Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the effects of deep brain stimulation (DBS) electrodes on the brain of a dystonic pediatric patient submitted to bilateral DBS of the globus pallidus internus (GPI).
Methods
An 8-year-old male patient underwent bilateral DBS of GPI for status dystonicus. He died 2 months later due to multiorgan failure triggered by bacterial pneumonia. A post-mortem pathological study of the brain was done.
Results
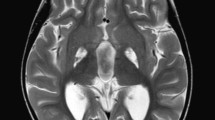
At visual inspection, no grossly apparent softening, hemorrhage, or necrosis of the brain adjacent to the DBS lead tracts was detected. High-power microscopic examination of the tissue surrounding the electrode trajectories showed lymphocyte infiltration, astrocytic gliosis, microglia, macrophages, and clusters of multinucleate giant cells. Significant astrocytosis was confirmed by GFAP staining in the electrode site. The T cell lymphocyte activity was overexpressed with activated macrophages detected with CD3, CD20, CD45, and CD68 stains respectively. There was no gliosis or leukocyte infiltration away from the surgical tracks of the electrodes.
Conclusion
This is the first post-mortem examination of a child’s brain after bilateral DBS of GPI. The comparison with adult post-mortem reports showed no significant differences and confirms the safety of DBS implantation in the pediatric population too.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Flora ED, Perera CL, Cameron AL, Maddern GJ (2010) Deep brain stimulation for essential tremor: a systematic review. Mov Disord 25(11):1550–1559
Deuschl G, Schade-Brittinger C, Krack P, et al (2006) A randomized trial of deep-brain stimulation for Parkinson's disease [published correction appears in N Engl J Med. 2006 Sep 21;355(12):1289]. N Engl J Med. 355(9):896–908
Weaver FM, Follett K, Stern M, et al (2009) Bilateral deep brain stimulation vs best medical therapy for patients with advanced parkinson disease: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 301(1):63–73
Sensi M, Cavallo MA, Quatrale R, et al (2009) Pallidal stimulation for segmental dystonia: long term follow up of 11 consecutive patients. Mov Disord 24(12):1829–1835. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.22686
Golfrè Andreasi N, Rispoli V, Contaldi E et al (2020) Deep brain stimulation and refractory freezing of gait in Parkinson’s disease: improvement with high-frequency current steering co-stimulation of subthalamic nucleus and substantia Nigra. Brain Stimul 13:280–283
Benabid AL, Benazzous A, Pollak P (2002) Mechanisms of deep brain stimulation. Mov Disord 17 Suppl 3:S73–S74
Carron R, Chabardès S, Hammond C (2012) Les mécanismes d'action de la stimulation cérébrale à haute fréquence. Revue de la littérature et concepts actuels [Mechanisms of action of high-frequency deep brain stimulation. A review of the literature and current concepts] . Neurochirurgie 58(4):209–217
Burbaud P, Vital A, Rougier A, et al (2002) Minimal tissue damage after stimulation of the motor thalamus in a case of chorea-acanthocytosis. Neurology 59(12):1982–1984
Caparros-Lefebvre D, Ruchoux MM, Blond S, Petit H, Percheron G (1994) Long-term thalamic stimulation in Parkinson’s disease: postmortem anatomoclinical study. Neurology 44(10):1856–1860
DiLorenzo DJ, Jankovic J, Simpson RK, Takei H, Powell SZ (2010) Long-term deep brain stimulation for essential tremor: 12-year clinicopathologic follow-up. Mov Disord 25(2):232–238
Henderson JM, O’Sullivan DJ, Pell M, et al (2001) Lesion of thalamic centromedian-parafascicular complex after chronic deep brain stimulation. Neurology 56(11):1576–1579
Henderson JM, Pell M, O’Sullivan DJ, et al (2002) Postmortem analysis of bilateral subthalamic electrode implants in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 17(1):133–137
Jarraya B, Bonnet AM, Duyckaerts C, et al (2003) Parkinson’s disease, subthalamic stimulation, and selection of candidates: a pathological study. Mov Disord 18(12):1517–1520
Kuroda R, Nakatani J, Yamada Y, Yorimae A, Kitano M (1991) Location of a DBS-electrode in lateral thalamus for deafferentation pain. An autopsy case report. Acta Neurochir Suppl (Wien) 52:140–142
Pienaar IS, Lee CH, Elson JL, et al (2015) Deep-brain stimulation associates with improved microvascular integrity in the subthalamic nucleus in Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 74:392–405
Nielsen MS, Bjarkam CR, Sørensen JC, Bojsen-Møller M, Sunde NA, Østergaard K (2007) Chronic subthalamic high-frequency deep brain stimulation in Parkinson’s disease—a histopathological study. Eur J Neurol 14(2), 132–138
Pal GD, Ouyang B, Serrano G, Shill HA, Goetz C, Stebbins G, Metman LV, Driver-Dunckley E, Mehta SH, Caviness JN, Sabbagh MN, Adler CH, Beach TG, Arizona Study of Aging Neurodegenerative Disorders (2017) Comparison of neuropathology in Parkinson’s disease subjects with and without deep brain stimulation. Movement disorders : official journal of the Movement Disorder Society 32(2):274–277
Sun DA, Yu H, Spooner J, Tatsas AD, Davis T, Abel TW, Kao C, Konrad PE (2008) Postmortem analysis following 71 months of deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus for Parkinson disease. J Neurosurg 109(2):325–329
Reddy GD, Lozano AM (2018) Postmortem studies of deep brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease: a systematic review of the literature. Cell Tissue Res 373:287–295. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-017-2672-2
Dilorenzo DJ, Jankovic J, Simpson RK, et al (2014) Neurohistopathological findings at the electrode-tissue interface in long-term deep brain stimulation: systematic literature review, case report, and assessment of stimulation threshold safety. Neuromodulation
Vedam-Mai V, Krock N, Ullman M, Foote KD, Shain W, Smith K, Yachnis AT, Steindler D, Reynolds B, Merritt S, Pagan F, Marjama-Lyons J, Hogarth P, Resnick AS, Zeilman P, Okun MS (2011) The national DBS brain tissue network pilot study: need for more tissue and more standardization. Cell Tissue Bank 12(3):219–231
Vedam-Mai V, Yachnis A, Ullman M, Javedan SP, Okun MS (2012) Postmortem observation of collagenous lead tip region fibrosis as a rare complication of DBS. Movement disorders : official journal of the Movement Disorder Society 27(4):565–569
Vedam-Mai V, Rodgers C, Gureck A, Vincent M, Ippolito G, Elkouzi A, Yachnis AT, Foote KD, Okun MS (2018) Deep brain stimulation associated gliosis: a post-mortem study. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 54:51–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2018.04.009
Haberler C, Alesch F, Mazal PR et al (2000) No tissue damage by chronic deep brain stimulation in Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 48:372–376. https://doi.org/10.1002/1531-8249(200009)48:3<372::AID-ANA12>3.0.CO;2-0
Hale AT, Monsour MA, Rolston JD, Naftel RP, Englot DJ (2018) Deep brain stimulation in pediatric dystonia: a systematic review. Neurosurg Rev 43(3):873–880
Tsering D, Tochen L, Lavenstein B, Reddy SK, Granader Y, Keating RF, Oluigbo CO (2017) Considerations in deep brain stimulation (DBS) for pediatric secondary dystonia. Child’s nervous system : ChNS : official journal of the International Society for Pediatric Neurosurgery 33(4):631–637
DiFrancesco MF, Halpern CH, Hurtig HH, Baltuch GH, Heuer GG (2012) Pediatric indications for deep brain stimulation. Child’snervous system : ChNS : official journal of the International Society for Pediatric Neurosurgery 28(10):1701–1714
Zorzi G, Marras C, Nardocci N, Franzini A, Chiapparini L, Maccagnano E, Angelini L, Caldiroli D, Broggi G (2005) Stimulation of the globus pallidus internus for childhood-onset dystonia. Movement disorders : official journal of the Movement Disorder Society 20(9):1194–1200
Cif L, Coubes P (2017) Historical developments in children’s deep brain stimulation. European journal of paediatric neurology : EJPN : official journal of the European Paediatric Neurology Society 21(1):109–117
Ben-Haim S, Flatow V, Cheung T, Cho C, Tagliati M, Alterman RL (2016) Deep brain stimulation for status dystonicus: a case series and review of the literature. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 94(4):207–215
Lumsden DE, King MD, Allen NM (2017) Status dystonicus in childhood. Curr Opin Pediatr 29(6):674–682
Cury RG, Fraix V, Castrioto A, Pérez Fernández MA, Krack P, Chabardes S, Seigneuret E, Alho E, Benabid AL, Moro E (2017) Thalamic deep brain stimulation for tremor in Parkinson disease, essential tremor, and dystonia. Neurology 89(13):1416–1423
Boockvar JA, Telfeian A, Baltuch GH, Skolnick B, Simuni T, Stern M, Schmidt ML, Trojanowski JQ (2000) Long-term deep brain stimulation in a patient with essential tremor: clinical response and postmortem correlation with stimulator termination sites in ventral thalamus. Case report. Journal of neurosurgery 93(1):140–144
Tsuboi T, Wong JK, Okun MS, Ramirez-Zamora A (2020) Quality of life outcomes after deep brain stimulation in dystonia: a systematic review. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 70:82–93
Gybels J, Dom R, Cosyns P (1980) Electrical stimulation of the central gray for pain relief in human: autopsy data. Acta Neurochir Suppl 30:259–268
Farrell SM, Green A, Aziz T (2018) The current state of deep brain stimulation for chronic pain and its context in other forms of neuromodulation. Brain Sci 8(8):158
Pilitsis JG, Chu Y, Kordower J, Bergen DC, Cochran EJ, Bakay RA (2008) Postmortem study of deep brain stimulation of the anterior thalamus: case report. Neurosurgery 62(2):E530–E532
Orlowski D, Michalis A, Glud AN et al (2017) Brain tissue reaction to deep brain stimulation—a longitudinal study of DBS in the Goettingen minipig. Neuromodulation 20:417–423. https://doi.org/10.1111/ner.12576
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the article content was composed in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giordano, F., Caporalini, C., Peraio, S. et al. Post-mortem histopathology of a pediatric brain after bilateral DBS of GPI for status dystonicus: case report and review of the literature. Childs Nerv Syst 36, 1845–1851 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-020-04761-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-020-04761-w