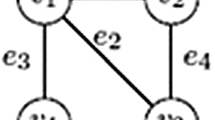
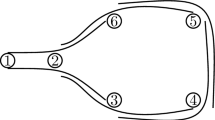
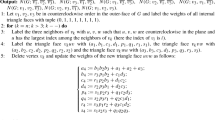Abstract
A graph is computable if there is an algorithm which decides whether given vertices are adjacent. Having a procedure for deciding the edge set might not help compute other properties or features of the graph, however. The goal of this paper is to investigate the extent to which features related to the planarity of a graph might or might not be computable. We propose three definitions for what it might mean for a computable graph to be computably planar and for each build a computable planar graph which fails to be computably planar. We also consider these definitions in the context of highly computable graphs, those for which there is an algorithm which computes the degree of a given vertex.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bean, D.R.: Effective coloration. J. Symbolic Logic 41(2), 469–480 (1976)
Bean, D.R.: Recursive Euler and Hamilton paths. Proc. Am. Math. Soc. 55(2), 385–394 (1976)
Carstens, H.G., Päppinghaus, P.: Recursive coloration of countable graphs. Ann. Pure Appl. Logic 25(1), 19–45 (1983). doi:10.1016/0168-0072(83)90052-0
Diestel, R.: Graph theory, Graduate Texts in Mathematics, vol. 173, 4th edn. Springer, Heidelberg (2010). doi:10.1007/978-3-642-14279-6
Erdös, P.: Some remarks on set theory. Proc. Am. Math. Soc. 1, 127–141 (1950)
Fáry, I.: On straight line representation of planar graphs. Acta Univ. Szeged. Sect. Sci. Math. 11, 229–233 (1948)
Gasarch, W.: A survey of recursive combinatorics. In: Handbook of Recursive Mathematics, vol. 2, Stud. Logic Found. Math., vol. 139, pp. 1041–1176. North-Holland, Amsterdam (1998). doi:10.1016/S0049-237X(98)80049-9
Harel, D.: Hamiltonian paths in infinite graphs. Israel J. Math. 76(3), 317–336 (1991). doi:10.1007/BF02773868
Jura, M., Levin, O., Markkanen, T.: Domatic partitions of computable graphs. Arch. Math. Logic 53(1–2), 137–155 (2014). doi:10.1007/s00153-013-0359-2
Kierstead, H.A.: Recursive colorings of highly recursive graphs. Can. J. Math. 33(6), 1279–1290 (1981). doi:10.4153/CJM-1981-097-8
Lipton, R.J., Tarjan, R.E.: A separator theorem for planar graphs. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 36(2), 177–189 (1979). doi:10.1137/0136016
Manaster, A.B., Rosenstein, J.G.: Effective matchmaking (recursion theoretic aspects of a theorem of Philip Hall). Proc. Lond. Math. Soc. 3(25), 615–654 (1972)
Schmerl, J.H.: Recursive colorings of graphs. Can. J. Math. 32(4), 821–830 (1980). doi:10.4153/CJM-1980-062-7
Simpson, S.G.: Subsystems of second order arithmetic, 2nd edn. Perspectives in Logic. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge; Association for Symbolic Logic, Poughkeepsie (2009). doi:10.1017/CBO9780511581007
Soare, R.I.: Recursively enumerable sets and degrees. Perspectives in Mathematical Logic. A Study of Computable Functions and Computably Generated Sets. Springer, Berlin (1987). doi:10.1007/978-3-662-02460-7
Thomassen, C.: Straight line representations of infinite planar graphs. J. Lond. Math. Soc. (2) 16(3), 411–423 (1977). doi:10.1112/jlms/s2-16.3.411
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the anonymous referee for a number of helpful suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Levin, O., McMillan, T. Computing Planarity in Computable Planar Graphs. Graphs and Combinatorics 32, 2525–2539 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00373-016-1725-8
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00373-016-1725-8