST, Meinhart CD (2001) Second-order accurate particle image velocimetry. Exp Fluids 31(3):258–268
Wieneke B, Pfeiffer K (2010) Adaptive PIV with variable interrogation window size and shape. In: 15th International symposium on applications of laser techniques to fluid mechanics, Lisbon, Portugal, 05–08 July
Willert CE, Gharib M (1991) Digital particle image velocimetry. Exp Fluids 10(4):181–193
Yang Z, Johnson M (2017) Hybrid particle image velocimetry with the combination of cross-correlation and optical flow method. J Vis 20(3):625–638
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Nuclear R&D Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by MSIP; Ministry of Science ICT & Future Planning (No. NRF-2019M2A8A1000630).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seong, J.H., Song, M.S., Nunez, D. et al. Velocity refinement of PIV using global optical flow. Exp Fluids 60, 174 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-019-2820-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-019-2820-4