Abstract
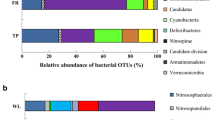
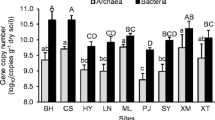
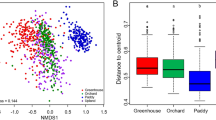
This study aims to provide first insights on the impact of land-use intensification and soil properties in shaping the composition of N-cycling microbial communities in Mediterranean peaty soils drained for agricultural purposes. An intensively cultivated peaty soil represented by an intensive maize cropping system was compared with an extensive grassland and an agricultural soil left abandoned for 15 years. Clone-library sequencing based on partial amoA and nirK functional genes was used to characterize the composition of ammonia-oxidizer microorganisms and nirK-type bacterial denitrifiers, respectively. The relative roles of land-use intensification and soil physico-chemical properties in community composition shaping were quantified by multivariate analyses. Phylogenetic and multivariate analyses showed that (i) the majority of sequences of ammonia-oxidizing archaea (AOA) and ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) grouped within the Nitrosotalea and Nitrosospira clusters, respectively; (ii) uncultured denitrifying bacteria were unique to our soil; (iii) land-use intensification shaped the composition of N-cycling communities; (iv) ammonia-oxidizing communities were driven by clay (AOA), bulk density (AOB), and exchangeable calcium (both AOA and AOB); and (v) nirK-type denitrifier bacteria were shaped by silt, ammonium, and exchangeable potassium. Based on the variation partitioning, soil properties were the primary determinants of the AOA and nirK-type denitrifier community composition, while land-use intensification was the major factor shaping the community composition of AOB. These findings improve the knowledge on such vulnerable agrosystems aiming to optimize the management of soil microbes in order to enhance the sustainability of N fertilization.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alef K., Nannipieri P (1995) Methods in applied soil microbiology and biochemistry. Academic press
Andert J, Wessén E, Börjesson G, Hallin S (2011) Temporal changes in abundance and composition of ammonia-oxidizing bacterial and archaeal communities in a drained peat soil in relation to N2O emissions. J Soils Sediments 11:1399–1407
Avrahami S, Bohannan BJ (2007) Response of Nitrosospira sp strain AF-like ammonia oxidizers to changes in temperature soil moisture content and fertilizer concentration. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:1166–1173
Bardgett RD, Usher MB, Hopkins DW (2005) Biological diversity and function in soils. Cambridge University Press Cambridge
Bruns MA, Stephen JR, Kowalchuk GA, Prosser JI, Paul EA (1999) Comparative diversity of ammonia oxidizer 16S rRNA gene sequences in native, tilled, and successional soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:2994–3000
Carney KM, Matson PA, Bohannan BJ (2004) Diversity and composition of tropical soil nitrifiers across a plant diversity gradient and among land-use types. Ecol Lett 7:684–694
Chen X, Zhang LM, Shen JP, Wei WX, He JZ (2011) Abundance and community structure of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in an acid paddy soil. Biol Fertil Soils 47:323–331
Chen YL, Hu HW, Han HY, Du Y, Wan SQ, Xu ZW, Chen BD (2014) Abundance and community structure of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in response to fertilization and mowing in a temperate steppe in Inner Mongolia. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 89:67–79
Ciccolini V, Bonari E, Pellegrino E (2015) Land-use intensity and soil properties shape the composition of fungal communities in Mediterranean peaty soils drained for agricultural purposes. Biol Fertil Soils 51:719–731. doi:10.1007/s00374-015-1013-4
Coleman BD (1981) On random placement and species-area relations. Math Biosci 54:191–215
Colwell RK (2013) EstimateS: statistical estimation of species richness and shared species from samples Version 9 and earlier User’s Guide and application. http://purl.oclc.org/estimates. Accessed 26 March 2015
Dandie CE, Wertz S, Leclair CL, Goyer C, Burton DL, Patten CL, Zebarth BJ, Trevors JT (2011) Abundance, diversity and functional gene expression of denitrifier communities in adjacent riparian and agricultural zones. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 77:69–82
De Boer W, Kowalchuk GA (2001) Nitrification in acid soils: micro-organisms and mechanisms. Soil Biol Biochem 33:853–866
de Gannes V, Eudoxie G, Hickey WJ (2014) Impacts of edaphic factors on communities of ammonia-oxidizing archaea, ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and nitrification in tropical soils. PLoS One 9:e89568
Delmont TO, Francioli D, Jacquesson S, Laoudi S, Mathieu A, Nesme J, Ceccherini MT, Nannipieri P, Simonet P, Vogel TM (2014) Microbial community development and unseen diversity recovery in inoculated sterile soil. Biol Fertil Soils 50:1069–1076
de Vries W, Leip A, Reinds GJ, Kros J, Lesschen JP, Bouwman AF (2011) Comparison of land nitrogen budgets for European agriculture by various modeling approaches. Environ Pollut 159:3254–3268
Di HJ, Cameron KC, Shen JP, Winefield CS, Callaghan MO, Bowatte S, He JZ (2009) Nitrification driven by bacteria and not archaea in nitrogen-rich grassland soils. Nat Geosci 2:621–624
Enwall K, Throbäck IN, Stenberg M, Söderström M, Hallin S (2010) Soil resources influence spatial patterns of denitrifying communities at scales compatible with land management. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:2243–2250
Felsenstein J (1989) PHYLIP—Phylogeny Inference Package (Version 32). Cladistics 5:164–166
Francis CA, Roberts KJ, Beman JM, Santoro AE, Oakley BB (2005) Ubiquity and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in water columns and sediments of the ocean. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:14683–14688
Gotelli NJ, Colwell RK (2001) Estimating species richness Frontiers in measuring biodiversity. Oxford University Press, New York
Gubry-Rangin C, Nicol GW, Prosser JI (2010) Archaea rather than bacteria control nitrification in two agricultural acidic soils. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 74:566–574
Hallin S, Jones CM, Schloter M, Philippot L (2009) Relationship between N-cycling communities and ecosystem functioning in a 50-year-old fertilization experiment. ISME J 3:597–605
Hayatsu M, Tago K, Saito M (2008) Various players in the nitrogen cycle: diversity and functions of the microorganisms involved in nitrification and denitrification. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 54:33–45
He JZ, Shen JP, Zhang LM, Zhu YG, Zheng YM, Xu MG, Di H (2007) Quantitative analyses of the abundance and composition of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and ammonia-oxidizing archaea of a Chinese upland red soil under long-term fertilization practices. Environ Microbiol 9:2364–2374
Herrmann M, Hädrich A, Küsel K (2012) Predominance of thaumarchaeal ammonia oxidizer abundance and transcriptional activity in an acidic fen. Environ Microbiol 14:3013–3025
IPCC (2006) 2006 IPCC agriculture, forestry and other land uses. In: Eggleston HS, Buendia L, Miwa K, Ngara T, Tanabe K (eds) Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories (volume 4) prepared by the National Greenhouse Gas Inventories Programme. IGES, Hayama, Kanagawa
Jiang X, Hou X, Zhou X, Xin X, Wright A, Jia Z (2015) pH regulates key players of nitrification in paddy soils. Soil Biol Biochem 81:9–16
Kastl EM, Schloter-Hai B, Buegger F, Schloter M (2015) Impact of fertilization on the abundance of nitrifiers and denitrifiers at the root–soil interface of plants with different uptake strategies for nitrogen. Biol Fertil Soils 51:57–64
Katoh K, Standley DM (2013) MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: improvements in performance and usability. Mol Biol Evol 30:772–780
Khan SA, Mulvaney RL, Ellsworth TR, Boast CW (2007) The myth of nitrogen fertilization for soil carbon sequestration. J Environ Qual 36:1821–1832
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120
Kowalchuk GA, Stephen JR (2001) Ammonia-oxidizing bacteria: a model for molecular microbial ecology. Annu Rev Microbiol 55:485–529
Kowalchuk GA, Stienstra AW, Heilig GHJ, Stephen JR, Woldendorp JW (2000) Molecular analysis of ammonia-oxidising bacteria in soil of successional grasslands of the Drentsche A (The Netherlands). FEMS Microbiol Ecol 31:207–215
Legendre P (2008) Studying beta diversity: ecological variation partitioning by multiple regression and canonical analysis. J Plant Ecol 1:3–8
Li S, Jiang X, Wang X, Wright AL (2015) Tillage effects on soil nitrification and the dynamic changes in nitrifying microorganisms in a subtropical rice-based ecosystem: a long-term field study. Soil Tillage Res 150:132–138
Muneer M, Oades JM (1989) The role of Ca-organic interactions in soil aggregate stability III mechanisms and models. Aust J Soil Res 27:411–423
Nannipieri P, Ascher J, Ceccherini M, Landi L, Pietramellara G, Renella G (2002) Microbial diversity and soil. Eur J Soil Sci 54:655–670
Nicol GW, Leininger S, Schleper C, Prosser JI (2008) The influence of soil pH on the diversity, abundance and transcriptional activity of ammonia oxidizing archaea and bacteria. Environ Microbiol 10:2966–2978
Oleszczuk R, Regina K, Szajdak L, Höper H, Maryganova V (2008) Impacts of agricultural utilization of peat soils on the greenhouse gas balance. In: Strack M (ed) Peatlands and climate change. International Peat Society, Jyväskylä, pp 70–98
Pastorelli R, Landi S, Trabelsi D, Piccolo R, Mengoni A, Bazzicalupo M, Pagliai M (2011) Effects of soil management on structure and activity of denitrifying bacterial communities. Appl Soil Ecol 49:46–58
Pastorelli R, Vignozzi N, Landi S, Piccolo R, Orsini R, Seddaiu G, Roggero PP, Pagliai M (2013) Consequences on macroporosity and bacterial diversity of adopting a no-tillage farming system in a clayish soil of Central Italy. Soil Biol Biochem 66:78–93
Pellegrino E, Di Bene C, Tozzini C, Bonari E (2011) Impact on soil quality of a 10-year-old short-rotation coppice poplar stand compared with intensive agricultural and uncultivated systems in a Mediterranean area. Agric Ecosyst Environ 140:245–254
Pellegrino E, Bosco S, Ciccolini V, Pistocchi C, Sabbatini T, Silvestri N, Bonari E (2014) Agricultural abandonment in Mediterranean reclaimed peaty soils: long-term effects on soil chemical properties, arbuscular mycorrhizas and CO2 flux. Agric Ecosyst Environ 199:164–175
Pereira e Silva MC, Poly F, Guillaumaud N, van Elsas JD, Falcão Salles J (2012) Fluctuations in ammonia oxidizing communities across agricultural soils are driven by soil structure and pH. Front Microbiol 3:77
Pester M, Schleper C, Wagner M (2011) The Thaumarchaeota: an emerging view of their phylogeny and ecophysiology. Curr Opin Microbiol 14:300–306
Philippot L, Bru D, Saby NP, Cuhel J, Arrouays D, Simek M, Hallin S (2009) Spatial patterns of bacterial taxa in nature reflect ecological traits of deep branches of the 16S rRNA bacterial tree. Environ Microbiol 11:3096–3104
Philippot L, Hallin S, Schloter M (2007) Ecology of denitrifying prokaryotes in agricultural soil. Adv Agron 96:249–305
Phillips CJ, Harris D, Dollhopf SL, Gross KL, Prosser JI, Paul EA (2000) Effects of agronomic treatments on structure and function of ammonia-oxidizing. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:5410–5418
Priemé A, Braker G, Tiedje JM (2002) Diversity of nitrite reductase (nirK and nirS) gene fragments in forested upland and wetland soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:1893–1900
Puglisi E, Zaccone C, Cappa F, Cocconcelli PS, Shotyk W, Trevisan M, Miano TM (2014) Changes in bacterial and archaeal community assemblages along an ombrotrophic peat bog profile. Biol Fertil Soils 50:815–826
Purkhold U, Pommerening-Röser A, Juretschko S, Schmid MC, Koops HP, Wagner M (2000) Phylogeny of all recognized species of ammonia oxidizers based on comparative 16S rRNA and amoA sequence analysis: implications for molecular diversity surveys. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:5368–5382
Rotthauwe JH, Witzel KP, Liesack W (1997) The ammonia monooxygenase structural gene amoA as a functional marker: molecular fine-scale analysis of natural ammonia-oxidizing populations. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:4704–4712
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, et al. (2009) Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:7537–7541
Shen JP, Zhang LM, Zhu YG, Zhang JB, He JZ (2008) Abundance and composition of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and ammonia-oxidizing archaea communities of an alkaline sandy loam. Environ Microbiol 10:1601–1611
Smil V (1997) Global population and the nitrogen cycle. Sci Am 277:76–81
Smith J, Wagner-Riddle C, Dunfield K (2010) Season and management related changes in the diversity of nitrifying and denitrifying bacteria over winter and spring. Appl Soil Ecol 44:138–146
Soil Survey Staff (1975) Soil taxonomy: a basic system of soil classification for making and interpreting soil surveys USDA-SCS Agric Handb 436 US Gov Print Office, Washington, DC
Stahl DA, de la Torre JR (2012) Physiology and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea. Annu Rev Microbiol 66:83–101
Stephen JR, McCaig AE, Smith Z, Prosser JI, Embley TM (1996) Molecular diversity of soil and marine 16S rRNA gene sequences related to beta-subgroup ammonia-oxidizing bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:4147–4154
Strack M (2008) Peatlands and climate change. International Peat Society, Jyväskylä
Stres B, Danevčič T, Pal L, Fuka MM, Resman L, Leskovec S, Hacin J, Stopar D, Mahne I, Mandic-Mulec I (2008) Influence of temperature and soil water content on bacterial, archaeal and denitrifying microbial communities in drained fen grassland soil microcosms. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 66:110–122
Szukics U, Abell GC, Hödl V, Mitter B, Sessitsch A, Hackl E, Zechmeister-Boltenstern S (2010) Nitrifiers and denitrifiers respond rapidly to changed moisture and increasing temperature in a pristine forest soil. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 72:395–406
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA 5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
ter Braak CJF, Šmilauer P (2012) Canoco reference manual and user’s guide: software for ordination (version 50) microcomputer power, Ithaca
Throbäck IN, Enwall K, Jarvis Å, Hallin S (2004) Reassessing PCR primers targeting nirS, nirK and nosZ genes for community surveys of denitrifying bacteria with DGGE. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 49:401–417
Tian XF, Hu HW, Ding Q, Song MH, Xu XL, Zheng Y, Guo LD (2014) Influence of nitrogen fertilization on soil ammonia oxidizer and denitrifier abundance, microbial biomass, and enzyme activities in an alpine meadow. Biol Fertil Soils 50:703–713
Tilman D, Cassman KG, Matson PA, Naylor R, Polasky S (2002) Agricultural sustainability and intensive production practices. Nature 418:671–677
Tourna M, Freitag TE, Prosser JI (2010) Stable isotope probing analysis of interactions between ammonia oxidizers. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:2468–2477
Treusch AH, Leininger S, Kletzin A, Schuster SC, Klenk HP, Schleper C (2005) Novel genes for nitrite reductase and Amo-related proteins indicate a role of uncultivated mesophilic crenarchaeota in nitrogen cycling. Environ Microbiol 7:1985–1995
Velthof G, Barot S, Bloem J, Butterbach-Bahl K, de Vries W, Kros J, Lavelle P, Olesen EJ, Oenema O (2011) Nitrogen as a threat to European soil quality. In: Sutton MA, Howard CM, Erisman JW, Billen G, Bleeker A, Grennfelt P, van Grinsven H, Grizzetti B (eds) The European nitrogen assessment. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp. 495–510
Wang X, Han C, Zhang J, Huang Q, Deng H, Deng Y, Zhong W (2015) Long-term fertilization effects on active ammonia oxidizers in an acidic upland soil in China. Soil Biol Biochem 84:28–37
Wang X, Wang C, Bao L, Xie S (2014) Abundance and community structure of ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms in reservoir sediment and adjacent soils. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:1883–1892
Webster G, Embley TM, Prosser JI (2002) Grassland management regimens reduce small-scale heterogeneity and species diversity of b-proteobacterial ammonia oxidizer populations. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:20–30
Wertz S, Dandie CE, Goyer C, Trevors JT, Patten CL (2009) Diversity of nirK denitrifying genes and transcripts in an agricultural soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:7365–7377
Wessén E, Söderström M, Stenberg M, Bru D, Hellman M, Welsh A, Thomsen F, Klemedtson L, Philippot L, Hallin S (2011) Spatial distribution of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea across a 44-hectare farm related to ecosystem functioning. ISME J 5:1213–1225
Wolsing M, Priemé A (2004) Observation of high seasonal variation in community structure of denitrifying bacteria in arable soil receiving artificial fertilizer and cattle manure by determining T-RFLP of nir gene fragments. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 48:261–271
Xie Z, Le Roux X, Wang C, Gu Z, An M, Nan H, Chen B, Li F, Liu Y, Du G, Huyuan Feng H, Ma X (2014) Identifying response groups of soil nitrifiers and denitrifiers to grazing and associated soil environmental drivers in Tibetan alpine meadows. Soil Biol Biochem 77:89–99
Xu YG, Yu WT, Ma Q, Zhou H (2012) Responses of bacterial and archaeal ammonia oxidisers of an acidic luvisols soil to different nitrogen fertilization rates after 9 years. Biol Fertil Soils 48:827–837
Yao H, Campbell CD, Chapman SJ, Freitag TE, Nicol GW, Singh BK (2013) Multifactorial drivers of ammonia oxidizer communities: evidence from a national soil survey. Environ Microbiol 15:2545–2556
Yoshida M, Ishii S, Otsuka S, Senoo K (2009) Temporal shifts in diversity and quantity of nirS and nirK in a rice paddy field soil. Soil Biol Biochem 41:2044–2051
Yu Y, Zhang J, Chen W, Zhong W, Zhu T, Cai Z (2014) Effect of land use on the denitrification, abundance of denitrifiers, and total nitrogen gas production in the subtropical region of China. Biol Fertil Soils 50:105–113
Zhalnina K, de Quadro PD, Camargo FA, Triplett EW (2012) Drivers of archaeal ammonia-oxidizing communities in soil. Front Microbiol 3:210
Zhang LM, Hu HW, Shen JP, He JZ (2012) Ammonia-oxidizing archaea have more important role than ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in ammonia oxidation of strongly acidic soils. ISME J 6:1032–1045
Zhang LM, Wang M, Prosser JI, Zheng YM, He JZ (2009) Altitude ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in soils of Mount Everest. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 70:208–217
Zhang X, Liu W, Schloter M, Zhang G, Chen Q, Huang J, Li L, James J, Elser JJ, Han X (2013) Response of the abundance of key soil microbial nitrogen-cycling genes to multi-factorial global changes. PLoS One 8:e76500
Zhao D, Luo J, Wang J, Huang R, Guo K, Li Y, Wu QL (2015) The influence of land use on the abundance and diversity of ammonia oxidizers. Curr Microbiol 70:282–289
Zumft G (1997) Cell biology and molecular basis of denitrification. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 61:533–616
Acknowledgments
This work represents a part of VC’s Ph.D. thesis, which was funded by the Scuola Superiore Sant’Anna, Pisa, Italy. The work was also supported by the “Consorzio di Bonifica Versilia-Massaciuccoli” and the “Regione Toscana” (“Restoration of a Mediterranean Drained Peatland”—https://sites.google.com/site/restomedpeatland/home).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Online resource 1
(DOCX 477 kb)
Online resource 2
(DOCX 4307 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ciccolini, V., Bonari, E., Ercoli, L. et al. Phylogenetic and multivariate analyses to determine the effect of agricultural land-use intensification and soil physico-chemical properties on N-cycling microbial communities in drained Mediterranean peaty soils. Biol Fertil Soils 52, 811–824 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-016-1121-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-016-1121-9